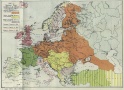
Themes Power
Survey Articles (Thematic)
- Antisemitism
- Burgfrieden/Union sacrée
- Civilian and Military Power
- Controversy: Total War
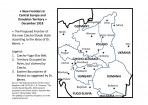
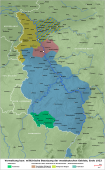
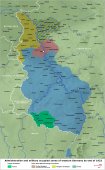
- Crumbling of Empires and Emerging States: Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia as (Multi)national Countries
- Enemy Aliens and Internment
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties
- International Labour Organization
- League of Nations
- Occupation during the War
- Pacifism
- Peace Initiatives
- Resettlement
- Revolutions
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions
- Willingly to War. Public Response to the Outbreak of War
- Xenophobia
Regional Thematic Articles
- African Colonies (Portugal)
- African Labour in Europe (Africa)
- Civilian and Military Power (Australia)
- Civilian and Military Power (Austria-Hungary)
- Civilian and Military Power (Belgium)
- Civilian and Military Power (China)
- Civilian and Military Power (France)
- Civilian and Military Power (Germany)
- Civilian and Military Power (Great Britain and Ireland)
- Civilian and Military Power (Italy)
- Civilian and Military Power (Japan)
- Civilian and Military Power (Ottoman Empire)
- Civilian and Military Power (South East Europe)
- Civilian and Military Power (USA)
- Civil-Military Relations during World War I (Portugal)
- Civil-Military Relations during World War I (Russian Empire)
- Colonial Society (Indochina)
- Colonial State Power and Politics (Africa)
- Colonial Warfare and Occupation (Africa)
- Colonies (Italy)
- Diplomacy (Portugal)
- Domestic Politics and Neutrality (Denmark)
- Domestic Politics and Neutrality (Norway)
- Domestic Politics and Neutrality (Spain)
- Domestic Politics and Neutrality (Sweden)
- Domestic Politics and Neutrality (Switzerland)
- Domestic Politics and Neutrality (The Netherlands)
- Dominions’ Military Relationship to Great Britain 1902-1914 (British Dominions)
- Easter Rising (Great Britain and Ireland)
- Foreign Policy and Business Diplomacy (Denmark)
- Foreign Policy (Norway)
- Foreign Policy (Spain)
- Foreign Policy (Sweden)
- Foreign Policy (The Netherlands)
- French Canada and the War (Canada)
- German versus US Intelligence in Latin America
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Australia)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Austria)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Belgium)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Canada)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (China)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (France)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Germany)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Great Britain and Ireland)
- Governments-Parliaments and Parties (Hungary)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Italy)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Japan)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties, Labour, Labour Movements and Strikes (Union of South Africa)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (New Zealand)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Ottoman Empire/Middle East)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties; Political Movements and Protostate Formation (East Central Europe)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Portugal)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (Russian Empire)
- Governments, Parliaments and Parties (USA)
- International Committee of the Red Cross
- International Responses to the Russian Civil War (Russian Empire)
- Jewish Responses to the War (East Central Europe)
- Military and Strategy (Spain)
- Military and Strategy (Switzerland)
- Occupation after the War (Belgium and France)
- Occupation during and after the War (Austria-Hungary)
- Occupation during and after the War (China)
- Occupation during and after the War (East Central Europe)
- Occupation during and after the War (Germany)
- Occupation during and after the War (Italy)
- Occupation during and after the War (Middle East)
- Occupation during and after the War (Ottoman Empire)
- Occupation during and after the War (Russian Empire)
- Occupation during and after the War (South East Europe)
- Occupation during the War (Belgium and France)
- Religion (Portugal)
- Religion (USA)
- Religious Missionaries and the Colonial State (Indochina)
- Resistance and Rebellions (Africa)
- Revolutionary Networks (India)
- Revolutions and Rebellions: Arab Revolt (Ottoman Empire/Middle East)
- Revolutions and Rebellions: Van Resistance as Rebellion (Ottoman Empire/Middle East)
- Revolutions (Austria-Hungary)
- Revolutions (East Central Europe)
- Revolutions (Germany)
- Revolutions (Portugal)
- Revolutions (Russian Empire)
- Teskilat-i Mahsusa (Ottoman Empire)
- War Aims and Peace Discussions (USA)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Africa)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Australia)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Austria-Hungary)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Belgium)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (China)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (East Central Europe)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (France)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Germany)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Great Britain and Ireland)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Italy)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Japan)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Ottoman Empire)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Portugal)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (Russian Empire)
- War Aims and War Aims Discussions (South East Europe)
Encyclopedic Entries
- ABC Pact (Alliance between Argentina, Brazil and Chile)
- Activisme
- Adler, Victor
- Ador, Gustave
- Albert I, King of the Belgians
- Albrecht, Duke of Württemberg
- al-Da’uq, Umar
- Alexandra, Empress, consort of Nicholas II, Emperor of Russia
- Alfonso XIII, King of Spain
- Almeida, José António de
- Anarchism (Latin America)
- Arab Bureau
- Arab Supporters of the Belligerent Countries
- Armenia
- Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF)
- Arslān, Shakīb, Amīr
- Asquith, Herbert Henry
- Azerbaijan
- Azmi, Jemal
- Baker, Newton D.
- Balfour, Arthur James Balfour, Earl of
- Balfour Declaration
- Ballhausplatz
- Battisti, Cesare
- Batum, Conference and Treaties of
- Bauer, Max
- Bauer, Otto
- Bäumer, Gertrud
- Beerenbrouck, Charles Ruijs de
- Bell, Gertrude
- Beneš, Edvard
- Berchtold, Leopold Graf
- Berlin Indian Independence Committee
- Bernstorff, Johann Heinrich, Graf von
- Beseler, Hans von
- Bethmann Hollweg, Theobald von
- Bettignies, Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de
- Bissing, Moritz Ferdinand Freiherr von
- Black Hand
- Bliss, Howard S.
- Bloch, Jan Gotlib
- Bloch, Jan Gotlib
- Bonar Law, Andrew
- Borders (The Netherlands)
- Borms, August
- Boselli, Paolo
- Bosnian Crisis
- Brás, Venceslau
- Brătianu, Ion I.C.
- Brazil
- Brest-Litovsk, Treaty of
- Briand, Aristide
- Brockdorff-Rantzau, Ulrich Carl Christian, Graf
- Broqueville, Charles Marie Pierre Albert, Baron de
- Brussels
- Bryan, William Jennings
- Bülow, Bernhard, Fürst von
- Burián von Rajecz, István, Graf
- Camacho, Brito
- Carnegie, Lancelot
- Carol I, King of Romania
- Casement, Roger, Sir
- Cavid Bey, Mehmed
- Cemal Paşa, Ahmed
- Charles I, Emperor of Austria
- Chattopadhyaya, Virendranath
- Churchill, Winston Leonard Spencer
- Circassian Nationalism
- Citizenship (Great Britain)
- Clam-Martinic, Heinrich, Graf
- Clemenceau, Georges
- Collaboration (Belgium and France)
- Collins, Michael
- Committee of Union and Progress (CUP)
- Concept of Mitteleuropa
- Conscientious Objectors
- Constantine I, King of Greece
- Constantinople Agreement
- Corfu Declaration
- Cort van der Linden, Pieter Wilhelm Adriaan
- Costa, Afonso
- Creel, George
- Croce, Benedetto
- Czernin, Ottokar Graf
- Daniels, Josephus
- Daszyński, Ignacy
- Dayal, Har
- Debs, Eugene V.
- Decree on Peace
- Defence of the Realm Act (DORA)
- Delesalle, Charles
- De Valera, Éamon
- Dmowski, Roman
- Dual Power
- Duan, Qirui
- Du Bois, W.E.B.
- Duma
- Ebert, Friedrich
- Elisabeth of Bavaria, Queen of the Belgians
- Empire
- Enver Pasha, Ismail
- Erzberger, Matthias
- Ethiopia
- Eyschen, Paul
- Falkenhausen, Ludwig Alexander Friedrich August Philipp Freiherr von
- Faysal I, King of Iraq
- Ferdinand I, Tsar of Bulgaria
- Ferry, Abel
- Flamenpolitik
- Flemish Movement
- Fourteen Points
- Francis Joseph I, Emperor of Austria
- Frank, Ludwig
- Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria-Este
- Freedom of the Seas
- Gabrys, Juozas
- Gallieni, Joseph-Simon
- Garcez, Arnaldo
- Garfield, Harry Augustus
- Garrison, Lindley M.
- Geddes, Eric Campbell, Sir
- Generalgouvernement Belgien
- Generalgouvernement Warschau
- General Headquarters (Germany)
- George V, King of Great Britain
- Georgia
- German Fatherland Party
- German Immigrants (Brazil)
- Germany's Blank Cheque to Austria-Hungary
- Ghadar Conspiracy
- Giolitti, Giovanni
- Goltz, Colmar Freiherr von der
- Göring, Hermann
- Gregory, Thomas Watt
- Grey, Sir Edward
- Grigorovich, Ivan Konstantinovich
- Grimm-Hoffmann Affair
- Grimm, Robert
- Groener, Wilhelm
- Gurko, Vasiliĭ Iosifovich
- Haase, Hugo
- Hague Conferences 1899-1907
- Hakkı, İsmail Bey
- Haldane, Richard Burdon
- Hankey, Maurice Pascal Alers Hankey, Baron
- Hertling, Georg, Graf von
- Hervé, Gustave
- Hindenburg, Paul von
- Hitler, Adolf
- Hồ Chí Minh
- Holmes, Oliver Wendell
- Hoover, Herbert
- Horthy, Miklós
- House, Edward Mandell
- Hoyek, Elias
- Husayn ibn Ali, King of Hejaz
- Ḥusayn Kāmil, Sultan of Egypt
- Husayn-McMahon Correspondence
- Interventionism (Italy)
- Ionescu, Dumitru
- Irish Home Rule
- Ishii-Lansing Agreement 1917
- Italian Irredentism
- Jabotinsky, Vladimir
- Jagow, Gottlieb von
- Japanese-German Relations during and after World War I
- Japanese Ministerial Bureaucrats and the First World War
- Jaurès, Jean
- Jeglič, Anton
- Judenzählung (Jewish Census)
- July Crisis 1917 (Russian Empire)
- Karadjordjević, Peter I.
- Kemal, Kara
- Kemal, Mustafa (Atatürk)
- Kerenskii, Aleksandr Fedorovich
- Khaki Election 1918
- King's African Rifles
- Kolchak, Aleksandr Vasil'evich
- Komuch (Committee of Members of the Constituent Assembly)
- Konoe, Fumimaro
- Koo, V. K. Wellington
- Kun, Béla
- La Dame Blanche
- La Fontaine, Henri
- Laidoner, Johan
- Lansing, Robert
- Lawrence, Thomas Edward
- Leipzig War Crimes Trials
- Lenin, Vladimir Il’ich
- Liebknecht, Karl Paul August Friedrich
- Lloyd George, David
- Lodge, Henry Cabot
- London Declaration of the League of Nations
- London, Treaty of (1915)
- Loucheur, Louis
- Ludendorff, Erich
- Luxburg Affair
- Luxemburg, Rosa
- MacDonald, James Ramsay
- Macedonia and the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization
- Machado, Bernardino
- Makhno, Nestor Ivanovich
- Malvy, Louis-Jean
- Mannerheim, Carl Gustaf Emil
- Mao, Zedong
- Marie Adelheid, Grand-Duchess of Luxembourg
- Marinegebiet
- Martial Law
- Martial Races, Theory of
- Martyrs/Separatists, Syrian and Lebanese
- Masaryk, Tomáš Garrigue
- Mata Hari
- Mata Hari
- Matos, Norton de
- Max, Adolphe
- Maximilian, Prince of Baden
- May Fourth Movement (China)
- McAdoo, William Gibbs
- Metaxas, Ioannis
- Mexican Revolution
- Michaelis, Georg
- Micronesia
- Mili︠u︡kov, Pavel Nikolaevich
- Millerand, Alexandre
- Morel, Edmund Dene
- Morgenthau, Henry, Sr.
- Moroccan Crises 1905-1911
- Movement of National Defence (Greece)
- Müller, Lauro
- Mussolini, Benito
- Naumann, Friedrich
- Naval Race between Germany and Great Britain, 1898-1912
- Neuilly-sur-Seine, Treaty of
- Neutrality
- Nicaragua
- Nicholas II, Emperor of Russia
- Nikolaĭ Nikolaevich, Grand Duke of Russia
- Nishihara Loans
- Nitti, Francesco Saverio
- Noske, Gustav
- Ober Ost
- Oberstenaffäre
- Occupation of Luxembourg
- Orlando, Vittorio Emanuele
- Paderewski, Ignacy Jan
- Painlevé, Paul
- Pais, Sidónio
- Pan Americanism
- Pan-German League
- Pan-Islamism (Ottoman Empire)
- Panturkism
- Pasha, Cavit
- Pasha, Talat
- Pašić, Nikola
- Päts, Konstantin
- Paul, Alice
- Payer, Friedrich von
- Pearse, Patrick
- Peasant Uprisings/Tambovshchina
- Pessoa, Epitácio
- Petit, Gabrielle
- Piłsudski, Józef
- Poincaré, Raymond
- Polish Paramilitary Organisations before 1914
- Portuguese India
- Portuguese Macau
- Portuguese Timor
- Prochaska Affair
- Provisional Government
- Punjab Disturbances 1919
- Radoslavov, Vasil
- Rasputin, Grigoriĭ Efimovich
- Rathenau, Walther
- Redl, Alfred
- Red Scare
- Renascença Portuguesa
- Renner, Karl
- Resistance (Belgium and France)
- Revolution of 1905 (Russian Empire)
- Ribot, Alexandre Félix Joseph
- Riezler, Kurt
- Russian Occupation of the Eastern Ottoman Empire
- Said Nursi
- Saint-Germain, Treaty of
- Salandra, Antonio
- Sarajevo Incident
- Sazonov, Sergeĭ Dmitrievich
- Scheidemann, Philipp
- Schnee, Heinrich
- Scutari crisis
- Sea Power
- Selective Service Act
- Sembat, Marcel
- Shakir, Bahaeddin
- Shaw, George Bernard
- Shti︠u︡rmer, Boris Vladimirovich
- Sixtus Affair
- Smetona, Antanas
- Smuts, Jan Christian
- Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD)
- Société Suisse de Surveillance Economique (SSS)
- Solf, Wilhelm Heinrich
- Sonnino, Sidney
- Sousa Lopes, Adriano de
- Spanish Intelligence
- Spanish Neutrality
- Štefánik, Milan Rastislav
- Stereotypes
- Stinnes, Hugo
- Stockholm Conference
- Stresemann, Gustav
- Stürgkh, Karl Graf
- Sun, Yat-sen
- Sussex Pledge
- Šusteršič, Ivan
- Suttner, Bertha von
- Sykes-Picot Agreement
- Terauchi, Masatake
- The Paris Peace Conference and Japan
- Thomas, Albert
- Tinoco Granados, Federico
- Tisza, István, Gróf
- Toynbee, Arnold J.
