Regions Belgium
Survey Articles (Regional)
Regional Thematic Articles
- Bereavement and Mourning (Belgium)
- Between Acceptance and Refusal - Soldiers' Attitudes Towards War (Belgium)
- Centenary (Belgium)
- Civilian and Military Power (Belgium)
- Commemoration, Cult of the Fallen (Belgium)
- Film/Cinema (Belgium)
- Food and Nutrition (Belgium)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Belgium)
- Historiography 1918-Today (Belgium)
- Labour (Belgium)
- Labour Movements, Trade Unions and Strikes (Belgium)
- Literature (Belgium)
- Making Sense of the War (Belgium)
- Occupation after the War (Belgium and France)
- Occupation during the War (Belgium and France)
- Organization of War Economies (Belgium)
- Post-war Economies (Belgium)
- Post-war Societies (Belgium)
- Press/Journalism (Belgium)
- Pre-war Military Planning (Belgium)
- Prisoners of War (Belgium and France)
- Propaganda at Home (Belgium)
- Science and Technology (Belgium)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Belgium)
- Warfare 1914-1918 (Belgium)
- War Finance (Belgium)
- War Losses (Belgium)
- Women's Mobilization for War (Belgium)
Encyclopedic Entries
- Activisme
- Albert I, King of the Belgians
- Amphibious Raids on Ostend and Zeebrugge
- Attrition Warfare
- Belgian Soldiers
- Bettignies, Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de
- Bissing, Moritz Ferdinand Freiherr von
- Borms, August
- Broqueville, Charles Marie Pierre Albert, Baron de
- Brussels
- Camouflage
- Charleroi, Battle of
- Collaboration (Belgium and France)
- Comité National de Secours et d'Alimentation
- Commission for Relief in Belgium (CRB)
- Discussion: Humanitarianism
- Elisabeth of Bavaria, Queen of the Belgians
- Eupen-Malmedy
- Feminist Pacifism
- Flamenpolitik
- Flemish Movement
- Forts
- Garde Civique
- Generalgouvernement Belgien
- German Communities and their Expulsion (Belgium)
- High Voltage Fence (The Netherlands and Belgium)
- Intimate Relations between Occupiers and Occupied (Belgium and France)
- La Dame Blanche
- La Fontaine, Henri
- Loppem Coup
- Marinegebiet
- Max, Adolphe
- Mémorial Interallié
- Mercier, Désiré Joseph
- Mons
- Neutrality
- Olympic Games 1920
- Patriotic Distance
- Petit, Gabrielle
- Pirenne, Henri
- Post-war Repression
- Prostitution
- Rape
- Rear Area on the Western Front
- Refugees (Belgium)
- Resistance (Belgium and France)
- Ruhr Occupation
- Russian Expeditionary Force
- Russian Expeditionary Force
- Solvay, Ernest
- University of Ghent
- Villalobar, Rodrigo de Saavedra y Vinent, Marqués de
- Ypres, Battles of
- Ypres Menin Gate
See also
- Alliance System 1914
- Antisemitism
- Atrocities
- Bereavement and Mourning
- Centenary (Battlefield Tourism)
- Centenary (Computer Games)
- Centenary (Education, Pedagogy, Youth Programs)
- Centenary (Internet)
- Centenary (Libraries)
- Centenary (Museums)
- Centenary (Visual Arts)
- Colonial Empires after the War/Decolonization
- Commemoration, Cult of the Fallen
- Controversy: War-related Changes in Gender Relations: The Issue of Women’s Citizenship
- Destruction of the Ecosystem
- Espionage
- Film/Cinema
- Food and Nutrition
- Forced Labour
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties
- Imperialism
- International Labour Organization
- International Law and the Laws of War
- Labor
- Labour Movements, Trade Unions and Strikes
- League of Nations
- Making Sense of the War
- Maps, Geography and the Representation of Space
- Media Discourse after the War
- Medicine and Medical Service
- Memory of the War: Popular Memory 1918-1945, 1945 to the Present
- Negotiating and Mediating Conduct of War
- Non-European Soldiers
- Occupation during the War
- Photography
- Post-war Societies
- Propaganda at Home and Abroad
- Refugees
- Resettlement
- Social Conflict
- Social Costs of War
- State, Civil Society and Relief Organizations for War
- The Everyday as Involved in War
- The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
- Visualization of Violence
- Wartime Emotions: Honour, Shame, and the Ecstasy of Sacrifice
- Willingly to War. Public Response to the Outbreak of War
- Women War Reporters
Survey Articles (Regional)
-
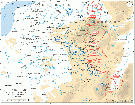
Belgium, a neutral state, was forced into the First World War by a German ultimatum, a fact with considerable international resonance. The war had a deep impact on what was, in 1914, the most … READ MORE
Regional
Regional Thematic Articles
-
World War I claimed the lives of approximately 60,000 Belgian civilians and soldiers. Belgium was uniquely situated in the middle of the conflict and suffered civilian massacres in August 1914 and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses the war experiences of Belgian soldiers: how did they endure four years of war and how did the Army Command keep up morale and maintain discipline? Insights into the morale of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The scope of the commemorations that developed in Belgium and in the remainder of Europe showed the population’s need to keep the memory of World War I alive. The majority of Belgian municipalities … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines cinema in relation to the First World War in Belgium from two focal points. First, it describes how film production as well as film exhibition and cinema-going became cultural … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War had a severe impact on the food supply in occupied Belgium. The prospect of famine turned food into an urgent political problem and the subject of far-reaching social-political … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War changed the balance of power in Belgium. From a strongly polarized system dominated by the Catholic Party, the country shifted towards a coalition system, marked by a tradeoff … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