- Trentino
- Trépont, Félix
- Trialism
- Trianon, Treaty of
- Troelstra, Pieter Jelles
- Trotsky, Leon
- Trumbić, Ante
- Turkestan
- Twenty-One Demands
- Ukraine
- Ulmanis, Kārlis
- Union of Democratic Control
- U.S. Intervention in the Caribbean
- Venizelos, Eleutherios
- Versailles, Treaty of
- Victor Emmanuel III, King of Italy
- Villalobar, Rodrigo de Saavedra y Vinent, Marqués de
- Viviani, René
- Voldemaras, Augustinas
- Vollmachtenregime
- Vorarlberg Referendum
- Wangenheim, Hans von
- War Requirement Acts
- War Surveillance Office (Austria-Hungary)
- Washington Conference 1921-1922
- Weber, Alfred
- Whitlock, Brand
- Wied, Wilhelm, Prinz zu
- Wilhelm II, German Emperor
- Wilhelmina, Queen of the Netherlands
- Wilson, Woodrow
- Workers' or Revolutionary Councils
- Yrigoyen, Hipólito
- Yuan, Shikai
- Zetkin, Clara
- Zhekov, Nikola
- Zimmermann Telegram
- Zimmerwald Conference
- Zionism
See also
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Australia
- Austria-Hungary
- Baltic States and Finland
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Burma
- China
- Denmark
- East and Central Africa
- France
- Germany
- Great Britain
- Greece
- Greece
- Ireland
- Korea
- Latin America
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Naval Blockade (of Germany)
- Newfoundland
- New Zealand
- Norway
- Ottoman Empire/Middle East
- Persia/Iran
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russian Empire
- Serbia
- Siam
- Southern Africa
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- The Netherlands
- Union of South Africa
- United States of America
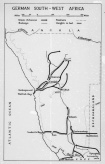
- West Africa
- Yugoslavia
Survey Articles (Thematic)
-
The First World War and its direct repercussions in the postwar period (revolution, counterrevolution, the founding of republics, and the Paris peace treaties) mark a profound caesura not only in the history of Jews in Europe but also in the history of … READ MORE
Thematic -
France and Germany remained principal protagonists of the First World War. This essay will examine the reasons why both nations believed they were in a legitimate war of defense, for which domestic unity was the indispensable precondition. The essay will … READ MORE
Thematic -
By 1914 the leading states had succumbed to varying degrees of militarism, subordinating other interests to those of the armed forces, yet all were governed by regimes in which the ultimate authority rested with civilian leaders. Civilians led the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Total war is a controversial term used in the past by politicians, publicists and military officers as well as by computer specialists and academics in the present. Since its conception by French politicians during the First World War in a time of severe … READ MORE
Thematic -
Crumbling of Empires and Emerging States: Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia as (Multi)national Countries
By Katrin Boeckh
During the First World War, Czechoslovakia and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (called “Yugoslavia” from 1929) emerged as new national states on the territories of the crumbling Habsburg Empire. Pre-dating the establishment of the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The internment of enemy aliens in the First World War was a global phenomenon. Camps holding civilian as well as military prisoners could be found on every continent, including in nation-states and empires that had relatively liberal immigration policies … READ MORE
Thematic -
One sees a wide range of political regimes from a democratic republic with universal male suffrage (France) to parliamentary, constitutional, or even oligarchical monarchies in the countries that entered the First World War. This article explores the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The Treaty of Versailles was signed on 28 June 1919, establishing both the League of Nations and another international organization: the International Labour Organization (ILO). The ILO was founded upon the conviction that “peace can be established only … READ MORE
Thematic -
After an initial wave of interest in 1914 and the immediate post-war period, international historiography long neglected the wartime occupation of territories inhabited by large civilian populations. Recently, new research has focused on the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The idea of peace in total war may seem irrelevant, but pacifism, or peace activism, did exist during the First World War. A seemingly robust European peace movement existed before 1914, but it contained internal divisions and mostly collapsed early in … READ MORE
Thematic -
This paper examines major peace initiatives during World War I. It describes efforts by the chief European belligerents to split apart enemy coalitions with separate peace settlements as well attempts by the United States and socialist Russia to spark … READ MORE
Thematic -
The conduct of warfare in 1914-1918 included extensive population resettlement in all theatres of war in Europe, both as a result of pre-emptive decisions by civilians to flee in order to evade the conflict or to avoid the consequences of occupation, and … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article surveys the various movements toward social, national, and political revolution that emerged during and in the wake of World War I. The Russian revolutions of 1917 serve as the first case study, followed by the mutinies in France, and the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Despite what some believe, there is still a lot to say and learn about the First World War, particularly with regard to war aims. A lot of focus is currently placed on the cultural, social and psychological facets of the Great War, much more than on the … READ MORE
Thematic -
It may surprise us to learn that some sectors of the European public were in favour of the war in 1914. The impact of modern weapons was not well understood and many people in the government, military and civilian population imagined that the conflict … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article provides an overview of xenophobia during the First World War - namely, the ways in which the conflict was justified and sustained by the growth of hatred for external enemies, and increasingly perceived internal ones. It discusses the … READ MORE
Thematic
Regional Thematic Articles
-
Between 1914 and 1918, between 150,000 and 200,000 Africans traveled to Europe to labor in support of the war effort. Most came from French colonies, but many also came from British colonies in Africa. They worked in diverse settings and on a variety of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Civilians in the Australian government contended with two types of military power in the Great War: generals of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF), and British army military commanders and the War Office who had operational control of the AIF. In most … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The relationship between civilian and military power in Austria-Hungary during the First World War was determined by a number of factors, including the dual state structure and the controversial nationality question. The joint army leadership tried to … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
From 1916 to 1928, the Republic China was divided among military cliques in the regions of mainland China. Provincial military power holders, by proving the impotence of Beijing, undermined the efforts to centralize power and strengthened the forces of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The responsibilities of politicians and military leaders are defined in times of war. The president commands the armed forces, the government - subject to the representatives of the nation - is in charge of conducting the war and the military operations … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Armed conflicts provide fertile ground for the military’s ambitions to gain authority over civilian institutions and actors, a process that played out in the German Empire between 1914 and 1918. While military authorities and politics were almost on an … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
By the early 20th century the United Kingdom had a well-established tradition of civilian control over the armed forces. This tradition came under strain during the Great War as the line dividing Britain’s military and political … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In Italy, as in the other European states involved in the First World War, the outbreak of hostilities saw extraordinary powers conferred upon the armed forces, so as to free them from the supervision of government and parliament. War legislation … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Like the Sino- and Russo-Japanese Wars, the First World War gave an enormous boost to Japanese military operations and authority. The Imperial Navy deployed for the first time to the South Pacific, the Indian Ocean, and the Mediterranean and the army … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War required the most comprehensive mobilization of men and resources in the history of the empire. It transformed the Ottoman state into a more centralized, authoritarian, and nationalist entity. This article explores the impact of total … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In pre-war South East Europe, both civilian and military powers focused on the creation of independent national states and the reclamation of imperial ''irredenta''. This goal, aggressively pursued, created serious regional tension between imperial and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During World War I, an unprecedented civil-military relationship developed among the U.S. government, its military, and civilian society. America struggled to find fair conscription policies despite class, ethnic, racial, and ideological differences. The … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Portugal went to war in March 1916 with a government and an army that did not sit comfortably with each other. The young republican regime’s relationship with its armed forces was difficult despite its popularity among a small number of officers and a … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the mechanisms, results, and characteristics of the national mobilization in Russia in the conditions of the First World War. Moreover, it considers the forms of cooperation between the government and the public, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When World War I broke out, the military conquest of the countries located between China, Siam and the South China Sea had been over for two decades. Nonetheless, French rule in Indochina was not entirely established and the exploitation of economic … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When the First World War came to Africa, European colonial rule was scarcely established in many parts of the continent. Some twenty years after the initial conquest, large parts of Africa remained beyond colonial control. An uneasy and fragile ceasefire … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In 1914, Allied leaders plunged Africans into a conflict that was not their own. In West Africa, British and French colonial troops quickly occupied Togo, while the conquest of Cameroon proved much more difficult. A relatively short campaign led by white … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Italian colonies, with the partial exception of Libya, played only a secondary role in the Great War. By virtue of not sharing borders with any German colonial territories, Italian overseas possessions were spared the conflict between the European … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The diplomacy of Portugal’s participation in the Great War was largely determined by the desire of elites to improve the international standing of the country, as well as by domestic factors related to the bitter quarrels of the republican … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During World War One, Denmark managed to remain neutral. But, as the country was extremely dependent on economic and political relations with both Germany and Great Britain, the war had great consequences for both foreign and domestic politics. Unlike … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The article focuses on how Norway’s neutrality during the First World War impacted domestic politics. A large majority of the country’s political elite supported neutrality throughout the war. In the early years of the war, the Norwegian economy … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Despite the official neutrality maintained by Spain throughout the First World War, the conflict had a considerable impact on that country’s internal politics. The political stances taken gave rise to a process that divided society into two opposing … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article focuses on how the Swedish neutrality policy during the First World War became a contentious topic''' '''in Swedish domestic politics. The food crisis in 1916–1917, social disquiet in connection with the Finnish Civil War, and the German … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Neutrality is a fundamental problem in modern Swiss history and played a pivotal role in both world wars. During the Second World War the danger came from the outside, while during the First World War Switzerland was also threatened from within. From 1914 … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When the First World War broke out, the Netherlands’ most important political parties put aside their differences to help uphold the country’s neutrality throughout the war. However, the Netherlands could not escape the severe strains the war put on … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The dominions of Australia, Canada, Newfoundland, New Zealand, and South Africa shared an ambiguous constitutional relationship with Britain. The self-governing dominions were free to implement their own policies in matters of defence, but their limited … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Although a military failure, the 1916 rebellion transformed Ireland by destroying the possibility of a political settlement between Irish nationalists and the British state and by popularising a republican movement prepared to use violence to achieve … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Danish government succeeded in maintaining neutrality and thus sparing the country from the most devastating consequences of the war. Denmark spent considerable effort in maintaining good relations with both Germany and Great Britain, its most … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Throughout the Great War, successive Spanish governments tried to advance traditional foreign policy claims – the annexation of Tangier, the return of Gibraltar and the possibility of intervening in Portugal – while at the same time facing the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Until 1917, Swedish neutrality was characterized by a certain “benevolence” towards Germany. Eventually, pressure from food shortages and social unrest, following the government’s reluctance to abide by British blockade regulations, led to the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Kingdom of the Netherlands upheld a foreign policy of strict neutrality during the First World War. That policy revolved around two main precepts: upholding the requirements associated with neutrality in international law (particularly the Hague … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In 1917, with tens of thousands of Canadian soldiers killed and wounded, the end of the war was nowhere in sight. As the supply of volunteers dried up, conscription became the dominant issue in Canada. French Canadians were singled out and accused of not … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Latin America figured prominently in Germany’s global war strategy, though after 1915, intelligence operations primarily focused on disrupting Allied supply lines and agitating for war between the United States and Mexico. Washington’s entry into the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Commonwealth of Australia, a self-governing Dominion of the British Empire, experienced splits during the Great War in the major parties of both the left and right. The Australian Labor Party, in 1914 the most successful social democratic party in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The closing of the parliament in Vienna in spring 1914 led to the consolidation of a wartime regime that was at once autocratic, decentralized, and poorly equipped to handle the demands of competing power centers, both within the government and throughout … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War changed the balance of power in Belgium. From a strongly polarized system dominated by the Catholic Party, the country shifted towards a coalition system, marked by a tradeoff between left and right. That shift was facilitated by the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the shifting nature of Canadian federal politics during the First World War with an emphasis on conscription and the formation of the Union Government. The impact of these issues on national unity is examined, as is the deterioration … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
China’s attempt to participate in the European war was complicated by domestic turbulence. Japan’s bid for supremacy in China compelled President Yuan Shikai to propose the Twenty-one Demands in 1915, and after Yuan’s death, there were two … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Despite its weaknesses, the French parliamentary republic survived the First World War without compromising the constitutional laws that had been in place since 1875. The ''Union sacrée'' was formed on 4 August 1914. While this initially resulted in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
At the beginning of World War I, Germany was a constitutional monarchy in which political parties were limited to the legislative arena. They could control neither the government nor the military. At the end of the war, the political system had been … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Great War marked a period of profound upheaval in British politics. The old controversies of Edwardian politics were replaced by new debates about military strategy, civil-military relations and the capacity of the state to mobilize the nation for … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Political life in the Hungarian part of the Dual Monarchy (particularly the constitutional framework, political traditions and mentality) can only be characterized as very different from that of the Cisleithanian half, with all the consequences upon the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During the period of neutrality, Italian public opinion was divided into two camps: one interventionist, and the other, in the majority, opposed to Italy’s entry into the war. Neutralism brought together the two most important political groupings in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Despite over 7,000 miles of separation from the Western Front, Imperial Japan underwent a political transformation during the First World War almost as dramatic as that in the vanquished capitals of Europe. As was the case with most belligerents, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Governments, Parliaments and Parties, Labour, Labour Movements and Strikes (Union of South Africa)
By Wessel Pretorius Visser
In South Africa the period between 1914 and 1918 was one of intense political and industrial turmoil. It entailed two violent strikes, eventually suppressed by the South African government, a rebellion against the state by Afrikaner insurgents and the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
New Zealand’s wartime parliament was dominated by a coalition between the two main parties, Reform and Liberal. Labour parliamentarians opposed the coalition and the war was a significant factor in the making of a new Labour … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
After the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) seized power in January 1913, it established a single-party government that dominated parliament from the 1914 elections until the end of the war. The CUP was a party of leaders and factions and not a … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Governments, Parliaments and Parties; Political Movements and Protostate Formation (East Central Europe)
By Klaus Richter and Piotr Szlanta
Political movements in Poland and the Baltics were heavily influenced by the German occupation, the Russian Revolution, and the political agency of their diasporas. While the establishment of an independent Polish State became a war aim of the Entente … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Founded in October 1910, the Portuguese Republic was soon mired in turmoil. The victorious Portuguese Republican Party, in reality a broad ideological coalition united only by the desire to topple the monarchy, soon fragmented acrimoniously, first into a … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
At the beginning of World War I, Russian political parties found themselves in deep crisis. In contrast, the State Duma had become the epicenter of the country’s political life. The “Holy Alliance” established between the authorities and society was … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This essay analyzes domestic politics in the United States during World War I, focusing chiefly on the Wilson administration’s relations with Congress and on electoral politics from 1914 to 1918. Throughout this period, war-related issues became … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article seeks to analyze how the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), the oldest existing humanitarian organization, coped with the outbreak of the First World War and its aftermath. By using innovative methods of work and by deploying an … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Russian Civil War of 1917-20 was closely related to the World War in terms of its cause, conduct, and results. This article discusses the two distinct phases of the Civil War, which were divided by the collapse of the Central Powers. It examines the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the history of the Spanish army during the First World War in the context of the Spanish strategic and security situation. It shows the interrelation between Spanish military weakness and strategic insecurity. Particularly focusing … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Armistice agreement foresaw the occupation of the left bank of the Rhine, the dates of which were set by the Treaty of Versailles. The inter-allied occupation was a long-term endeavour: the French settled in the south and the Belgians in the north of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
While on the Western Front there were only limited territorial movements, the Eastern Front and warfare in southeastern Europe, including parts of Italy, had all the characteristics of mobile warfare. During the course of the war, Austria-Hungary took … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article surveys the occupation of the formerly German-leased territory around the Jiaozhou Bay with Qingdao as its capital city by the Japanese during and after the First World War. It first describes the initial ultimatum of the Japanese to the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the politics of the German (''Generalgouvernement'' Warschau) and Austro-Hungarian (''Militärgeneralgouvernement'' Lublin) occupation of the Kingdom of Poland during World War One. Both occupation governments strove to exploit the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article studies Germany’s experiences of occupation during and immediately after the First World War. The first section examines the French attack on Alsace-Lorraine in August 1914 and the Russian invasions of East Prussia from August 1914 until … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During and after the First World War, Italy experienced different kinds of occupation. The Italian occupation of the border areas in 1915-1917 was followed by the Austro-German occupation in 1917-1918 after the Caporetto defeat. Then, in 1918-1919, in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The occupation of the Arab lands of the Ottoman Empire was essentially the by-product of the war, but it had been in the making for a long time. Despite their attempt to appear as liberators rather than occupiers, the British and, later, the French … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Memories of occupation by foreign forces are not usually articulated except when prisoners of war speak of their experiences when debriefed. These are usually shameful episodes in the lives of those who survived. Collaboration with the enemy often … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Occupation played a crucial role in Eastern Europe between 1914 and 1921: the highly mobile front allowed trenches to be shifted over hundreds of miles, resulting in the usurpation of foreign lands. While Russia only managed to occupy Habsburg Galicia and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The occupation of South East Europe 1915-1918 had a complex structure reflecting different and often conflicting territorial claims and goals. In the fall of 1915 Serbia was divided into Austro-Hungarian, Bulgarian and German occupation zones. The … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the German occupation of Belgium and Northern France in 1914–1918. Besides focussing on the occupiers’ motives and logic of action regarding their policy and practices, it gives an idea of the complexity of the occupier/occupied … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
World War One represented a turning point in the relationship between churches and the Portuguese state. Both Catholics and Protestants perceived the conflict as an opportunity to expand their scope of influence in a society then dominated by a sector … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article charts the contours of the Great War as an American religious experience, focusing on the ways in which the study of religion and the Great War in America forces an examination of what is meant by “religion.” American clergy and American … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Great War helped to ease the Church-state tensions that had shaped French politics and society during the preceding generation. However, the very different context of the French colonial empire prevented a similar reconciliation overseas. This article … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Africans across the continent resisted colonial demands and took up arms against European colonizers during World War I. This essay presents three ways of recognizing and analyzing such acts of resistance. First, many Africans refused increased colonial … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Revolutionary movements in India haunted the imagination of post-war British officialdom. They were used in the aftermath of the First World War to justify everything from colonial massacres to the indefinite censorship of the press. But what were these … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article provides an overview of the 1916-1918 Arab Revolt against the Ottoman government during World War I, led by Sharif Husayn bin ‘Ali of Mecca in conjunction with British support. The main aim of the revolt was to establish an independent Arab … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Revolutions and Rebellions: Van Resistance as Rebellion (Ottoman Empire/Middle East)
By Yasar Tolga Cora
Violent clashes took place between the Ottoman troops and the Armenian guerilla bands in the city of Van on the eastern edge of the Ottoman Empire in April-May of 1915. The armed struggle in the city and the subsequent occupation of the region by the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The following pages - focusing on the collapse of the Habsburg Empire and the incidents in Austria in 1918/20 - are subdivided into four different periods and aspects: Firstly, World War One until the increasing protest movements of 1917/18, secondly, … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses the influence the Russian Revolution had on countries in East Central Europe. In the Polish Kingdom and Lithuania there was no direct impact because of the German occupation. The parties which sympathized with the Bolsheviks had no … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article focuses on the upheaval between 1917 and 1923. These years were marked by crumbling empires, national mobilisation, and conflicting ideologies and forms of government. Rather than single out specific revolutionary or counter-revolutionary … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Portugal’s participation in the First World War, never consensual, was marked by a number of violent episodes that first undermined and then overthrew the Sacred Union government. Some of these were rural and urban mutinies occasioned by inflation and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Russian Revolution was one of the most influential events to emerge from the furnace of the First World War. It transformed Russia and its Empire and firmly planted the flag of world revolution at the centre of 20th century world history. … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
''Teşkilat-ı Mahsusa'' (TM), or Special Organization, was a secret paramilitary intelligence organization under the control of the CUP’s inner circle and attached to the Ministry of War. Due to its secrecy, the TM is debated in the scholarship. This … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
From the outbreak of World War I, Woodrow Wilson pursued two goals: a non-punitive peace settlement to end the conflict and a reformation of world politics through an international peace-keeping organization to prevent such wars in the future. Before the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War led to a renewed imperialist scramble for territory in Africa. Allied victory and African campaigns allowed British, French, Belgian, Portuguese and South African leaders to acquire Germany’s colonies. Their wartime colonial aims … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Although Britain declared war on the Dominions’ behalf, Australia had its own war aims. The most important of these was the survival of the British Empire, which the vast majority of Australians believed was key to the country's cultural identity and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In July 1914 the Habsburg monarchy went to war with Serbia declaring it sought no territorial gain from the struggle. Soon discussions of possible territorial acquisitions, along with economic and political aims, started among the governing elite and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war aims were a direct consequence of the way in which the country was created. The treaties finalized in 1839 left Belgium with part of Luxembourg and Limburg, and also left the Scheldt access to Antwerp under Dutch control. During World War … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses China’s war aims during the First World War, as well as the intra-Chinese discussion over which side to enter the war on. It surveys the extent of the different aims, most of which were related to regaining control over foreign … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Already in autumn 1914, East Central Europe became a main theatre of operational warfare and an object of strategic planning for the Central Powers, Russia, and later the Entente. After strategic failure in the West, Germany focused on this region as an … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
On 4 August 1914, in his first speech after the declaration of war, Raymond Poincaré, president of the French Republic, did not outline any aims other than the ''Union sacrée'' (sacred union) and the defence of the country’s borders. Once the hopes … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
On 1 August 1914, the government of the German ''Reich'' declared war on Russia. Directly afterwards, an intense debate over its war aims flared up. This article traces the development of the war aims discussion: The nationalist War Aims Movement … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When Britain entered the First World War its war aims were simple: to restore Belgian sovereignty (as it was obliged to do, by the Treaty of London, 1839), and to maintain the balance of power in Europe by defending France and chastening Germany. … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
At the outbreak of the First World War, Italian diplomacy did not have a clear vision of the goals to be achieved. Therefore, in negotiations with the countries already involved in the conflict, excessive territorial claims were made. The errors of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses Japan’s war aims during the First World War, as well as the different policy approaches Japanese leaders employed to achieve those aims. It explores Japan’s entrance into the war on the side of its ally Britain, its military … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Ottoman Empire fought the First World War for the sake of survival in the short term and independence and security in the long. Its diplomatic, territorial, economic, and domestic war aims were shaped to this end. Its military strategy acknowledged … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Portugal’s wartime governments never formulated a concrete set of war aims. The nature of the country’s intervention did not lend itself to this kind of debate. With a long-defined border with Spain, and more colonial territory than it could … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Russia reluctantly entered the Great War to preserve its status as a great power. However, once the fighting began, it was the first amongst the Allies to state its territorial desiderata, which were to annex lands along the borders of Germany and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article offers a survey of the main currents in South East Europe in regard to the war aims of the belligerents from 1914. Some war aims had deep roots in the pre-war years. The author puts emphasis on the emerging Yugoslav state in the Balkans. The … READ MORE
Regional Thematic
Encyclopedic Entries
-
On 25 May 1915, Argentina’s, Brazil’s and Chile’s ministers of foreign affairs signed a treaty to facilitate the peaceful solution of international controversies in Buenos Aires. Mired in diplomatic discussions for more than ten years, this treaty, … READ MORE
Entry -
A minority of the adherents of the Flemish movement were willing to collaborate with the German occupier in the context of ''Flamenpolitik''. This minority labelled themselves “activists”, stressing their dislike of the Belgian patriotic … READ MORE
Entry -
Until his death in 1918, Victor Adler was the most prominent Austrian socialist leader and among the leading personalities of the Second Socialist International. During the war, he aimed to preserve Austrian Social Democracy’s impressive prewar gains … READ MORE
Entry -
Ador was the third president of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and a Swiss minister during WWI. He displayed the charisma, the diplomatic skills and the decisiveness necessary to give the ICRC a crucial role in the protection of … READ MORE
Entry -
Albert I, the third king of the Belgians, played a leading role as supreme commander of the Belgian army during the First World War. For four years he defended the last piece of unoccupied Belgium behind the Yser River, refusing to sacrifice his troops in … READ MORE
Entry -
Albrecht Duke of Württemberg was the commander-in-chief of the German 4th Army from 1914-1917 and the ''"Heeresgruppe Herzog Albrecht"'' ("Army Group Duke Albrecht") from 1917-1918. The 4th Army fought under Duke Albrecht’s … READ MORE
Entry -
Umar al-Da’uq was a merchant and notable of Beirut in the late Ottoman period. He was Mayor of Beirut during WWI and participated in his official and private capacities in the famine relief efforts. He became president of the short-lived Arab government … READ MORE
Entry -
Born Princess of Hesse-Darmstadt, Aleksandra Fedorovna married the future Russian Emperor Nicholas II in 1894 and became empress. She was engaged in charity work and served as a nurse during the First World War. However, she was suspected of treason and … READ MORE
Entry -
Alfonso XIII was a controversial Spanish king during the first decades of the 20th century. During the First World War he established a humanitarian office for prisoners and civilian relief at the Royal Palace in … READ MORE
Entry -
The diffusion of anarchism in Latin America, which began in the 1870s, was boosted by large migration flows. Between 1890 and 1920, anarchism was an essential element in the process of workers’ self-organization. Opposition to the war characterized the … READ MORE
Entry -
A short lived agency, the Arab Bureau (1916-1920), was ostensibly established to co-ordinate British wartime policy in the Near East, track the regional direction of Turco-German activity and disseminate propaganda among Indian Muslims. In fact, its … READ MORE
Entry -
There were a number of Arab intellectuals who actively cooperated with the Entente and Central Powers during the Great War through their actions, writings and speeches. The entry focuses on the actions of Shakib Arslan, Muhammed Kurd Ali and the al-Khatib … READ MORE
Entry -
Armenians contributed greatly to the Allied victories in Europe and Western Asia, both as non-state and state combatants. They scored important victories, but also suffered defeats. The war precipitated an ethnic disaster and the loss of lands, but also … READ MORE
Entry -
With branches in the Ottoman Empire, Russia, and Iran, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (''Hay Heghapokhagan Dashnaktsutiun'') was the leading Armenian political party during the First World War. The party leaders and cadres in the Russian and … READ MORE
Entry -
Shakib Arslan was a prominent Arab politician, polemicist, and man of letters. Arslan, an ardent supporter of the Ottoman Empire, lobbied for the maintenance of the Islamic Caliphate after World War I, becoming an outspoken activist for Panislamism and … READ MORE
Entry -
Asquith was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom at the outbreak of war. He formed a coalition in May 1915 but accusations of ineffectiveness led to his replacement by David Lloyd George in December 1916. He remained out of office and subsequently lost … READ MORE
Entry -