After a promising start, academic historiography of the First World War in Belgium fell silent after 1928. There was nothing that resembled an academic field of World War I studies in Belgium for … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The standard of living of Belgian workers declined in the First World War as a consequence of the economic standstill, as well as German monetary and economic exploitation, which led to a sharp … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War had a decisive, but paradoxical impact on the development of labour movements in Belgium. The occupation abruptly interrupted the development of labour movement structures. In the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war literature, in both Dutch (Flemish) and in French, covers different war experiences: not just that of the front but also that of military occupation. Although none of it became … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war experience was ''sui generis''. The vast majority of Belgians experienced the war neither at the front nor on the home front, but under German occupation. The article analyzes the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Armistice agreement foresaw the occupation of the left bank of the Rhine, the dates of which were set by the Treaty of Versailles. The inter-allied occupation was a long-term endeavour: the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the German occupation of Belgium and Northern France in 1914–1918. Besides focussing on the occupiers’ motives and logic of action regarding their policy and practices, it … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
As it became clear that the war would last a long time, the German occupying administration set up a system to control Belgian industry, in order to guarantee that the Belgian economy would … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium had suffered considerable economic losses during the war, which was fought on part of its territory. Aside from the direct damages as a result of warfare, industry nearly came to a standstill … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The end of the First World War marked, to a certain extent, Belgium’s entry into the 20th century. The country suffered greatly from the occupation and an explosion of patriotism, … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Belgian press world was turned upside down by the German occupation. Most of the editorial offices of the news dailies ceased all activity or went abroad. Yet a press under censorship did … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Following the Treaty of London in 1839, pre-war planning theories in Belgium oscillated between two positions: secure and defend endangered borders or create a powerful military stronghold in … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During the First World War, France was faced with creating a system of mass captivity for German prisoners of war and German civilian internees, both at home and in its overseas Empire. It largely … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
August 1914: “Poor Little Belgium”, martyred by the German invader, became an effective symbol used by international belligerents to sharpen their propaganda weapons. However, in 1916, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The invasion and subsequent occupation of most of Belgian territory paralyzed the scientific and technological capacities of the country during the war and its aftermath. At the same time, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war aims were a direct consequence of the way in which the country was created. The treaties finalized in 1839 left Belgium with part of Luxembourg and Limburg, and also left the Scheldt … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Between August 1914 and November 1918 the Belgian army took part in the First World War against the German aggressor. This article describes the way the Belgian army fought this war that began … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Belgian monetary system evolved dramatically during World War I. The ''Société Générale'', a large private bank, replaced the National Bank as issuing house. New banknotes were printed and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Belgian situation was unique in the sense that military losses were relatively limited compared to neighbouring countries due to the wait-and-see strategy pursued by King Albert I and a less … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium experienced the war in an exceptional position: it never issued a declaration of war, but was drawn into it by the brutal invasion of its territory. Both men and women were subject to a harsh … READ MORE
Regional Thematic
Encyclopedic Entries
-
A minority of the adherents of the Flemish movement were willing to collaborate with the German occupier in the context of ''Flamenpolitik''. This minority labelled themselves “activists”, … READ MORE
Entry -
Albert I, the third king of the Belgians, played a leading role as supreme commander of the Belgian army during the First World War. For four years he defended the last piece of unoccupied Belgium … READ MORE
Entry -
On the night of 22-23 April 1918, the Royal Navy attacked the German occupied towns of Ostend and Zeebrugge in an effort to block the canals that linked the two cities to the German naval base at … READ MORE
Entry -
Attrition warfare is the term used to describe the sustained process of wearing down an opponent so as to force their physical collapse through continuous losses in personnel, equipment and supplies … READ MORE
Entry -
This article briefly describes the 320,000 Belgian soldiers of the Great War. Who were they and what was special about the way they experienced the war compared to other … READ MORE
Entry -
Louise de Bettignies created an intelligence network for the British in occupied France. She was arrested, sentenced to death in March 1916 and deported to the prison of Siegburg. Sick, she died in … READ MORE
Entry -
Moritz von Bissing was born on 30 January 1844, in Bellmannsdorf, Silesia, then part of the German Empire. He served as governor general of the Prussian Army from December 1914 until his death on 18 … READ MORE
Entry -
As a Flemish nationalist, August Borms actively collaborated with the Germans during the First World War. As a result of his ten-year imprisonment and his death sentence he became a true symbol of … READ MORE
Entry -
Charles de Broqueville, chief of the Belgian government during the First World War, acted as liaison between the king and the Belgian government. He supported the king in his attempts to obtain peace … READ MORE
Entry -
The Belgian capital was spared the anguish of combat, but the city suffered four long years of occupation. In fact, it became the most important occupied city during the First World War. For the … READ MORE
Entry -
A technique of concealment and protection, a means to deceive but not kill, camouflage was significantly developed during the First World War. The technique enabled many artists to put their talents … READ MORE
Entry -
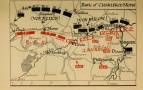
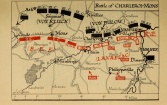
The Battle of Charleroi (21-23 August 1914), in which General Charles Lanrezac’s Fifth Army was nearly surrounded by German First, Second and Third Armies, was one of the deadliest combats that … READ MORE
Entry -
Collaboration is often associated with the military occupations of the Second World War, but there was a precursor to this multi-faceted phenomenon in occupied France and Belgium during the First … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Comité national de Secours et d’Alimentation'' (National Committee for Relief and Food) was created in Brussels a few days after the start of the war to coordinate the action of notables, … READ MORE
Entry -
From 1914 to 1919, the Commission for Relief in Belgium directed an innovative and successful international food relief program for more than 9 million Belgian and French civilians who lived in … READ MORE
Entry -
This is the first in what it is hoped will become a series of discussion forums hosted by ''1914-1918-online''. In this discussion forum, General Editor Peter Gatrell invited contributions that … READ MORE
Entry -
Queen Elisabeth was the third queen of the Belgians. Her attitude during the First World War propelled her to the mythic rank of "Queen … READ MORE
Entry -
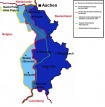
Eupen-Malmedy is the name given to the two districts that Germany ceded to Belgium in 1920 as a consequence of the Treaty of Versailles. This cession and the semblance of a “referendum”, … READ MORE
Entry -
A minority section of the women’s movements opposed World War I and organized the International Congress of Women at The Hague in April 1915. Its participants demanded women’s rights and more … READ MORE
Entry -
The German ''Flamenpolitik'' during the First World War aimed to instrumentalise the Flemish movement in order to ensure lasting German control over Belgium. It did not divide the Belgian or even … READ MORE
Entry -
The First World War engendered a rift within the Flemish movement, with some wishing to pursue the advocacy for Flemish rights and others preferring to await the end of the war to obtain new laws. … READ MORE
Entry -
European militaries considered fortifications before the First World War as vital to their strategic planning. Advancements in weapons technology after the mid-19th century caused … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1830, Belgium constituted a ''Garde Civique'' or Civic Guard''', '''a national institution to be deployed both for maintaining law and order and for territorial defence. In 1914, the Garde Civique … READ MORE
Entry -
After the German Army had occupied wide areas of Belgium, the “Imperial Government General in Belgium” was established on 23 August 1914 with a governor-general at its head. Organized into a … READ MORE
Entry -
At the start of the First World War, tens of thousands of Germans lived in Belgium, with noted communities in Antwerp and Brussels. How the Germans in Belgium experienced the war years, ranging from … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1915 the Germans built an electric fence along the Belgian-Dutch border, consisting of three lines of wires which were intended to stop all disturbing border activities that might severely harm … READ MORE
Entry -
During the invasion and occupation of 1914-1918, German soldiers had sexual relations with local women in Belgium and France. There were many cases of rape during the invasion, but the occupation … READ MORE
Entry -
La Dame Blanche was an intelligence network created in Belgium in 1916. It was essentially devoted to the observation of railways. At the end of the war, it was comprised of over 1,000 agents and … READ MORE
Entry -
Although he was a Nobel Prize winner, the name of Henri La Fontaine has somewhat fallen into obscurity. At the time of his Nobel Peace Prize award in 1913, however, he was a fundamental figure in the … READ MORE
Entry -
A few weeks before his entry in Brussels, on 22 November 1918, Albert I, King of the Belgians, held talks with various politicians in Loppem Castle. Some particularly important decisions were made, … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Marinegebiet'' on the Belgian coast was the Imperial German Navy’s base for attritional warfare against Entente shipping in the North Sea. The resulting occupation regime was particularly … READ MORE
Entry -
Adolphe Max, the mayor of Brussels, was known for his peaceful resistance against the Germans and his resulting jail-time. He was considered by the Belgian public as a hero of the Great … READ MORE
Entry -
The inter-allied memorial commemorates the First World War and the fallen, as well as the wartime cooperation between the Allies. Its inter-allied character and its scale make this memorial one of a … READ MORE
Entry -
After his pastoral letter ''Patriotisme et endurance'', which had a worldwide impact, the Cardinal Archbishop of Mechlin, Désiré Mercier, was seen both in Belgium and abroad as the incarnation of … READ MORE
Entry -
The city of Mons took on great symbolic importance during the Great War. In both August 1914 and November 1918, the region was the scene of clashes between Commonwealth troops and German soldiers. … READ MORE
Entry -
During the 19th century, neutrality evolved into a set of legal and political tools designed to limit the impact of wars on the international system. This form of neutrality did not … READ MORE
Entry -
The 1920 Olympic Games in Antwerp, Belgium were the first instalment of the Games since before the war. The planned 1916 Games awarded to Berlin had been … READ MORE
Entry -
Civilians under military occupation in World War One found their existences severely circumscribed, but they exercised agency – not through large-scale, decisive actions, but through small-scale … READ MORE
Entry -
Gabrielle Petit was a secret intelligence agent working for the British General Headquarters (GHQ) in occupied Belgium. She collected information on the German Sixth Army in the Tournai-Lille area. … READ MORE