The Republic of Azerbaijan is a majority Turkic and secular Muslim nation in the South Caucasus. This republic was proclaimed on 28 May 1918, during World War I. The Bolshevik invasion on 27 April 1920 ended Azerbaijan’s brief independence. The nation … READ MORE
Entry -
Cemal Azmi was an Ottoman official who served during the Great War as governor (''vali'') of the province (''vilayet'') of Trebizond. Being the mastermind of the Armenian genocide in this province he earned the surname of the butcher of Trebizond. His … READ MORE
Entry -
A lawyer, Progressive, and pacifist, Newton Baker was U.S. Secretary of War during World War I. He oversaw a massive mobilization that relied on a sweeping draft law and cooperation between government officials, business elites, and reformers. Baker’s … READ MORE
Entry -
Arthur James Balfour was a British Conservative politician and statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and was later Foreign Secretary. In the latter post, he issued the Balfour Declaration of 1917 on behalf of the British government, … READ MORE
Entry -
The Balfour Declaration, the document that set the stage for establishing the state of Israel, was the product of months of wordsmithing and political jockeying. The evolution of its final wording sheds light on the goals and agendas of political powers … READ MORE
Entry -
The Imperial and Royal Ministry of the Imperial and Royal House and of Foreign Affairs, informally called “Ballhausplatz” after the Viennese square on which the central office was located, was one of only three joint ministries of Austria-Hungary. … READ MORE
Entry -
Cesare Battisti was the leader of the socialist party of the Italian Tirol (Trentino) and, from 1911, a member of the Austrian parliament. At the outbreak of war he went to Italy to engage in pro-intervention propaganda. In 1915 he joined the Italian … READ MORE
Entry -
The Batum Conference (May 1918) and treaties ended the state of war between the Ottoman Empire and various governments of the South Caucasus. Additional treaties were signed with the North Caucasus. By these treaties, the empire won 20,000 square … READ MORE
Entry -
Max Bauer was a German artillery expert and a key suborndinate in the German Supreme Command. A loyal suporter of Ludendorff, Bauer intrigued against Falkenhayn and consistently pushed for the further militarisation of German everyday life. He played a … READ MORE
Entry -
Otto Bauer was a leading Austro-Marxist and socialist politician who served during the war as an officer in the Austro-Hungarian army. After returning from Russian internment to Vienna in 1917, he joined the Leftist opposition within the Social Democratic … READ MORE
Entry -
Gertrud Bäumer was one of the most well known leaders of the German women’s movement. In 1914, as the president of the Federation of German Women’s Associations (''Bund Deutscher Frauenvereine'', BDF), she co-founded the National Women’s Service … READ MORE
Entry -
Ruijs de Beerenbrouck was a Dutch Prime Minster who successfully dealt with the threat of revolution in November … READ MORE
Entry -
Gertrude Bell’s earlier travels and intellectual interests, alongside her wartime intelligence-gathering activities, prefigured the role she would play in administering the new Iraqi state. In recent years, scholars have drawn more attention to her … READ MORE
Entry -
Edvard Beneš was a Czech politician, diplomat, and close collaborator of Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk. As Secretary General of the Czechoslovak National Council in Paris from 1916 to 1918, he successfully organized Czechoslovak propaganda; helped create the … READ MORE
Entry -
Graf Leopold Berchtold, Habsburg foreign minister from 1912 to 1915, was confronted with military action during and after the Balkan Wars, yet kept peace. Then, the Sarajevo assassinations, blamed on Serbia, convinced him that only war with Serbia would … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, Berlin became an organisational hub for Indian nationalist and revolutionary activities. By September 1914, a group of South Asian emigrants had organized – with permission of and in cooperation with the German Foreign Office … READ MORE
Entry -
Count Bernstorff was German ambassador to the United States from 1908 to 1917. He tried in vain to warn the Reich government against unrestricted submarine warfare which would result in America’s entry into the … READ MORE
Entry -
Hans Hartwig von Beseler was a German general and military engineer who oversaw the conquest of several fortresses early in the war. He was then named commander of German-occupied Poland, a post he held until the end of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Bethmann was a career civil servant who became Imperial Germany’s fifth Reich Chancellor and took Germany into the First World War. Despite heading the imperial German political administration, his power was circumscribed by the role of Kaiser Wilhelm … READ MORE
Entry -
Louise de Bettignies created an intelligence network for the British in occupied France. She was arrested, sentenced to death in March 1916 and deported to the prison of Siegburg. Sick, she died in Cologne in September 1918, and was commemorated … READ MORE
Entry -
Moritz von Bissing was born on 30 January 1844, in Bellmannsdorf, Silesia, then part of the German Empire. He served as governor general of the Prussian Army from December 1914 until his death on 18 April 1917 in Trois Fontaines, a village in … READ MORE
Entry -
This article looks at the Black Hand from its origins to the demise of its leader, Dragutin Dimitrijević "Apis", in the Salonika Trial of 1917, focussing on the role the association played in Serbia’s foreign and domestic affairs before and during the … READ MORE
Entry -
Howard Sweetser Bliss was the President of the Syrian Protestant College (SPC) during the war. His congenial relationship with Jamal Pasha helped to ensure the security of the college and American community throughout the war. At the Paris Peace … READ MORE
Entry -
Jan Bloch was an entrepreneur, social activist and pacifist. At the end of his life, he published a comprehensive work in which he predicted the course and consequences of World War I. He warned of the dangers of a total, destructive war and urged … READ MORE
Entry -
Jan Bloch was an entrepreneur, social activist and pacifist. At the end of his life, he published a comprehensive work in which he predicted the course and consequences of World War I. He warned of the dangers of a total, destructive war and urged … READ MORE
Entry -
Bonar Law was leader of the Conservative Party in Britain during the war. He entered Asquith’s coalition government in May 1915, and in December 1916 played a crucial role in Lloyd George becoming Prime Minister. For the rest of the war, he was a key … READ MORE
Entry -
The borders of the Netherlands were an important site of war experience for the Dutch, as well as a contested site of war interaction for the … READ MORE
Entry -
As a Flemish nationalist, August Borms actively collaborated with the Germans during the First World War. As a result of his ten-year imprisonment and his death sentence he became a true symbol of Flemish … READ MORE
Entry -
After a long parliamentary career, Paolo Boselli became Italy’s 22nd prime minister in June 1916 after the fall of Antonio Salandra’s government. Charged with forming a unity government, his leadership was uninspiring and he was forced to … READ MORE
Entry -
In the narrow sense, the so-called “Bosnian Crisis” (or “Annexation Crisis”) of 1908 and 1909 was a political conflict between Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire caused by the (formal) incorporation of Bosnia and Herzegovina into the territory … READ MORE
Entry -
Venceslau Brás was president of Brazil between 1914 and 1918. On 26 October 1917, he signed the Brazilian declaration of war against … READ MORE
Entry -
Liberal Prime Minister Ionel Brătianu led the charge to transform Romania's foreign policy, after three decades on the same side with the Triple … READ MORE
Entry -
Brazil was the only South American country that participated actively in the First World War. Before the war, the country was economically dependent on European and North American markets and modelled itself on Western culture and science. After the war, … READ MORE
Entry -
At Brest-Litovsk, from 22 December 1917 to 10 February 1918 (Julian calendar: 9 December − 28 January), Soviet representatives and the Central Powers negotiated a separate peace. On 3 March 1918, following the breakdown of the talks and a new German … READ MORE
Entry -
As an imperial diplomat, first Foreign Minister of the Weimar Republic, leader of the German Peace Delegation in Versailles and also first ambassador to the Soviet Union, he acted in decisive positions in pre- and post-war German foreign policy. His … READ MORE
Entry -
Charles de Broqueville, chief of the Belgian government during the First World War, acted as liaison between the king and the Belgian government. He supported the king in his attempts to obtain peace and his efforts to break free from the … READ MORE
Entry -
The Belgian capital was spared the anguish of combat, but the city suffered four long years of occupation. In fact, it became the most important occupied city during the First World War. For the population, these were times of scarcity, repression, and … READ MORE
Entry -
Williams Jennings Bryan was a powerful Democratic politician, from his emergence on the American political scene in the 1890s to his death in 1925. A three-time Democratic nominee for president, Bryan served as secretary of state under President Woodrow … READ MORE
Entry -
During his career as a diplomat and courtier (knighted count in 1899 and prince in 1905), Bernhard von Bülow became Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs (after 1897) and German Chancellor (1900-1909). He hoped to attain a “place at the sun” for his … READ MORE
Entry -
István Burián was a leading Austro-Hungarian career diplomat and politician, rising to become the Monarchy’s longest-serving foreign minister during the First World War. Burián’s wartime policies included trying to pacify neighboring neutrals and … READ MORE
Entry -
Minister plenipotentiary for England in Lisbon, there was consensus about Lancelot Carnegie as a diplomat in Portuguese public opinion. He was recognized as one of the people responsible for the consolidation of the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance. With the … READ MORE
Entry -
For three decades Romania’s foreign policy depended almost entirely upon King Carol I’s will. The secret alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary was his sole political project. His death, which occurred shortly after the outbreak of the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
Following a career as British consul and humanitarian investigator, Roger Casement became involved in the Irish nationalist movement and the Irish Volunteers. On the outbreak of war, he sought help in Germany for Irish independence. On learning of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Mehmed Cavid Bey was born in Thessaloniki to a Sabbatean (''dönme'') family in either 1878 or 1879. After studying in his hometown, he moved to Istanbul and worked in the education ministry. Prior to the 1908 Constitutional Revolution, he was a teacher … READ MORE
Entry -
Cemal Paşa belonged to the top leadership of the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), which ruled the Ottoman Empire during World War I. He served as wartime minister of the navy and autocratic governor general and commander of the Fourth Army in … READ MORE
Entry -
In his youth, the archduke was introduced to the idea of federalism by Archduke Franz Ferdinand. During the first part of World War I, he became a skillful military leader without any political influence. The young emperor’s two main aims, the reform of … READ MORE
Entry -
Virendranath Chattopadhyaya belonged to the transnational networks of Indian political activists who, during the first decades of the 20th century, carried out anti-imperial and anti-colonial propaganda outside India, first in Europe and North … READ MORE
Entry -
Churchill was Navy Minister during the early stages of the war but was widely criticized over his handling of the Dardanelles campaign. He was demoted and soon afterwards resigned from the government in order to serve on the Western Front. He quickly … READ MORE
Entry -
Circassian nationalism refers to national movements among Adyghe people, a North Caucasian ethnic group. The term is also used to include other North Caucasian peoples who share historical commonalities with the Adyghes. By 1914, the overwhelming majority … READ MORE
Entry -
World War I had a profound impact on concepts of citizenship. Not only did hosts of people find themselves under new sovereignty at the end of the war, but many individuals had to contend with the experience of statelessness or redefinition as “enemy … READ MORE
Entry -
Count Heinrich Karl Clam-Martinic was a German-speaking Bohemian high aristocrat and close friend to heir apparent Archduke Franz Ferdinand. Under Emperor and King Charles I, Clam-Martinic was Austrian (Cisleithanian) prime minister from 1916 to 1917 and … READ MORE
Entry -
During the war, Georges Clemenceau fought for a more efficient war effort and for parliamentary control of military affairs and, as a journalist, rejected unlimited censorship. As French premier, he embodied the “integral war” and the struggle for … READ MORE
Entry -
Collaboration is often associated with the military occupations of the Second World War, but there was a precursor to this multi-faceted phenomenon in occupied France and Belgium during the First World War. This article examines the meaning of … READ MORE
Entry -
Michael Collins was a revolutionary leader who rose to become chairman of the Irish provisional government in 1922 and Commander-in-chief of its army in the brief interval that supervened before his death the same year. He sought to use violence in a … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich Naumann’s ''Mitteleuropa'' (1915) was a liberal voice in the largely illiberal German discussion on the future of East Central and South East Europe. His reasoning, based on principles of free trade and voluntary cooperation, did not dominate … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War I, many conscription age-men sought exemptions from combat duty for reasons of conscience. Religious beliefs formed the large majority of objections, but other reasons included humanitarian and political opposition to the war. While most … READ MORE
Entry -
King Constantine I, a brave army officer but rather controversial in his political choices, is mainly known for his strong disagreement with Prime Minister Eleutherios Venizelos over the role of Greece in World War I, which resulted in the painful … READ MORE
Entry -
The Constantinople Agreement, alternatively known as the Straits or Istanbul Agreement, was a secret agreement concluded between Britain, Russia, and France on 18 March 1915. The most important stipulation of the agreement was the Allies’ promise to … READ MORE
Entry -
The Corfu Declaration was a formal agreement between the government-in-exile of the kingdom of Serbia and the Yugoslav Committee (anti-Habsburg South Slav émigrés) that pledged to unify Serbia with Austria-Hungary’s South Slav territories in a … READ MORE
Entry -
P.W.A. Cort van der Linden was the Dutch prime minister from 1913 to 1918. His cabinet managed to preserve Dutch neutrality throughout the … READ MORE
Entry -
Afonso Costa’s name is indelibly attached to Portuguese interventionism. He led the government when Portugal entered the First World War in March 1916; participated in the first Sacred Union cabinet; and led the second, starting in April 1917. He also … READ MORE
Entry -
George Creel is most famous as Chairman of the Committee on Public Information (CPI) in the United States during the First World War. Under his leadership, the CPI pioneered public relations and propaganda techniques that were later used both by … READ MORE
Entry -
Benedetto Croce is an important figure for both Italian intellectual life (through his philosophical and historical writings) and the political history of Italy (through his work as a politician). Croce began his political life in 1910 and was a member of … READ MORE
Entry -
Ottokar Graf Czernin was an Austrian politician and the minister of foreign affairs for Austria-Hungary from 1916 to … READ MORE
Entry -
Josephus Daniels was United States secretary of the Navy from 1913–1921. He democratized, expanded, and modernized the United States Navy, preparing it for service in the First World War. During the war Daniels championed the North Sea mining barrage … READ MORE
Entry -
Ignacy Daszyński was one of the foremost figures on the Polish political scene in the first half of the 20th century. He personified a subset of elites who merged the struggle for social justice with respect for the principles of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Har Dayal was one of the chief architects of a quixotically sketched blueprint to effect a republican-socialist revolution in British India during the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
As a socialist, Eugene Debs unsuccessfully ran for president four times. He served two prison sentences: the first due to his role in the Pullman Strike in 1894, and the second after being indicted under the Espionage Act as result of his criticism of … READ MORE
Entry -
Following the Bolshevik seizure of power in October 1917, Lenin issued his Decree on Peace, calling for a truce and demanding that peace be agreed upon by people’s assemblies to be convened across Europe. There was no popular European uprising, however, … READ MORE
Entry -
The Defence of the Realm Act (DORA) afforded the British government extraordinary emergency powers during the First World War. DORA’s remit was expansive, and grew in severity throughout the war, though public reaction was generally muted. DORA’s … READ MORE
Entry -
A local notable and mayor of Lille during the occupation, Charles Delesalle was forced to work with the Germans but also sought to protect the population as best as possible. In particular, he played an important role in food provision, overseeing … READ MORE
Entry -
De Valera was a prominent figure in the Easter 1916 rebellion against British rule. He subsequently became head of the Irish … READ MORE
Entry -
Roman Stanisław Dmowski was a Polish politician and most importantly the co-founder of National Democracy in Poland before the First World War and during the interwar period. He was also the co-founder of Polish National Committee in 1917 and served as … READ MORE
Entry -
In February 1917 two centres of power emerged to replace the tsarist government: the Provisional Government and the Petrograd Soviet. The Provisional Government had formal authority but the Soviet controlled the actual levers of power, including the … READ MORE
Entry -
W.E.B. Du Bois, sociologist, historian, and socialist, promoted African American advancement and expected the war to improve the position of nonwhite minorities in the United States and globally. He was the editor of the NAACP magazine, which protested … READ MORE
Entry -
The Tsar reluctantly granted an elected legislative assembly, the State Duma, during the 1905 Russian Revolution. The first two Dumas were dissolved amidst bitter conflict and the third did little to resolve Russia’s pressing social and economic issues. … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich Ebert became the most important leader of the SPD during the First World War, alongside Philipp Scheidemann. During the revolution, Ebert rose to the top position within party hierarchy and drew Germany towards parliamentary democracy, first as … READ MORE
Entry -
Queen Elisabeth was the third queen of the Belgians. Her attitude during the First World War propelled her to the mythic rank of "Queen … READ MORE
Entry -
World War I was not simply a conflict among European states but a global war of empires. The fighting took place not only in Europe, but also in Africa, Asia, and across the Middle East, and it involved, as soldiers or laborers, millions of Africans and … READ MORE
Entry -
After leading the coup that brought the Committee of Union and Progress to power, Enver was appointed chief of staff and war minister. Convinced of a German victory, he decided to join World War One. In November 1918, he fled to Germany and then to … READ MORE
Entry -
As a Member of Parliament 1917, Erzberger, the former annexationist, played an important role in drafting the Reichstag’s Peace Resolution and the setting up of the ''Interfraktioneller Ausschuss'' (Interparty Committee). As secretary of state of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Before the war, Ethiopia had many diplomatic connections with European states and found itself in a strong position relative to them, particularly after defeating Italy in 1896. Once war broke out, it positioned itself as neutral. However, it also had an … READ MORE
Entry -
Paul Eyschen, prime minister of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg from 1888 to 1915, insisted on the neutral status of Luxembourg, but practiced a policy of accommodation towards German occupying forces during the war. This policy was disapproved of by the … READ MORE
Entry -
Ludwig Freiherr von Falkenhausen was a German General and military writer who served in different leadership positions during World War One. From 1917 until the end of the war he was governor-general in … READ MORE
Entry -
Faysal ibn Husayn commanded the Northern Army of the Arab Revolt and was raised to the throne of Syria in October 1918. The French invasion drove him from Damascus in April 1921. Made king of Iraq under British tutelage, Faysal guided the country to … READ MORE
Entry -
Tsar Ferdinand I of Bulgaria undoubtedly contributed to the modernization of the country. His name, however, is linked to two national catastrophes: Bulgaria’s participation in the Second Balkan War, and the failure of Bulgarian national ideals during … READ MORE
Entry -
Abel Ferry was a French politician and minister as well as an infantry combatant, who used his first-hand knowledge of the war to try and shape the official war effort. He died as a result of his parliamentary inquiries at the front. His diaries and … READ MORE
Entry -
The German ''Flamenpolitik'' during the First World War aimed to instrumentalise the Flemish movement in order to ensure lasting German control over Belgium. It did not divide the Belgian or even Flemish population as a whole, but managed to split the … READ MORE
Entry -
The First World War engendered a rift within the Flemish movement, with some wishing to pursue the advocacy for Flemish rights and others preferring to await the end of the war to obtain new laws. After the war, the Flemish movement broadened its base and … READ MORE
Entry -
The Fourteen Points were U.S. President Woodrow Wilson’s post World War I blueprint to end territorial disputes in Europe, promote international commerce, and make the world safe for democracy. They were based on the ideas of open trade and collective … READ MORE
Entry -
Under the terms of the 1867 constitution, Francis Joseph retained his prerogatives in foreign policy. His decision to opt for war in 1914 was largely a result of the frustrations of Austria’s policy during the Balkan Wars of 1912-13. Francis Joseph … READ MORE
Entry -
Ludwig Frank was a member of the Reichstag for the Social Democratic Party. When Germany entered the war, he strongly supported voting for war loans and volunteered for war service at the age of forty. He was killed in combat shortly afterwards in … READ MORE
Entry -
This biographical overview of Archduke Franz Ferdinand examines the evolution of his difficult personality through the traumatic experiences of barely surviving tuberculosis and fighting for the right to marry; his political orientation and imperial … READ MORE
Entry -
“Freedom of the seas” was the early 20th century idea that the world’s oceans served as a global commons for carrying cargo and facilitating commerce. As both a communal property and throughway, the seas thus could not be controlled by … READ MORE
Entry -
Juozas Gabrys was one of the major advocates of Lithuanian political aspirations in the international arena from 1911 to 1918. He contributed to the establishment of the Council of Lithuania in 1917. However, by acting mainly abroad, he gradually lost … READ MORE
Entry -
General Joseph-Simon Gallieni was a colonial officer who became the Governor of Paris in 1914 and Minister of War in … READ MORE
Entry -
Arnaldo Garcez was the only official photographer of the Portuguese army on the Western Front, a fact that hints at the importance of his mission. Arriving in France in 1917, he thoroughly reported on a specific sector amidst the British lines, from the … READ MORE
Entry -
Harry Garfield worked in a number of civic positions during his life. When the United States entered World War I, President Woodrow Wilson asked him to oversee the Fuel Administration. As the leader of the Fuel Administration, Garfield successfully … READ MORE
Entry -
Lindley Garrison was a prominent lawyer and politician from New Jersey who rose to the rank of vice chancellor of the state in the early 1910s. Because of his prominence, Woodrow Wilson selected him to be his first secretary of war. However, the two … READ MORE
Entry -
Eric Geddes was the most prominent example of Britain’s deployment of businessmen in government. He was the driving force behind the reorganization of the British Expeditionary Force’s (BEF) logistics on the Western Front and the political head of the … READ MORE
Entry -
After the German Army had occupied wide areas of Belgium, the “Imperial Government General in Belgium” was established on 23 August 1914 with a governor-general at its head. Organized into a military administration (the “Government General”) and a … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1915, Germany set up the “''Generalgouvernement'' Warschau”, or General Governorate Warsaw, as the administrative unit for its occupied territories in Russian Poland. Under the leadership of Governor General Hans von Beseler and Wolfgang von Kries, … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Große Hauptquartier'' (Great Headquarters or GHQ) was the strategic command centre of the German armed forces for the duration of the war. It comprised representatives of all political and military decision-making … READ MORE
Entry -
King George V served as a figurehead for the nations of the British Empire throughout the war. He and his wife, Queen Mary, provided inspiration and support for both the armed forces and the civilian populations through hundreds of official visits and … READ MORE
Entry -
World War One was a catalyst for Georgian independence, which was declared on 26 May 1918. The war demonstrated the significance of Georgian territories as a transit route and source of raw materials for contending empires. During the war, Transcaucasia … READ MORE
Entry -
The German Fatherland Party (1917-1918/1919) aspired to mobilize members of the broader radical right as well as the milieus of the German Conservative Party and the National Liberal Party. It aimed to gather broad support for the annexationist War Aims … READ MORE
Entry -
German-speaking elites in Brazil were traditionally in contact with German colonial actors, and during World War I, many middle-class immigrants sympathized with Germany. This led to a conflict within Brazilian society, where people predominantly sided … READ MORE
Entry -
Germany’s offer of unconditional support to its Austro-Hungarian ally in July 1914 remains one of the most controversial decisions in modern history. Historians have interpreted the blank cheque in several, often contradictory, ways – either as a … READ MORE
Entry -
Although sometimes characterized as a quixotically hatched scheme to overthrow British rule in India, the Ghadar “conspiracy” is best understood as a failed bid to foment a democratic revolution in India in the midst of the First World War. The … READ MORE
Entry -
Giovanni Giolitti favored the increased liberalization of Italy, which encouraged its estrangement from the Triple Alliance. He consistently refused to recognize that Italy’s partners’ aggressive policies could trigger the ''casus foederis'' for war. … READ MORE
Entry -
Colmar von der Goltz was one of pre-war Germany’s most outstanding and controversial military theoreticians. His publications had a considerable impact on military thought and the role of armed forces within society around the world. His ideas were … READ MORE
Entry -
Hermann Göring was a highly decorated and well-known fighter pilot of the First World War and later a high-ranking National Socialist … READ MORE
Entry -
Thomas Watt Gregory served as Attorney General of the United States during World War I. He played a key role in developing the Espionage and Sedition Acts to suppress dissent during World War I and enforcing Selective Service draft laws. He served as an … READ MORE
Entry -
Grey was the longest-serving British foreign secretary of the 20th century. His time in office is controversial for his role in the outbreak of the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
Grigorovich was Navy Minister between 1911 and 1917. He sought cooperation with parliament and secured funds to rebuild fleets ravaged by war with Japan. His support for mobilisation in 1914 helped push Russia into a conflict for which the navy was … READ MORE
Entry -
Robert Grimm was the most powerful socialist politician in Switzerland throughout the first half of the 20th century. As the organiser of the Zimmerwald and Kiental Conferences, he was one of the prominent figures of the international socialist … READ MORE
Entry -
As head of the Railway Section at the General Staff, Groener was responsible for the timely transport of troops to the front in August 1914. He was sacked from the Supreme Army Command (''Oberste Heeresleitung'', OHL) in August 1917 and deployed to the … READ MORE
Entry -
General Vassillii Iosifovich Gurko was a Russian military commander during the First World War. Between November 1916 and February 1917 he was the chief of staff in the General Headquarters of the Russian … READ MORE
Entry -
Hugo Haase was a prominent social democrat in the ''Kaiserreich'', who opposed German war aims and formed the Independent Social Democratic Party (USPD) of Germany in 1917. He co-chaired the Council of People’s Representatives (''Rat der … READ MORE
Entry -
İsmail Hakkı was an experienced civil servant. He collected and published detailed statistics on the population, economic activities, education, natural resources and means of transportation in his provinces, and attempted relief efforts to alleviate … READ MORE
Entry -
Liberal Secretary of State for War 1905-1912. Haldane’s reforms of the British Regular Army and its auxiliaries were instrumental in ensuring that Britain could dispatch an expeditionary force to assist the Belgians and French in August … READ MORE
Entry -
Maurice Hankey was responsible for adapting the British government’s administrative machinery to the needs of modern war. He became an influential behind-the-scenes adviser to British prime ministers during the … READ MORE
Entry -
Georg von Hertling was the chancellor of Germany from 1 November 1917 to 3 October … READ MORE
Entry -
Gustave Hervé’s dates of birth and death (1871-1944) correspond broadly to those of the Third Republic (1870-1940). His path is strongly linked to it and his ideas partly reflect its contradictions. Fervently anti-militarist and anti-patriotic before … READ MORE
Entry -
Paul von Hindenburg shot to fame after the Battle of Tannenberg in August 1914. He was Germany’s national hero of wartime, soon eclipsing the Kaiser. Appointed to the Supreme Command in 1916, he increasingly took on a political role. His myth survived … READ MORE
Entry -
After the First World War, Hitler created a mythical account of his war years for political gain. This account was a far cry from the realities of his war experience on the Western … READ MORE
Entry -
The Great War had a decisive influence on Hồ Chí Minh. In France, his acquaintance with the history of the 1789 French Revolution drove him to socialism, then to the 1917 Russian Revolution in its Leninist guise, which led him to … READ MORE
Entry -
After working first as a lawyer and legal scholar, Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. accepted positions on the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts and the United States Supreme Court. As a Supreme Court justice Holmes wrote opinions that shaped the debate on … READ MORE
Entry -
Herbert Hoover obtained political prominence during World War I through his roles as chairman of the Committee for the Relief of Belgium (CRB) and the U.S. Food Administration. Following the war, Hoover served as head of the American Relief Association … READ MORE
Entry -
Horthy was a naval officer of Austria-Hungary. During the First World War he was first in command of a cruiser and then chief commander of the navy. After the war he took part in the counter-revolution in Hungary against the Bolshevik regime; following … READ MORE
Entry -
Edward House was an advisor to President Woodrow Wilson. He aided Wilson in diplomatic matters and in crafting the Fourteen Points that became the framework for the League of … READ MORE
Entry -
Elias Hoyek was Patriarch of Antioch for the Maronites. He is considered to be one of the fathers of Lebanonism, a symbol of resistance against Ottoman hegemony, and the founder of Lebanese … READ MORE
Entry -
Husayn ibn Ali launched the Arab Revolt in alliance with Great Britain. His relations with his European allies remained uneasy and deteriorated further when a unified Arab state under his rule failed to materialize after the war. Ibn Sa‘ud’s conquest … READ MORE
Entry -
Husayn Kamil was the first sultan of Egypt after the declaration of the British protectorate, from 1914-1917. After ascending to the throne on 18 December 1914, he survived two assassination attempts and collaborated with British military … READ MORE
Entry -
The Husayn-McMahon Correspondence mapped out with studied ambiguity the terms of the wartime alliance between Great Britain and Hashemites that underpinned the Great Arab Revolt (July 1916-October 1918) against Ottoman … READ MORE
Entry -
Italy entered the First World War in May 1915, roughly ten months after it began. During those ten months, the battle of opinions for and against intervention raged on. Public meetings, demonstrations, and street clashes that occasionally left partisans … READ MORE
Entry -
A Romanian politician, Dumitru Ionescu, commonly known as Take Ionescu, was considered by his contemporaries to be one of the most erudite statesmen in Eastern Europe. He was one of the main politicians who manoeuvred Romania’s entrance into the First … READ MORE
Entry -
The campaign for Irish Home Rule lasted from 1870 until 1914. When Home Rule became a realistic possibility in 1912, a period of political turmoil ensued. Parliamentary solutions to the impasse were overtaken by the emergence of rival armed paramilitary … READ MORE
Entry -
This article examines the history of Italian irredentism before 1915; and its place its role in Italy’s entry into the war in May 1915 and in Austro-Hungary’s military governance of the Italian-speaking Habsburg territories until 1918. It also … READ MORE
Entry -
Russian-Jewish author, playwright, journalist, orator, and political activist; co-founder of the Zion Mule Corps (1915-16) and the Jewish Legion (1917-21, the unofficial name of the 38th Battalion of the Royal Fusiliers), composed of Jewish volunteers who … READ MORE
Entry -
Gottlieb von Jagow was a German diplomat. He served as the German Foreign Secretary from January 1913 to November … READ MORE
Entry -
A philosopher, historian, and journalist (creator of'' L’Humanité''), Jean Jaurès defended the socialist program for workers and small farmers in the Chamber of Deputies and throughout France. Within the Second International, an organisation of … READ MORE
Entry -
Bishop Jeglič was one of the most prominent Slovenian Church figures in the era leading up to the outbreak of the First World War. His political actions during the war decisively shaped the people’s perspective on the Habsburg Monarchy and had an … READ MORE
Entry -
In October 1916, the Prussian War Ministry conducted the ''Judenzählung'', also referred to as the “Jew Count” or “''Judenstatistik'',” a census of Jewish soldiers serving in the German army. The ''Judenzählung'' operated on unfounded … READ MORE
Entry -
In July 1917, economic chaos and unpopular preparations for military action provoked armed demonstrations by workers and troops demanding the Petrograd Soviet take power from Russia’s Provisional Government. The uprising failed and reprisals were … READ MORE
Entry -
Peter I Karadjordjević was King of Serbia from 1903 to 1918, and King of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes from 1918 to 1921. He also translated the essay “On Liberty” by John Stuart Mill (1806–1873) into … READ MORE
Entry -
Mustafa Kemal Pasha gained fame during World War I both as a successful commander on three Ottoman fronts and as a fierce critic of the Young Turk government and its German allies. After the war, his reputation enabled him to position himself as the … READ MORE
Entry -
Aleksandr Kerenskii was Minister of War in Russia’s Provisional Government from April to October 1917 and Prime Minister from July to October. He embodied the hopes of the February Revolution of 1917, the doomed military offensive of June 1917, and the … READ MORE
Entry -
The "khaki" general election of 1918 was held in Great Britain almost immediately after the Armistice. It was the first held under what was almost universal adult suffrage. The result was a crushing victory for a coalition comprised of Liberals supporting … READ MORE
Entry -
The King’s African Rifles (KAR) were the British colonial military within East Africa before and during the First World War. While initially rarely involved in the British operations in East Africa, the continued resistance of the German … READ MORE
Entry -
Aleksandr Vasil'evich Kolchak was a Russian admiral and political figure. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War, the First World War, and the Russian Civil War. He was one of the leaders of the White movement in eastern Russia and was proclaimed … READ MORE
Entry -
Prince Fumimaro Konoe was a pivotal figure in Japanese history during the first half of the 20th century. He is primarily recognized for his tenure as prime minister and his significant involvement in formulating the concept that became known … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War I, V. K. Wellington Koo worked in the Chinese foreign ministry before becoming Chinese minister to the United States and a member of the Chinese delegation at the Paris Peace Conference. In these capacities, Koo utilized international law … READ MORE
Entry -