Entry -
Accused of refusing to collaborate with the German authorities, the Belgian historian Henri Pirenne was deported to Germany in 1916. His captivity led him to reconsider his view on German historical … READ MORE
Entry -
After fifty months of German occupation, a minority of French, and the majority of 7 million Belgians, experienced a new and massive process of retribution. A comparative study of these retribution … READ MORE
Entry -
Prostitution was considered among the most important societal problems facing civilian-military authorities in belligerent countries during World War I. Despite growing military control of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Although rape was not usually systematic, it occurred frequently on all fronts during the First World War, during both invasion and occupation periods. It was often used in propaganda to discredit … READ MORE
Entry -
The rear area was the space behind the front, linking the operational zone with the home territory. While this area constituted a place of calm and recreation for soldiers returning from front duty, … READ MORE
Entry -
In Belgium, the outbreak of the First World War and subsequent German invasion caused massive population movements. Hundreds of thousands of Belgian refugees fled the country to seek asylum in the … READ MORE
Entry -
In occupied Belgium and France, citizens opposed the German army with organized but non-violent resistance. They created networks dedicated to military intelligence gathering, escape lines, … READ MORE
Entry -
The 1923-1925 Ruhr occupation by France and Belgium was triggered when Germany defaulted on its reparations obligations. A passive resistance campaign obstructed the invaders but collapsed in … READ MORE
Entry -
The Russian Expeditionary Force in France and in Macedonia (“Brigades russes en France et en Macédoine” in French and “Russkij èkspedicionnyj korpus” in Russian) was an ensemble of four … READ MORE
Entry -
The Russian Expeditionary Force in France and in Macedonia (“Brigades russes en France et en Macédoine” in French and “Russkij èkspedicionnyj korpus” in Russian) was an ensemble of four … READ MORE
Entry -
Industrial tycoon and philanthropist Ernest Solvay transformed the chemical industry by developing a groundbreaking process for the manufacturing of soda ash. At the outbreak of World War I, he … READ MORE
Entry -
During the war, the Germans created a Flemish university in Ghent. By doing so, they fulfilled one of the Flemish movement’s principal … READ MORE
Entry -
Rodrigo de Saavedra y Vinent, Marqués de Villalobar was the diplomatic representative of Spain to Belgium from 1913 to 1926. During the war, his humanitarian activities in occupied Belgium … READ MORE
Entry -
The Belgian city of Ypres is synonymous with the First World War. Ypres gave its name to three major battles: First Ypres (19 October - 22 November 1914), Second Ypres (21 April - 25 May 1915) and … READ MORE
Entry -
The Menin Gate in Ypres is the best known of the memorials to the missing in the Commonwealth War Graves Commission's care. Designed by architect Sir Reginald Blomfield it is where the Last Post, the … READ MORE
Entry
See also
-
Alliances were an important feature of the international system on the eve of World War I. The formation of rival blocs of Great Powers has previously considered a major cause of the outbreak of war … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War and its direct repercussions in the postwar period (revolution, counterrevolution, the founding of republics, and the Paris peace treaties) mark a profound caesura not only in the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The term "atrocity" describes an act of violence condemned by contemporaries as a breach of morality or the laws of war. "Atrocities" are culturally constructed; by 1914, an international discourse … READ MORE
Thematic -
In the modern era, new forms of mourning and meaning-making for fallen soldiers emerged. The human losses of the First World War were largely mourned, honoured and remembered within … READ MORE
Thematic -
The centenary of the First World War has been a catalyst for battlefield tourism. The creation of new museums, memorials, statues, commemorative trails and the like has strengthened the Great War’s … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War centenary saw an emergence of new portrayals of the conflict in computer games. These new games sought either to tell new stories of war and conflict during the time period or to … READ MORE
Thematic -
The centenary of the First World War revealed palpable anxieties around a loss of connection to an event that was now 100 years old and without any living survivors. As a result, a good degree of … READ MORE
Thematic -
The centenary events surrounding the First World War have produced a significant amount of digital content in various forms, and thus has set a precedent for how large scale post-war memorisation can … READ MORE
Thematic -
Libraries (local, specialist, and national) contributed in numerous and important ways to commemorative activities during the centenary of the First World War. These included making use of their … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article discusses how European museums – in particular, national war museums – dealt with the centenary of World War I. These museums still tend to tell the story of World War I from a … READ MORE
Thematic -
The commemorative period between 2014 and 2018 was marked globally by numerous exhibitions of original artworks that had been commissioned and created during and immediately after World War 1. Most … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War saw the colonial empires of France and Britain mobilised to aid European and imperial war efforts. This mobilisation and the difficulties of demobilisation placed considerable … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War ushered in an unprecedented wave of commemorations. Mass death elicited a construction spree in memorial objects and sites across all countries and territories involved in the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Controversy: War-related Changes in Gender Relations: The Issue of Women’s Citizenship
By Birgitta Bader-Zaar