Béla Kun was a Hungarian communist politician. He began his career as a social democrat. During the First World War he was captured by the Russians and later became a Bolshevik in Russia. From 1918 onward, he filled significant positions in the … READ MORE
Entry -
La Dame Blanche was an intelligence network created in Belgium in 1916. It was essentially devoted to the observation of railways. At the end of the war, it was comprised of over 1,000 agents and covered a large part of the occupied … READ MORE
Entry -
Although he was a Nobel Prize winner, the name of Henri La Fontaine has somewhat fallen into obscurity. At the time of his Nobel Peace Prize award in 1913, however, he was a fundamental figure in the pacifist movement. The prize was a reward for his … READ MORE
Entry -
Johan Laidoner, Estonian general and statesman, started his career in the Russian army during World War I. He was crucial in establishing an Estonian army, which he commanded in the War of Independence (1918-20). In 1934 he participated in a coup … READ MORE
Entry -
Robert Lansing served as U.S. Secretary of State from June 1915 until February 1920. A career lawyer, Lansing was a leading proponent of “benevolent neutrality” in the years before the United States entered the war. He also served as a member of the … READ MORE
Entry -
T.E. Lawrence’s exploits during the Arab Revolt have acquired mythical status, making it difficult to distinguish between what he actually achieved and what was the product of his overactive imagination. Less contested is his role in brokering the … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1921 and 1922 the highest German court, the ''Reichsgericht'' in Leipzig, under pressure from the Allied powers, put seventeen Germans on trial for suspected war crimes in twelve trials. The trials and their results were criticized in both Germany and … READ MORE
Entry -
Vladimir Il’ich Lenin was the founder and leader of the Bolshevik Party and of the Soviet state up until his death. Theoretically and practically he combined the strategy of a socialist revolution with imperialism and war. After thus successfully … READ MORE
Entry -
Karl Liebknecht was the leading German socialist opponent of the First World War. He was the first member of parliament to vote against the financing of the war. On 1 May 1916 he was arrested and imprisoned for giving an anti-war speech in central Berlin. … READ MORE
Entry -
Lloyd George was a leading Liberal politician before World War I, who went on to play a central role in the United Kingdom’s war effort as Chancellor of the Exchequer (1908-1915), Minister of Munitions (1915-1916), Secretary of State for War (1916) and … READ MORE
Entry -
Henry Cabot Lodge was a Republican senator from Massachusetts. Close friend to Theodore Roosevelt, Lodge supported imperialist endeavors and favored military preparedness following the outbreak of World War I. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of London was a secret agreement signed by Italy, Great Britain, France, and Russia on 26 April 1915, bringing Italy into the First World War on the Entente side. It therefore had a crucial impact on the conflict. Its content, however, included … READ MORE
Entry -
Louis Loucheur was a French industrialist and politician. From December 1916 until the end of the war, he served as undersecretary of state for artillery and munitions and later as armaments minister. After the war, he continued a brilliant political … READ MORE
Entry -
Erich Ludendorff was the effective commander of the German armed forces during the war. He also became a quasi-dictatorial figure, the ruthless symbol of the army’s political power. After the war he became the new republican government’s most bitter … READ MORE
Entry -
Named after the German ''chargé d’affaires'' in Buenos Aires, Count Karl von Luxburg, the Luxburg Affair was the diplomatic issue that brought Germany and Argentina to the brink of war in … READ MORE
Entry -
A Socialist and a vocal critic of the German Social Democratic Party’s (SPD) war policies, co-founder of the anti-war Spartacus League in 1916 and the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) in 1918, Rosa Luxemburg supported the German Revolution of 1918. In … READ MORE
Entry -
Ramsay MacDonald opposed British entry into the European conflict in 1914. Although often represented as anti-war, he subsequently supported the Allied cause. He criticised balance of power diplomacy in the hands of a cloistered elite. Despite tensions, … READ MORE
Entry -
Macedonia was one of the main battlefields on the Balkan Front during World War I. The article describes the pre-war activities of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO), its role in the Bulgarian occupation regime, and the fall of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Bernardino Machado was the prime minister of Portugal during the July Crisis of 1914. As president of the Portuguese Republic (1915-1917) he promoted the formation of a Sacred Union Cabinet that dispatched expeditionary forces to Flanders and to … READ MORE
Entry -
Nestor Makhno was a commander of peasant insurgents who fought the Bolsheviks, Whites and Ukrainian nationalists in the South East of present-day Ukraine. His espousal of anarchism has won him supporters among many Western anarchists, but some historians … READ MORE
Entry -
French Interior Minister when the war was declared, Louis Malvy embodied the Union sacrée and the quest for social peace. In 1917, he was accused of treason and involved in a political scandal that led to the fall of the … READ MORE
Entry -
A Finnish aristocrat, Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim served as cavalry commander in the Imperial Russian army during the First World War. After the Russian Revolution, he commanded Finnish White forces in the Finnish Civil War of 1918. He served as the Head … READ MORE
Entry -
Marie Adelheid reigned from 1912 to 1919 as the Grand-Duchess of Luxembourg. Because of her friendly attitude towards the German occupying forces during World War I, the Luxembourgers and Allies accused her of sympathizing with the Germans. Failing to … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Marinegebiet'' on the Belgian coast was the Imperial German Navy’s base for attritional warfare against Entente shipping in the North Sea. The resulting occupation regime was particularly harsh on civilians; their plight was compounded by British … READ MORE
Entry -
Martial law refers to the exercise of governmental power over the civilian population by military authorities. The use of martial law varied among belligerent countries, and its geographical scope and material extent changed over the course of the war. … READ MORE
Entry -
The notion of “martial races” was formally developed and codified in the wake of the Indian Uprising of 1857 and became an important basis for the recruitment policy of the Indian Army. Constantly manipulated and adapted to changing political and … READ MORE
Entry -
The terms "martyrs" and "separatists" refer to the decentralist Arabists of Syria who were executed by Cemal Pasha during World War I as a result of their alleged plot to separate the Syrian land from the Ottoman … READ MORE
Entry -
Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk was a Czech politician who started the Czechoslovak independence movement abroad. As head of the Czechoslovak National Council from 1916 to 1918, he provided an ideological basis for Czechoslovak propaganda, helped create the … READ MORE
Entry -
Mata Hari was a famous Dutch female dancer, who spied in France for the German intelligence during the war. Arrested by the French, she was condemned to death and executed in October … READ MORE
Entry -
Mata Hari was a famous Dutch female dancer, who spied in France for the German intelligence during the war. Arrested by the French, she was condemned to death and executed in October … READ MORE
Entry -
Norton de Matos was minister of war during the first two years of Portuguese participation in the conflict (1916-1917). He was the main organizer of the Expeditionary Corps that fought on the Western Front. In December 1917, he was deposed by a military … READ MORE
Entry -
Adolphe Max, the mayor of Brussels, was known for his peaceful resistance against the Germans and his resulting jail-time. He was considered by the Belgian public as a hero of the Great … READ MORE
Entry -
For many years Prince Maximilian of Baden was portrayed as a positive figure in German history - the liberal Chancellor who in 1918 helped to turn Germany into a republic. This view has been considerably altered by recent scholarship, including letters … READ MORE
Entry -
William G. McAdoo was an American politician and businessman. During World War I, he served as Secretary of the Treasury and director of the US Railroad Administration. In these positions he was the architect of the USA's wartime financial planning and … READ MORE
Entry -
Ioannis Metaxas was a conservative army officer and politician, who influenced decision-making in Greece during World War I by collaborating with King Constantine I. In 1936 he became head of an oppressive dictatorial regime and in 1940 he was responsible … READ MORE
Entry -
It was the complex and far-reaching transformation of the Mexican Revolution rather than the First World War that left its mark on Mexican history in the second decade of the 20th century. Nevertheless, although the country maintained its … READ MORE
Entry -
Georg Michaelis is usually portrayed as the politically failed chancellor of 1917. His resignation after fourteen weeks in office was the first overthrow of a Reich chancellor initiated by Reichstag political parties. Before he was appointed chancellor, … READ MORE
Entry -
Micronesia
By Niko Tillmann and Yuko Maezawa
Japanese interest in expansion into the South Pacific began in the 1870s. World War I provided a long sought after chance for the Japanese Imperial Navy to enhance its standing and gain a strategically important base. Japanese claims to the South Sea … READ MORE
Entry -
One of the founders and leaders of the Constitutional Democratic Party, Pavel Nikolaevich Miliukov took an active part in the organisation of the Progressive Bloc. He made a famous speech in the Duma on 1 November 1916 (“Stupidity or Treason?”) … READ MORE
Entry -
Between 1890 and 1925, Alexandre Millerand was one of France’s leading politicians. From August 1914 to September 1915, he served as war minister in the first ''Union sacrée'' government. In 1920, he was elected president of the republic, but he had to … READ MORE
Entry -
E. D. Morel was one of the earliest critics of the secret diplomacy and alliance system that led to the start of the Great War. Imprisoned during the war by the British government for his writings, he later became a foreign policy leader in the Labour … READ MORE
Entry -
Naturalized American lawyer, real estate investor, and Jewish activist, Henry Morgenthau Senior served as United States Ambassador to the Ottoman Empire from 1913-1916. During 1915-1916 Morgenthau reported extensively on the wholesale ethnic cleansing and … READ MORE
Entry -
The two Moroccan crises represent the product of “rapacious joint imperialism.” Morocco could not escape the ambitions of its immediate neighbours, Spain and France, who secretly plotted to divide the country between them in 1904. The Reich provoked … READ MORE
Entry -
The Movement of National Defence was an organisation of Venizelist army officers and politicians who rose up against the royalist government in Athens in August 1916. They established a separate Provisional Government of National Defence in Thessaloniki … READ MORE
Entry -
Lauro Müller was the Brazilian minister of foreign affairs between 1912 and 1917. A pro-German politician and intellectual, he was heavily criticised during World War I by the Brazilian press and pro-United States intellectuals. Brazil maintained … READ MORE
Entry -
Italian Socialist Benito Mussolini envisioned war as the prerequisite for revolution. He helped push Italy into World War I. After combat service and medical discharge in 1917, he demanded war until victory. In 1919, he founded the Fascist movement. Using … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich Naumann was a key figure in German liberalism in the late Kaiserreich, where he tried to reunite Left and National Liberals. In 1915, he published a widely read book on “''Mitteleuropa''” (Central Europe) which sought to give a liberal … READ MORE
Entry -
The Anglo-German naval race was the most spectacular strand of the general maritime arms build-up before World War I. Often, albeit misleadingly, described as both the first and the prototypical arms race among modern industrial nations, this arms race … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Neuilly was signed on 27 November 1919 between Bulgaria and the Allied and Associated Powers in Neuilly-sur-Seine, France. Its territorial clauses were considered by Bulgarian society to be a national catastrophe and the definitive failure … READ MORE
Entry -
During the 19th century, neutrality evolved into a set of legal and political tools designed to limit the impact of wars on the international system. This form of neutrality did not survive the first “total war”; remaining neutral was still … READ MORE
Entry -
Nicaragua’s experience during the First World War was influenced by the geopolitics of the Central American isthmus. The American occupation of Nicaragua between 1912 and 1925 impacted both Nicaraguan neutrality, which ended once the United States … READ MORE
Entry -
Nicholas II ruled Russia from 1894 and was commander of the army from September 1915 until his abdication in March 1917 amidst popular demonstrations against bread shortages, the war and autocracy. Historians dispute the relative importance of … READ MORE
Entry -
Nikolai Nikolaevich, a senior Russian officer and close relative of Tsar Nicholas II, was involved in attempts to reform the Russian army from 1905. He was named Commander-in-Chief at the onset of war in 1914 but was removed a year later following … READ MORE
Entry -
Francesco Nitti was minister of the Treasury in the Orlando Cabinet after the defeat of Caporetto in 1917 and prime minister of Italy in 1919. During his mandate he signed the treaty of Saint-Germain, started the economic reconversion of the country and … READ MORE
Entry -
Gustav Noske was a social democratic politician and the first politician to be awarded with military responsibilities. His role as first ''Reichswehrminister'' (Reich minister of defense) during the revolution was controversial and ambivalent. He was … READ MORE
Entry -
Over the entire course of German occupation in Eastern Europe during the First World War, the Ober Ost administration wavered between domination by military leaders – and their efforts to create a settlement colony – and continued attempts by … READ MORE
Entry -
The so-called “''Oberstenaffäre''” (colonel’s affair) was a political scandal in Switzerland which erupted after details of a close cooperation between Swiss, German, and Austro-Hungarian military intelligence agencies emerged during World War I. … READ MORE
Entry -
The violation of Luxembourg’s neutrality started with the invasion on 1 August 1914, with the real occupation beginning on 2 August and lasting until 21 November 1918 when the first Allied troops arrived in … READ MORE
Entry -
A renowned jurist with lasting influence, Vittorio Emanuele Orlando served as justice and interior minister between 1916 and 1917, implementing liberal policies despite strong opposition. As prime minister after the Caporetto crisis he rallied Italy, … READ MORE
Entry -
Ignacy Jan Paderewski was a virtuoso pianist. He made use of his popularity in the United States and western Europe to propagate the idea of Polish independence and state sovereignty. In 20th century Poland, he became a symbol of patriotism and … READ MORE
Entry -
Paul Painlevé was a prominent French political leader from 1914-1917. He was the head of the Inventions Committee in charge of defining modern warfare. In 1917, at the turning point of the war, he was the minister of war and president of the Council. His … READ MORE
Entry -
The army major and university teacher Sidónio Pais served as the Portuguese minister (ambassador) in Berlin between August 1912 and March 1916. In December 1917, after a military coup, Pais became president of the Republic. He was murdered in December … READ MORE
Entry -
The First World War elicited various responses from the Wilson administration based on Pan Americanism, a conception of regional integration under U.S. leadership that calls for more political cooperation and greater trade and investment. The first goal … READ MORE
Entry -
The Pan-German League (''Alldeutscher Verband'') mobilized members of the ''Bildungsbürgertum'' and the broader middle classes in the service of a class-based vision of ''Volksgemeinschaft'', territorial expansion, and cultural homogeneity in Germany. … READ MORE
Entry -
Pan-Islamism was one of the major geopolitical and civilizational concepts of the First World War. The German-Ottoman alliance campaigned for Muslim solidarity against European colonialism both by anti-imperial and imperial means. Pan-Islamism altered the … READ MORE
Entry -
Pan-Turkism is the nationalist ideology that emphasizes the common ethnic, cultural, and linguistic roots of Turkic peoples living across Eurasia. Developed as a social and political movement among the Turkic-Muslim peoples of the Russian Empire, the … READ MORE
Entry -
A talented administrator but a mediocre general, Cavit Pasha served in various parts of the empire, including commander of Iraq during the first year of the … READ MORE
Entry -
A first father of modern Turkey before Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, and the driving force of the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) during the war, Talat organized the removal of Armenian and other Christian citizens to secure exclusive Turkish power in … READ MORE
Entry -
Nikola Pašić was a Serbian/Yugoslav politician and statesman. He served twenty-two terms as prime minister and fourteen terms as foreign minister, some only a few months … READ MORE
Entry -
Konstantin Päts, a leading Estonian politician, was a key figure in the establishment of Estonian independence during and after World War I. In 1934, he and Johan Laidoner organized a putsch and Päts became an authoritarian … READ MORE
Entry -
Alice Paul was an American suffragist and political rights activist. Jailed repeatedly for her activities running up to and during World War I, her work in the United States led to the passing of the 19th Amendment and the introduction of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich von Payer was vice-chancellor of the German Empire from November 1917 to November 1918. In November 1918, he was offered the position of Reich chancellor, which he declined. After the First World War, Payer became a founding member of the German … READ MORE
Entry -
Patrick Pearse was one of the leaders of the 1916 Easter Rising in which the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB), an extremely nationalist organization, attempted to establish an independent Ireland by force. His execution was an important catalyst for the … READ MORE
Entry -
During the Russian Civil War, peasant uprisings swept the former Russian Empire. In 1918 and 1919, these uprisings were mainly local responses to requisitioning and conscription. In 1920 and 1921, the uprisings became larger in scale, above all in Tambov. … READ MORE
Entry -