The idea that World War I was a watershed in gender relations has pervaded both contemporary narratives and historiography. In contrast to earlier studies, research now tends to give a more nuanced … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article examines the First World War’s ecological impact and shows that protracted environmental transformations resulted more from expanded industrial modes of production than heavy combat. … READ MORE
Thematic -
During the entire war, warring powers used the “secret war” to try to break the balance of the battlefield. Generally created in the previous few decades, intelligence and security services saw … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War played a significant role in the evolution of film both as a medium for reporting war and as a tool for the propagandist manipulation of public opinion to support the war effort. … READ MORE
Thematic -
During the First World War, food became a major issue for military and civilian matters. This contribution aims to discuss the food situation in the belligerent countries in connection with global … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article examines the conditions, forms and consequences of forced labor and recruitment during the First World War, especially in German-occupied northern France, Belgium, Russian-Poland and … READ MORE
Thematic -
One sees a wide range of political regimes from a democratic republic with universal male suffrage (France) to parliamentary, constitutional, or even oligarchical monarchies in the countries that … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article focuses on the extent to which imperialism contributed to the outbreak of the First World War. The first part describes the emergence of specific imperialist cultures and attitudes in … READ MORE
Thematic -
The Treaty of Versailles was signed on 28 June 1919, establishing both the League of Nations and another international organization: the International Labour Organization (ILO). The ILO was founded … READ MORE
Thematic -
The article examines international efforts to curb states’ war-making prerogatives in the second half of the “long” 19th century. It captures new humanitarian sentiments circulating … READ MORE
Thematic -
Across the major belligerent powers, industrial production and the mobilization and organization of industrial labor became central to the conduct of the First World War. States and private … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article compares the history of labour movements during the war across a range of European countries. It charts the impact of the economic realities of the war upon labour and analyses the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Claims to “just war” formed the basis for the propaganda campaigns of the First World War. Propaganda on all sides focused on three interrelated issues to endorse the decision to enter the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The discourse about the Great War during the interwar period was shaped by numerous factors. The emergence of new media facilitated the use of new forms of expression and profoundly changed the … READ MORE
Thematic -
It is impossible to talk about “the” medical care or “the” medical service of World War I. Medical care varied greatly, depending on geography, strategy, and national, social, or economic … READ MORE
Thematic -
What role do representations of the First World War play in media that reach a wide audience beyond the circle of experts? The following contribution focuses on this important question. Given the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Many issues surrounding the conduct of war in the years 1914-1918 were impervious to international negotiation or mediation, due either to a complete lack of consensus or to an absence of trust and … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article examines the use by Great Britain and France of colonial subjects from their empires to fight during the First World War. Other Great War soldiers hailed from locations outside of … READ MORE
Thematic -
After an initial wave of interest in 1914 and the immediate post-war period, international historiography long neglected the wartime occupation of territories inhabited by large civilian populations. … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War represents a watershed in the history of war photography. It was the first conflict to be photographed in detail by all the participants and the first in which photography was … READ MORE
Thematic -
The First World War caused unprecedented disruption to societies across the globe, from Western and (especially) Central and Eastern Europe to East Africa. While many survivors could celebrate an end … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article summarizes and compares the principal arguments and strategies of propaganda at the home front, the military front, as well as in neutral and enemy countries. These included the … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article addresses the scale of wartime population displacement in continental Europe, the relief efforts made on behalf of refugees, their impact on host communities, and the cultural … READ MORE
Thematic -
The conduct of warfare in 1914-1918 included extensive population resettlement in all theatres of war in Europe, both as a result of pre-emptive decisions by civilians to flee in order to evade the … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article deals with the nature of social conflict during the war. The length of the conflict and growing food shortages on the home front strained relations between individuals and between social … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article explores how the anticipation, reality, and memory of sacrifice informed experiences and legacies of World War I. Drawing on representative examples from multiple nations, I suggest that … READ MORE
Thematic -
A vast array of initiatives designed to counteract the destructiveness of the First World War was developed by states and societies across the world. Protecting the bodies and minds of soldiers from … READ MORE
Thematic -
This essay examines how the "everyday" functions in war, not only for those on the home fronts, but for those in combat roles and for those living between the lines. Five important qualities, among … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article offers an overview of peacemaking after the First World War from the armistices of 1918 until 1923. It considers the outcomes of the five Parisian treaties (Versailles, Saint-Germain and … READ MORE