Epitácio Pessoa served as the president of Brazil between 1919 and 1922. He led the Brazilian delegation to the Paris Peace Conference. He was also a member of the Permanent Court of International Justice in The … READ MORE
Entry -
Gabrielle Petit was a secret intelligence agent working for the British General Headquarters (GHQ) in occupied Belgium. She collected information on the German Sixth Army in the Tournai-Lille area. She was condemned to death and executed in the spring of … READ MORE
Entry -
Józef Klemens Piłsudski was a Polish statesman, socialist politician, freedom fighter, and soldier. He commanded the Polish Legions during the First World War, and served as the first chief of state (1918–1922), marshal (from 1920 onward), prime … READ MORE
Entry -
Raymond Poincaré, the president of the French Republic, asserted his authority as early as 1914, in a manner contrary to institutional practices that had prevailed since 1877. After his August 1914 call for a political truce or “''union sacrée''”, … READ MORE
Entry -
Polish paramilitary organizations were active in Galicia from 1910 to 1914 with the permission of the Austro-Hungarian army’s intelligence service. Their ostensible aim was to militarily train young people and improve their shooting skills. The actual … READ MORE
Entry -
Although not directly involved in military operations, Portuguese India was linked to World War I through the capture of German and Austrian ships and the imprisonment of their crewmen. This period was also one of internal political turmoil and there was … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War One, Macau's main problem was its relationship with China. This stemmed from the consequences of its internal tensions and the lack of recognition of the Portuguese borders. However, its defence was weak, mainly based on local … READ MORE
Entry -
The Portuguese territory of Timor was affected by the war mainly because of its proximity to the Dutch colony, the Dutch East Indies. Furthermore, without lines of transportation and communication, Timor became more isolated and imports and exports … READ MORE
Entry -
The Prochaska Affair was a diplomatic dispute between Austria-Hungary and Serbia, ostensibly concerning the fate of the Austro-Hungarian consul in Prizren. However, it carried deeper implications for the Austro-Hungarian efforts to prevent the Serbians … READ MORE
Entry -
When the tsarist government collapsed in February 1917, liberal politicians from the State Duma (parliament), later joined by moderate socialists, formed a Provisional Government. Unable to satisfy popular expectations for peace, or to enact social and … READ MORE
Entry -
This entry revisits the political upheavals that swept across several towns and cities of Punjab in April 1919, in protest against the passage of the Rowlatt Act in the Imperial Legislative Council. It argues that the moment marks a fundamental break in … READ MORE
Entry -
Dr. Vasil Radoslavov was a Bulgarian politician and Prime Minister from 1913 to 1918. As Prime Minister he played a decisive role in Bulgaria’s decision to enter the First World War on the side of the Central … READ MORE
Entry -
Rasputin was a peasant turned pilgrim who became a close associate of the Russian royal family. Accounts of his wartime influence on government may be exaggerated but public perceptions of his power and rumours of his debauchery undermined the authority … READ MORE
Entry -
Walther Rathenau was one of the most influential entrepreneurs before the First World War. In 1914/1915 he became one of the main organizers of Germany’s war economy. After World War I he supported the “policy of fulfilment”. As German Minister of … READ MORE
Entry -
On 25 May 1913 Colonel Alfred Redl, the former head of Austria-Hungary’s military espionage, committed suicide in Vienna. As it turned out, Redl had betrayed Austria-Hungary’s spy-network in Russia and had sold sensitive information on war … READ MORE
Entry -
The Red Scare was a period of heightened fear of radicalism in the United States after World War I. Labor unrest, the growth of bolshevism internationally, and a series of bombings triggered a number of government raids on suspected radicals, often in … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Renascença Portuguesa'' (1912-1932) was an important cultural movement during the republican regime (1910-1926) in Portugal. This intellectual group was founded in Porto, in the northern part of Portugal. It supported the participation of Portugal … READ MORE
Entry -
Karl Renner quickly became one of the main theoreticians of a policy of support for the war effort. He saw World War I as a chance for social democratic advance, with state intervention laying the groundwork for socialism. He made the case for the … READ MORE
Entry -
In occupied Belgium and France, citizens opposed the German army with organized but non-violent resistance. They created networks dedicated to military intelligence gathering, escape lines, clandestine postal networks and underground newspapers. Many of … READ MORE
Entry -
Social and political unrest swept the Russian Empire in 1905, forcing the autocratic tsarist regime to grant the creation of a popularly-elected legislative body; the State Duma. However, the army remained largely loyal to the Tsar, unlike in the wartime … READ MORE
Entry -
Alexandre Ribot belonged to the French political elite for more than forty years. During the war, he was finance minister from 1914 to 1917 and prime minister (''Président du Conseil'') from March to September … READ MORE
Entry -
Riezler was a German politician, diplomat, journalist and philosopher, as well as a trusted assistant of the chancellor. Although some of his surviving diary entries dated from July and August 1914 as representative of the German Foreign Office’s Press … READ MORE
Entry -
The Russian occupation of the eastern Ottoman Empire entailed the wartime administration of captured territory comprising approximately 95,000 square kilometers. A military governorate-general was established in 1916; this was replaced by a … READ MORE
Entry -
Said Nursi was a prominent Kurdish intellectual. He fervently supported constitutionalism and sought to improve the Kurds’ condition during the late Ottoman Empire. After World War I and the consequent fall of the Ottoman Empire, Nursi founded the … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Saint-Germain was signed by Austria and twenty-seven Allied and associated countries in the ''Château Neuf'' in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, southwest of Paris, on 10 September 1919. It officially ended World War I for the successor states of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Antonio Salandra was an important Italian politician in the early 20th century. When the Great War broke out, he was prime minister of Italy and had a decisive yet controversial role in the Italian … READ MORE
Entry -
The Sarajevo incident refers to the events surrounding the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife Archduchess Sophie during a state visit to Sarajevo on 28 June 1914. It is traditionally regarded as … READ MORE
Entry -
Sergei Sazonov became Russian Foreign Minister in autumn 1910. In July 1914 he argued for a firm stance against Austrian aggression and general mobilisation of the army, but historians dispute his responsibility for the outbreak of war. His wartime … READ MORE
Entry -
Philipp Scheidemann was a key figure in the German Social Democratic Party (SPD) during the First World War. On 9 November 1918, Scheidemann proclaimed the republic in Germany and became the first head of government in the Weimar … READ MORE
Entry -
Heinrich Schnee was the governor of German East Africa between 1912 and 1919. During the war, he remained with the German colonial troops under the command of Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck until their surrender in November 1918. In the interwar years, Schnee … READ MORE
Entry -
The Scutari Crisis illustrates questions surrounding the creation of the new Albanian state at the beginning of the 20th century. It also shows the transformation of the aims of the First Balkan War, which was seen as a liberating war against … READ MORE
Entry -
Much attention has been accorded to the massive scale of military operations in the European theatre. However, sea power, which determined the control of global communications and was the key to exploiting global resources of manpower, food, industrial … READ MORE
Entry -
The Selective Service Act of 1917 was the official name of the military draft signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson following the United States’ entry into World War I. It authorized the federal government to expand the American armed services … READ MORE
Entry -
Marcel Sembat was one of the leading French socialists of the pre-war years. As minister of public works, he represented the socialist party in the ''union sacrée'' government formed at the end of August … READ MORE
Entry -
Bahaeddin Şakir was the reorganizer of the Committee of Union and Progress, a political party that became the government of the Ottoman Empire during the war. As a major functionary of the Special Organization, a paramilitary network which took orders … READ MORE
Entry -
An Irish-born writer and critic, best known as a playwright, George Bernard Shaw was an ardent opponent to World War I. Already in his fifties at the start of the war, Shaw was outspoken in his antiwar speeches and also published a pamphlet entitled … READ MORE
Entry -
Boris Shtiurmer was Prime Minister from January to November 1916, also serving as Interior Minister between March and July 1916 and Minister of Foreign Affairs from July to November. Denunciations of Shtiurmer in Russia’s parliament, or Duma, for … READ MORE
Entry -
The Sixtus Affair was the failed attempt by Emperor Charles I. of Austria and his bother-in-law Prince Sixtus of Bourbon-Parma to conclude a compromise peace with the members of the Entente-Powers between January and May … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, political writer and editor of Lithuanian magazines, Antanas Smetona in 1917 became chairman of the Council of Lithuania, which declared Lithuania as an independent state in 1918. He was twice President of Lithuania, 1919-1920 … READ MORE
Entry -
Jan Smuts was a South African lawyer and statesman who ultimately became deputy prime minister of the Union of South Africa. During the war, Smuts was Minister of Defence, Finance and Mines. He served for a time in German South West Africa before … READ MORE
Entry -
At the outbreak of the First World War, the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) voted, as the largest party in the German Empire, for the granting of war loans. However, the thus-introduced "truce" policy was rejected by more and more members of … READ MORE
Entry -
The privately organized SSS existed from October 1915 to July 1919 to prevent Swiss companies from forwarding goods and raw materials produced by the Entente to the Central Powers. The SSS grew from an international agreement between the governments of … READ MORE
Entry -
Wilhelm Solf, long-term governor of German Samoa, served as Colonial Secretary between 1911 and 1918 and as the last imperial Foreign Secretary in winter 1918. During the war Solf supported expansionist war aims in Africa and a policy of restraint in … READ MORE
Entry -
Sidney Sonnino was the Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs during World War I. He negotiated the Treaty of London, defining the terms with which Italy would enter into the war alongside the Triple Entente. His actions during the Paris Peace Conference … READ MORE
Entry -
The painter Adriano de Sousa Lopes was the only official Portuguese war artist in the Great War, stationed on the Western Front. Like most of his international colleagues, he produced remarkable field drawings and etchings. This article explores his … READ MORE
Entry -
Spain became a centre of international espionage in 1914. Its strategic location in terms of the Anglo-French trade soon attracted German attention. The Germans waged an economic and propaganda war against the Allies from Spain, while the British took … READ MORE
Entry -
The Spanish government maintained a benevolent neutrality policy towards the Entente Powers during the First World War. Liberal and Conservative cabinets decided it was the only position consistent with their country's traditionally friendly relations … READ MORE
Entry -
Milan Rastislav Štefánik was a Slovak astronomer, diplomat, politician, general, one of the organizers of the Czechoslovak legions and one of the founding fathers of Czechoslovakia. In today’s Slovakia he is seen as a national … READ MORE
Entry -
This article summarises the main wartime stereotypes that defined war propaganda in Germany, France, Great Britain, the USA and Russia. It focuses less on particular details of each national enemy image and more on the basic make-up of wartime stereotypes … READ MORE
Entry -
Hugo Stinnes was a highly successful and politically influential heavy industrialist. During the First World War, he adopted a German nationalist position and advocated the colonisation of Belgium and parts of France. After the defeat, Stinnes negotiated … READ MORE
Entry -
The Stockholm Conference, or Third Zimmerwald Conference, was held from 5 to 12 September 1917. The subject of the discussions was the way in which a certain part of the socialist movement conceived peace and its approach to fighting war. The genesis of … READ MORE
Entry -
Stresemann was a leading wartime annexationist and proponent of moderate domestic reforms. Committed to restoring national strength after defeat and revolution, he became one of the Weimar Republic’s foremost statesmen. He served as chancellor during … READ MORE
Entry -
Karl Graf von Stürgkh was an Austrian member of the Imperial Council, Minister for Education, and Minister President of Cisleithania from 3 November 1911 until his assassination on 21 October 1916 by the Social Democrat Friedrich Adler. Stürgkh was one … READ MORE
Entry -
In May 1916, the German government issued a pledge to the United States that the Imperial navy would not attack passenger ships and would further allow the crew of merchant ships which carried war material to exit their vessels before they would be … READ MORE
Entry -
Ivan Šušteršič was a leading figure in the Slovenian and Habsburg political milieu prior to and during World War One. A prominent member of the Catholic People’s Party, he was at the forefront of the pro-Habsburg political currents in Carniola, … READ MORE
Entry -
Bertha von Suttner (1843-1914) was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1905. She wrote an internationally acclaimed antiwar novel ''Die Waffen nieder!'' (''Lay Down Your Arms!'') and co-founded the Austrian Peace Society (1891) and the journal, ''Die Waffen … READ MORE
Entry -
In dividing the Fertile Crescent into British and French spheres, the wartime Sykes-Picot Agreement laid the foundation of the colonial division of the region ratified at the St. Remo (1920) and Lausanne (1923) conferences, when Palestine … READ MORE
Entry -
Albert Thomas was a French socialist who served as minister of armaments in the French government during the war. In the postwar period, he became the first director of the International Labour … READ MORE
Entry -
Federico Tinoco Granados was the Costa Rican president from 1917-1919 who declared war on Germany in April 1917. With his support for the United States during the last two years of the war, he tried to gain President Woodrow Wilson’s acceptance. The … READ MORE
Entry -
István Tisza was a Hungarian politician and minister. He served as Prime Minister from 1903 to 1905 and from 1913 to 1917. Austria-Hungary entered the First World War during Tisza's second period as prime … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War I, Arnold J. Toynbee, as a member of the Political Intelligence Department, was charged with preparing analyses on the Middle East for the Paris Peace Conference. The global war was pivotal for the elaboration of his philosophy of … READ MORE
Entry -
Trentino
By Nicola Fontana and Mirko Saltori
Trentino is an Italian-speaking region which was the southernmost part of the Tyrol. With Italy’s entry into the war, it found itself in the front area. After the war it was annexed to the Kingdom of … READ MORE
Entry -
As prefect of the ''département ''of the Nord at the outbreak of war, Félix Trépont encouraged the defence of Lille during the invasion, eventually oversaw the evacuation of men and material, and resisted collaboration with the Germans during the … READ MORE
Entry -
Before and at the beginning of World War I, various proposals concerning the creation of a third part of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy were brought up for discussion. Each of the aspiring groups (Czech, South Slavic and Polish) assumed that becoming a new … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Trianon is one of the Paris peace treaties that ended the First World War. It was concluded between Hungary and the Allied and Associated Powers on 4 June 1920 in the Grand Trianon Palace situated in the Versailles Palace park. It sanctioned … READ MORE
Entry -
Troelstra was a charismatic socialist leader who overestimated his influence and called for a socialist revolution in November 1918. His call was ignored and after suffering a nervous breakdown, he re-entered … READ MORE
Entry -
Leon Trotsky's communist leadership was partially responsible for bringing about the October Revolution of 1917, after which Russia exited the First World War. Starting as an activist, he became People’s Commissar for Foreign Affairs and People’s … READ MORE
Entry -
Ante Trumbić was a Croat politician who played an instrumental role in the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslavia) in December 1918. Between 1905 and 1934, he served in a range of influential posts including as mayor of Split; … READ MORE
Entry -
The province of Turkestan - modern-day Central Asia -, a Russian military colony since 1865-1875, truly entered WWI in 1916, when Tsar Nicholas II and his military staff decided, on 7 July (Gregorian calendar), to conscript a new labour force from the … READ MORE
Entry -
At the beginning of the 20th century Ukrainian lands were part of the Austro-Hungarian (Galicia, Transcarpathia, Bukovina) and Russian (the nine right-bank and left-bank provinces) Empires. Therefore, with the beginning of the First World War … READ MORE
Entry -
Kārlis Ulmanis was the first prime minister of the Republic of Latvia. His four terms of office saw the successful conclusion of the Latvian War of … READ MORE
Entry -
The Union of Democratic Control was a prominent opposition group in Britain that particularly criticised the operation of British foreign policy and the role of "secret diplomacy". It advocated public oversight of diplomacy and was an early advocate of … READ MORE
Entry -
Since the beginning of the 20th century, political conflicts determined relations between the German Empire and the USA. The Caribbean became one of the scenes of these conflicts during and following World War I. General reasons were the … READ MORE
Entry -
One of the most prominent and important statesmen in modern Greek history, Eleutherios Venizelos full-heartedly favored Greek participation in World War I on the side of the Entente. This caused tension with King Constantine I, who favored neutrality. … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Versailles was the first peace treaty that the victorious powers signed with a former adversary. The treaty with Germany was the most important treaty for the Allied and Associated Powers, and served as a blueprint for subsequent agreements … READ MORE