Thematic -
This piece explores the visualisation of violence for home front audiences and shows that violence was often hinted at very strongly, but the actual act was avoided. All home front audiences were … READ MORE
Thematic -
Through investigating the pivotal role of honour in private and public matters, in foreign and domestic relations, and in propaganda and everyday life during the First World War, this article … READ MORE
Thematic -
It may surprise us to learn that some sectors of the European public were in favour of the war in 1914. The impact of modern weapons was not well understood and many people in the government, … READ MORE
Thematic -
Female war reporters from belligerent and neutral countries were present in the major war theatres in Europe and the Middle East throughout 1914 to 1918. While admission of journalists to the war … READ MORE
Thematic
Survey Articles (Regional)
-
Belgium, a neutral state, was forced into the First World War by a German ultimatum, a fact with considerable international resonance. The war had a deep impact on what was, in 1914, the most … READ MORE
Regional
Regional Thematic Articles
-
World War I claimed the lives of approximately 60,000 Belgian civilians and soldiers. Belgium was uniquely situated in the middle of the conflict and suffered civilian massacres in August 1914 and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses the war experiences of Belgian soldiers: how did they endure four years of war and how did the Army Command keep up morale and maintain discipline? Insights into the morale of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The scope of the commemorations that developed in Belgium and in the remainder of Europe showed the population’s need to keep the memory of World War I alive. The majority of Belgian municipalities … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines cinema in relation to the First World War in Belgium from two focal points. First, it describes how film production as well as film exhibition and cinema-going became cultural … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War had a severe impact on the food supply in occupied Belgium. The prospect of famine turned food into an urgent political problem and the subject of far-reaching social-political … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War changed the balance of power in Belgium. From a strongly polarized system dominated by the Catholic Party, the country shifted towards a coalition system, marked by a tradeoff … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
After a promising start, academic historiography of the First World War in Belgium fell silent after 1928. There was nothing that resembled an academic field of World War I studies in Belgium for … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The standard of living of Belgian workers declined in the First World War as a consequence of the economic standstill, as well as German monetary and economic exploitation, which led to a sharp … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War had a decisive, but paradoxical impact on the development of labour movements in Belgium. The occupation abruptly interrupted the development of labour movement structures. In the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war literature, in both Dutch (Flemish) and in French, covers different war experiences: not just that of the front but also that of military occupation. Although none of it became … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war experience was ''sui generis''. The vast majority of Belgians experienced the war neither at the front nor on the home front, but under German occupation. The article analyzes the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Armistice agreement foresaw the occupation of the left bank of the Rhine, the dates of which were set by the Treaty of Versailles. The inter-allied occupation was a long-term endeavour: the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the German occupation of Belgium and Northern France in 1914–1918. Besides focussing on the occupiers’ motives and logic of action regarding their policy and practices, it … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
As it became clear that the war would last a long time, the German occupying administration set up a system to control Belgian industry, in order to guarantee that the Belgian economy would … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium had suffered considerable economic losses during the war, which was fought on part of its territory. Aside from the direct damages as a result of warfare, industry nearly came to a standstill … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The end of the First World War marked, to a certain extent, Belgium’s entry into the 20th century. The country suffered greatly from the occupation and an explosion of patriotism, … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Belgian press world was turned upside down by the German occupation. Most of the editorial offices of the news dailies ceased all activity or went abroad. Yet a press under censorship did … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Following the Treaty of London in 1839, pre-war planning theories in Belgium oscillated between two positions: secure and defend endangered borders or create a powerful military stronghold in … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During the First World War, France was faced with creating a system of mass captivity for German prisoners of war and German civilian internees, both at home and in its overseas Empire. It largely … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
August 1914: “Poor Little Belgium”, martyred by the German invader, became an effective symbol used by international belligerents to sharpen their propaganda weapons. However, in 1916, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The invasion and subsequent occupation of most of Belgian territory paralyzed the scientific and technological capacities of the country during the war and its aftermath. At the same time, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war aims were a direct consequence of the way in which the country was created. The treaties finalized in 1839 left Belgium with part of Luxembourg and Limburg, and also left the Scheldt … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Between August 1914 and November 1918 the Belgian army took part in the First World War against the German aggressor. This article describes the way the Belgian army fought this war that began … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Belgian monetary system evolved dramatically during World War I. The ''Société Générale'', a large private bank, replaced the National Bank as issuing house. New banknotes were printed and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Belgian situation was unique in the sense that military losses were relatively limited compared to neighbouring countries due to the wait-and-see strategy pursued by King Albert I and a less … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium experienced the war in an exceptional position: it never issued a declaration of war, but was drawn into it by the brutal invasion of its territory. Both men and women were subject to a harsh … READ MORE
Regional Thematic
Encyclopedic Entries
-
A minority of the adherents of the Flemish movement were willing to collaborate with the German occupier in the context of ''Flamenpolitik''. This minority labelled themselves “activists”, … READ MORE
Entry -
Albert I, the third king of the Belgians, played a leading role as supreme commander of the Belgian army during the First World War. For four years he defended the last piece of unoccupied Belgium … READ MORE
Entry -
On the night of 22-23 April 1918, the Royal Navy attacked the German occupied towns of Ostend and Zeebrugge in an effort to block the canals that linked the two cities to the German naval base at … READ MORE
Entry -
Attrition warfare is the term used to describe the sustained process of wearing down an opponent so as to force their physical collapse through continuous losses in personnel, equipment and supplies … READ MORE
Entry -
This article briefly describes the 320,000 Belgian soldiers of the Great War. Who were they and what was special about the way they experienced the war compared to other … READ MORE
Entry -
Louise de Bettignies created an intelligence network for the British in occupied France. She was arrested, sentenced to death in March 1916 and deported to the prison of Siegburg. Sick, she died in … READ MORE
Entry -
Moritz von Bissing was born on 30 January 1844, in Bellmannsdorf, Silesia, then part of the German Empire. He served as governor general of the Prussian Army from December 1914 until his death on 18 … READ MORE
Entry -
As a Flemish nationalist, August Borms actively collaborated with the Germans during the First World War. As a result of his ten-year imprisonment and his death sentence he became a true symbol of … READ MORE
Entry -
Charles de Broqueville, chief of the Belgian government during the First World War, acted as liaison between the king and the Belgian government. He supported the king in his attempts to obtain peace … READ MORE
Entry -
The Belgian capital was spared the anguish of combat, but the city suffered four long years of occupation. In fact, it became the most important occupied city during the First World War. For the … READ MORE
Entry -
A technique of concealment and protection, a means to deceive but not kill, camouflage was significantly developed during the First World War. The technique enabled many artists to put their talents … READ MORE
Entry -
The Battle of Charleroi (21-23 August 1914), in which General Charles Lanrezac’s Fifth Army was nearly surrounded by German First, Second and Third Armies, was one of the deadliest combats that … READ MORE
Entry -
Collaboration is often associated with the military occupations of the Second World War, but there was a precursor to this multi-faceted phenomenon in occupied France and Belgium during the First … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Comité national de Secours et d’Alimentation'' (National Committee for Relief and Food) was created in Brussels a few days after the start of the war to coordinate the action of notables, … READ MORE
Entry -
From 1914 to 1919, the Commission for Relief in Belgium directed an innovative and successful international food relief program for more than 9 million Belgian and French civilians who lived in … READ MORE
Entry -
This is the first in what it is hoped will become a series of discussion forums hosted by ''1914-1918-online''. In this discussion forum, General Editor Peter Gatrell invited contributions that … READ MORE
Entry -
Queen Elisabeth was the third queen of the Belgians. Her attitude during the First World War propelled her to the mythic rank of "Queen … READ MORE
Entry -
Eupen-Malmedy is the name given to the two districts that Germany ceded to Belgium in 1920 as a consequence of the Treaty of Versailles. This cession and the semblance of a “referendum”, … READ MORE
Entry -
A minority section of the women’s movements opposed World War I and organized the International Congress of Women at The Hague in April 1915. Its participants demanded women’s rights and more … READ MORE
Entry -
The German ''Flamenpolitik'' during the First World War aimed to instrumentalise the Flemish movement in order to ensure lasting German control over Belgium. It did not divide the Belgian or even … READ MORE
Entry -
The First World War engendered a rift within the Flemish movement, with some wishing to pursue the advocacy for Flemish rights and others preferring to await the end of the war to obtain new laws. … READ MORE
Entry -
European militaries considered fortifications before the First World War as vital to their strategic planning. Advancements in weapons technology after the mid-19th century caused … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1830, Belgium constituted a ''Garde Civique'' or Civic Guard''', '''a national institution to be deployed both for maintaining law and order and for territorial defence. In 1914, the Garde Civique … READ MORE
Entry -
After the German Army had occupied wide areas of Belgium, the “Imperial Government General in Belgium” was established on 23 August 1914 with a governor-general at its head. Organized into a … READ MORE
Entry -
At the start of the First World War, tens of thousands of Germans lived in Belgium, with noted communities in Antwerp and Brussels. How the Germans in Belgium experienced the war years, ranging from … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1915 the Germans built an electric fence along the Belgian-Dutch border, consisting of three lines of wires which were intended to stop all disturbing border activities that might severely harm … READ MORE
Entry -
During the invasion and occupation of 1914-1918, German soldiers had sexual relations with local women in Belgium and France. There were many cases of rape during the invasion, but the occupation … READ MORE
Entry -
La Dame Blanche was an intelligence network created in Belgium in 1916. It was essentially devoted to the observation of railways. At the end of the war, it was comprised of over 1,000 agents and … READ MORE
Entry -
Although he was a Nobel Prize winner, the name of Henri La Fontaine has somewhat fallen into obscurity. At the time of his Nobel Peace Prize award in 1913, however, he was a fundamental figure in the … READ MORE
Entry -
A few weeks before his entry in Brussels, on 22 November 1918, Albert I, King of the Belgians, held talks with various politicians in Loppem Castle. Some particularly important decisions were made, … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Marinegebiet'' on the Belgian coast was the Imperial German Navy’s base for attritional warfare against Entente shipping in the North Sea. The resulting occupation regime was particularly … READ MORE
Entry -
Adolphe Max, the mayor of Brussels, was known for his peaceful resistance against the Germans and his resulting jail-time. He was considered by the Belgian public as a hero of the Great … READ MORE
Entry -
The inter-allied memorial commemorates the First World War and the fallen, as well as the wartime cooperation between the Allies. Its inter-allied character and its scale make this memorial one of a … READ MORE
Entry -
After his pastoral letter ''Patriotisme et endurance'', which had a worldwide impact, the Cardinal Archbishop of Mechlin, Désiré Mercier, was seen both in Belgium and abroad as the incarnation of … READ MORE
Entry -
The city of Mons took on great symbolic importance during the Great War. In both August 1914 and November 1918, the region was the scene of clashes between Commonwealth troops and German soldiers. … READ MORE
Entry -
During the 19th century, neutrality evolved into a set of legal and political tools designed to limit the impact of wars on the international system. This form of neutrality did not … READ MORE
Entry -
The 1920 Olympic Games in Antwerp, Belgium were the first instalment of the Games since before the war. The planned 1916 Games awarded to Berlin had been … READ MORE
Entry -
Civilians under military occupation in World War One found their existences severely circumscribed, but they exercised agency – not through large-scale, decisive actions, but through small-scale … READ MORE
Entry -
Gabrielle Petit was a secret intelligence agent working for the British General Headquarters (GHQ) in occupied Belgium. She collected information on the German Sixth Army in the Tournai-Lille area. … READ MORE
Entry -
Accused of refusing to collaborate with the German authorities, the Belgian historian Henri Pirenne was deported to Germany in 1916. His captivity led him to reconsider his view on German historical … READ MORE
Entry -
After fifty months of German occupation, a minority of French, and the majority of 7 million Belgians, experienced a new and massive process of retribution. A comparative study of these retribution … READ MORE
Entry -
Prostitution was considered among the most important societal problems facing civilian-military authorities in belligerent countries during World War I. Despite growing military control of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Although rape was not usually systematic, it occurred frequently on all fronts during the First World War, during both invasion and occupation periods. It was often used in propaganda to discredit … READ MORE
Entry -
The rear area was the space behind the front, linking the operational zone with the home territory. While this area constituted a place of calm and recreation for soldiers returning from front duty, … READ MORE
Entry -
In Belgium, the outbreak of the First World War and subsequent German invasion caused massive population movements. Hundreds of thousands of Belgian refugees fled the country to seek asylum in the … READ MORE
Entry -
In occupied Belgium and France, citizens opposed the German army with organized but non-violent resistance. They created networks dedicated to military intelligence gathering, escape lines, … READ MORE
Entry -
The 1923-1925 Ruhr occupation by France and Belgium was triggered when Germany defaulted on its reparations obligations. A passive resistance campaign obstructed the invaders but collapsed in … READ MORE
Entry -
The Russian Expeditionary Force in France and in Macedonia (“Brigades russes en France et en Macédoine” in French and “Russkij èkspedicionnyj korpus” in Russian) was an ensemble of four … READ MORE
Entry -
The Russian Expeditionary Force in France and in Macedonia (“Brigades russes en France et en Macédoine” in French and “Russkij èkspedicionnyj korpus” in Russian) was an ensemble of four … READ MORE
Entry -
Industrial tycoon and philanthropist Ernest Solvay transformed the chemical industry by developing a groundbreaking process for the manufacturing of soda ash. At the outbreak of World War I, he … READ MORE
Entry -
During the war, the Germans created a Flemish university in Ghent. By doing so, they fulfilled one of the Flemish movement’s principal … READ MORE
Entry -
Rodrigo de Saavedra y Vinent, Marqués de Villalobar was the diplomatic representative of Spain to Belgium from 1913 to 1926. During the war, his humanitarian activities in occupied Belgium … READ MORE
Entry -
The Belgian city of Ypres is synonymous with the First World War. Ypres gave its name to three major battles: First Ypres (19 October - 22 November 1914), Second Ypres (21 April - 25 May 1915) and … READ MORE
Entry -
The Menin Gate in Ypres is the best known of the memorials to the missing in the Commonwealth War Graves Commission's care. Designed by architect Sir Reginald Blomfield it is where the Last Post, the … READ MORE
Entry