Entry -
Victor Emmanuel III played an important, if often overlooked part in Italy’s decision to intervene in World War I on the side of the Entente. During the war, he managed to solve two political crises and to defend Italy’s position within the Entente … READ MORE
Entry -
Rodrigo de Saavedra y Vinent, Marqués de Villalobar was the diplomatic representative of Spain to Belgium from 1913 to 1926. During the war, his humanitarian activities in occupied Belgium alleviated the suffering of the … READ MORE
Entry -
René Viviani was a leading French politician in the early 20th century. When the war broke out, he was prime minister (''Président du Conseil'') and contributed to the formation of the ''Union … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, as professor at the University of Perm (Russia), Augustinas Voldemaras actively participated in the activities of Lithuanian exiles in Russia. In 1917 he argued for Lithuanian independence. On 11 November, 1918 he headed the … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, the Swiss federal government imposed a state of emergency, which was established to ensure the maintenance of Swiss neutrality, supply and integrity. As the war progressed, legal measures under this regime became more frequent … READ MORE
Entry -
The latter Austrian ''Land'' Vorarlberg saw the rise of a grass root movement for a political union with Switzerland between autumn 1918 and spring 1919. These ideas never materialized, however, as the Paris Peace Treaties vetoed their … READ MORE
Entry -
Baron Hans von Wangenheim was the German ambassador to the Ottoman capital between 1912 and … READ MORE
Entry -
The War Requirements Acts were passed in Austria-Hungary in 1912. They placed military requisitions under parliamentary control and helped the army to obtain the most needed products and services during wartime in a more organized … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, Austria-Hungary implemented a state of emergency with several emergency laws overseen by the ''kaiserlich und königlich ''(''k.u.k.'') ''Kriegsüberwachungsamt'' (war surveillance office, abbreviated KÜA). Although it … READ MORE
Entry -
The Washington Conference was held from November 1921 to February 1922 with the aim of creating a new order in the Asia-Pacific. The main agenda were naval disarmament and an improvement of China’s status, and the conference negotiated the Five-Power … READ MORE
Entry -
As an adviser in the imperial office of the treasury (1916-1918), the Heidelberg economist Alfred Weber helped establish Poland and Lithuania as satellite states under the hegemony of the German Reich (''Mitteleuropa''). During the Weimar Republic, he … READ MORE
Entry -
Brand Whitlock served as the U.S. minister and ambassador to Belgium from 1914–1921. During the war, Whitlock facilitated the humanitarian activities of the Commission for Relief in Belgium, which imported food for more than 9 million civilians in … READ MORE
Entry -
Wilhelm Friedrich Heinrich Prince of Wied, born to a German Protestant noble family, reigned briefly as Prince of Albania from 7 March 1914 until 3 September 1914. In addition to domestic issues and his lack of political experience, the outbreak of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Kaiser Wilhelm II’s ambitious policies played a major part in bringing about the First World War, yet with the onset of hostilities he was sidelined by his generals. In certain key areas, however, notably in appointments to top positions and in the … READ MORE
Entry -
Queen Wilhelmina was by nature a forceful leader. The First World War showed that she lacked the meekness and patience that the head of a small neutral state … READ MORE
Entry -
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the twenty-eighth president of the United States (1913-1921). Wilson unsuccessfully attempted to bring the belligerents to the negotiating table, but in 1917 reluctantly concluded that the U.S. should join the war as an … READ MORE
Entry -
At the end of the First World War, Workers’ and Soldiers’ Councils spread throughout Germany, culminating in a mutiny among sailors at the end of October in Kiel that inaugurated the revolution of November 1918. Their leaders wanted to erect a … READ MORE
Entry -
Hipólito Yrigoyen was president of Argentina during a critical moment of the First World War. He maintained neutrality despite internal and external pressures, and promoted Pan-Hispanism to counteract United States … READ MORE
Entry -
Referred to as the “grandmother of German communism” at the time of her death in 1933 by the ''Manchester Guardian'', Clara Zetkin was a prominent feminist leader within the German social democratic movement and the Socialist International in the … READ MORE
Entry -
Nikola Zhekov was a Bulgarian infantry general, the Bulgarian minister of war from August through October 1915, and commander-in-chief of the Bulgarian army during the First World War, from 1915 to … READ MORE
Entry -
Named for its author, the German minister of foreign affairs Arthur Zimmermann, the so-called Zimmermann Telegram threw a disturbing light on German wartime diplomacy in Mexico and it catalyzed the United States' entry into the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
Anti-war socialists from ten countries met in Zimmerwald in September 1915. They adopted a manifesto and founded the International Socialist Commission (ISC), with its headquarters in Bern. A subsequent conference in Kiental in April 1916 criticised … READ MORE
Entry -
Zionism is a movement that aspired to the creation of a sovereign Jewish state. Having emerged at the end of the 19th century, the Zionist ambition was achieved in 1948 with the founding of the state of … READ MORE
Entry
See also
-
Since 1905 Britain had paid the Afghan ruler, Amir Habibullah, a subsidy and had controlled Afghanistan’s foreign relations, and he maintained Afghanistan’s neutrality throughout World War I in spite of strong pressure to induce him to join the … READ MORE
Regional -
The impact of the First World War on Australia was so profound that its memory dominates the national political culture even today, in the form of the Anzac “legend.” The mass casualties suffered in the Gallipoli campaign, Palestine and on the Western … READ MORE
Regional -
The article surveys the social and military history of Austria-Hungary during the First World War. The war brought a harsh military dictatorship along with innovations in economy, labor deployment, gender conventions, and the elaboration of camps meant … READ MORE
Regional -
This article presents a survey of the First World War in the region of today’s states of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Finland. Chronologically the article begins with the outbreak of the war in August 1914 and ends with the conclusion of the … READ MORE
Regional -
Belgium, a neutral state, was forced into the First World War by a German ultimatum, a fact with considerable international resonance. The war had a deep impact on what was, in 1914, the most densely-populated country in the world. Most of Belgium came … READ MORE
Regional -
From 1912 to 1918 Bulgaria engaged in a prolonged conflict that began in victory in 1913 and ended in defeat in 1918. During that period, the conflict exhausted Bulgaria’s manpower and material resources. By the end of the fighting in 1918, Bulgaria was … READ MORE
Regional -
Burma’s participation in World War I was limited mainly to the provision of troops and engineering units to the Palestine and Mesopotamian Fronts as well as labourers to the Western Front and hosting Turkish and German prisoners-of-war. Nevertheless, … READ MORE
Regional -
This article discusses China’s role in the First World War with a focus on the country’s contribution to the war and the role of the war in shaping Chinese development and its place in the world. Contrary to common knowledge, China was not only … READ MORE
Regional -
With its economy highly reliant on Great Britain, Germany and other European nations, Denmark had to navigate between the two belligerent blocks during the war. This combined with shortages and inflationary pressures lead to a massive growth in state … READ MORE
Regional -
The war in East and Central Africa was one of the longest running of the Great War. It started on 8 August 1914 when the wireless station at Dar es Salaam was bombed and ended on 25 November 1918 when the Germans officially surrendered'' ''at Abercorn. … READ MORE
Regional -
To study France during the “Great War” – as it was called as early as 1914 – involves focusing on a major Western state that was confronted with a growing demand for resources to fuel the war machine and enable the country to hold out until … READ MORE
Regional -
When war broke out, in light of increasingly inflexible constellations and alliances among European powers, Germany was initially hoping to keep the war limited to Austria-Hungary and Serbia. Soon the conflict involved Russia, Germany, France, and Great … READ MORE
Regional -
Great Britain was with its Empire the most powerful of the major belligerents, the most politically and socially stable, and the best able to endure the strains of the war. Its great naval, financial and diplomatic strengths were critical to the Allied … READ MORE
Regional -
Greece officially entered the Great War rather belatedly in June 1917, despite informal involvement since 1914. The war divided Greek political elites, leading the whole country into a civil strife that lasted for decades. This text aims to present the … READ MORE
Regional -
Greece officially entered the Great War rather belatedly in June 1917, despite informal involvement since 1914. The war divided Greek political elites, leading the whole country into a civil strife that lasted for decades. This text aims to present the … READ MORE
Regional -
Ireland’s war experience cannot be separated from Irish politics. Indeed, the story is not one of 1914-18 but of 1912-23, as the vast majority of people sought to change Ireland’s place in the United Kingdom, resisted by others who, though a minority, … READ MORE
Regional -
When the First World War broke out in Europe, Latin Americans of all social strata soon felt that the conflict would plunge the world into a crisis of hitherto unknown dimensions. Due to its globally entangled structures, the continent experienced the … READ MORE
Regional -
Despite its neutrality, Luxembourg was occupied in August 1914, mainly for its strategic value. For four years, the national elite engaged in a difficult policy of cooperation with the German occupier. This choice did not prevent the deterioration of … READ MORE
Regional -
Montenegro entered the First World War politically and militarily exhausted. The outcome of the First and Second Balkan Wars in 1912 and 1913 had a devastating impact on the future of Montenegro. From 1914 until January 1916, the Montenegrin army fought … READ MORE
Regional -
Blockades, part of economic warfare, had been employed throughout history. The Allied blockade (1914-1919), which aimed to prevent war supplies reaching Germany, ultimately also targeted the civilian population. It had its counterpart in the German … READ MORE
Regional -
Newfoundland entered the Great War with great enthusiasm, but was unprepared for what lay ahead. The war greatly stimulated the local economy, since fish prices rose to unprecedented heights. The mining industry also eventually prospered, but the … READ MORE
Regional -
New Zealand was the British Dominion furthest from the conflict in Europe, the Middle East and Africa. Nonetheless with Britain’s declaration of war on Germany, New Zealand and its one million inhabitants were enmeshed in the Great War. The whole … READ MORE
Regional -
Norway managed to stay neutral during the First World War, but the war still crept into Norwegian life and impacted it in numerous ways. With a large merchant fleet – the fourth largest in the world – and heavily dependent upon imports, Norway’s … READ MORE
Regional -
During the Great War, the Ottoman Empire fought on several major and minor fronts, both in the Middle East and in the Balkans. Although initially seen as a military liability by its allies and a weak enemy by its foes, Ottoman armies delivered some heavy … READ MORE
Regional -
The outbreak of the First World War coincided with a period in Persian history when, following the Constitutional Revolution of 1905-1909, the Iranians were poised to refashion the constitutional order and establish an independent, accountable and … READ MORE
Regional -
This paper presents the process of building an independent Polish state during the First World War, which, from the Polish perspective, was the most important result of this conflict. The article focuses mainly on the political and military developments … READ MORE
Regional -
Portugal’s participation in the First World War was depicted by its supporters as a vital component of the consolidation of the country’s young republican regime (established in 1910) and its affirmation abroad. However, there was never any consensus … READ MORE
Regional -
Romania
By Harald Heppner and Rudolf Gräf
World War I afforded the first opportunity for modern Romania to participate in a war which had a larger than regional horizon (South East Europe). The most important reason for participation was interest in gaining territories belonging to … READ MORE
Regional -
The Russian Empire entered the war in order to preserve its Great Power status, but it ended the war in a bout of revolution and decolonization. The army had a mixed record in the war, losing several key battles but remaining a dangerous force until the … READ MORE
Regional -
A short synthesis on Serbia's role and experience in the Great War encompasses several questions that still provoke controversies and offer many carefully reexamined data on issues such as war efforts in general, war casualties, war financing, refugees … READ MORE
Regional -
Siam
By Stefan Hell
Siam (Thailand) declared war on Germany and Austria-Hungary in mid-1917. In 1918 it sent a small expeditionary force to France, the only troops of an independent Southeast Asian country to participate in the war in Europe and the occupation of Germany. … READ MORE
Regional -
The people of Southern Africa experienced the First World War as a continuation of late 19th century European imperialism. The war did not introduce new historical trends as much as it extended and exacerbated imperialism’s ill effects. In … READ MORE
Regional -
This article examines Spain’s neutrality during the Great War, highlighting factors such as the lack of military resources; the division of public opinion and internal conflicts; and actors such as King Alfonso XIII (whose mediating role helped to … READ MORE
Regional -
For Sweden, the impact of the war was twofold. On the one hand, it was a test to the neutrality policy. Concessions and violations of neutrality got consequences for both foreign affairs and the economy. On a domestic level, it meant shortages and … READ MORE
Regional -
As a neutral country, Switzerland was not involved in the devastating military conflicts of 1914-18. Nevertheless, concerning the economy, communications, diplomacy, secret services and war propaganda, it was intensely entangled with the “Great War.” … READ MORE
Regional -
Taiwan, Japan’s first colony, sat geographically far removed from the European battlefields of the Great War, but closer to the Japanese expeditions to Shandong and Micronesia. Japan’s engagement brought the war home to Taiwan in multiple forms: mass … READ MORE
Regional -
The Netherlands remained neutral during the First World War, but was nevertheless significantly affected by it. Its army remained fully mobilized to counter any possible threat, and its economy felt the strain of both belligerents’ attempts to control … READ MORE
Regional -
In 1914, the Union of South Africa was four years old; its military only two. British supremacy in the South African War (1899-1902) provoked different responses from English and Afrikaner white South Africans to World War I. Prime Minister Botha, seeing … READ MORE
Regional -
The American debate over neutrality ended when Woodrow Wilson decided in April 1917 that German aggression on the high seas threatened US national security. From 1917-18 the Wilson administration vastly expanded the power of the federal government by … READ MORE
Regional -
This article examines the deployment of West African soldiers for military service in West Africa, including the manner of mobilization and recruitment. By demonstrating the heavy reliance on West African soldiers for the ‘European’ conduct of the … READ MORE
Regional -
The idea for the unification of the Southern Slavs emerged in the 19th century and the strength of its appeal varied over the course of its development. During the First World War, unification became the main war aim of the government of the … READ MORE
Regional
Survey Articles (Thematic)
-
The First World War and its direct repercussions in the postwar period (revolution, counterrevolution, the founding of republics, and the Paris peace treaties) mark a profound caesura not only in the history of Jews in Europe but also in the history of … READ MORE
Thematic -
France and Germany remained principal protagonists of the First World War. This essay will examine the reasons why both nations believed they were in a legitimate war of defense, for which domestic unity was the indispensable precondition. The essay will … READ MORE
Thematic -
By 1914 the leading states had succumbed to varying degrees of militarism, subordinating other interests to those of the armed forces, yet all were governed by regimes in which the ultimate authority rested with civilian leaders. Civilians led the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Total war is a controversial term used in the past by politicians, publicists and military officers as well as by computer specialists and academics in the present. Since its conception by French politicians during the First World War in a time of severe … READ MORE
Thematic -
Crumbling of Empires and Emerging States: Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia as (Multi)national Countries
By Katrin Boeckh
During the First World War, Czechoslovakia and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (called “Yugoslavia” from 1929) emerged as new national states on the territories of the crumbling Habsburg Empire. Pre-dating the establishment of the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The internment of enemy aliens in the First World War was a global phenomenon. Camps holding civilian as well as military prisoners could be found on every continent, including in nation-states and empires that had relatively liberal immigration policies … READ MORE
Thematic -
One sees a wide range of political regimes from a democratic republic with universal male suffrage (France) to parliamentary, constitutional, or even oligarchical monarchies in the countries that entered the First World War. This article explores the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The Treaty of Versailles was signed on 28 June 1919, establishing both the League of Nations and another international organization: the International Labour Organization (ILO). The ILO was founded upon the conviction that “peace can be established only … READ MORE
Thematic -
After an initial wave of interest in 1914 and the immediate post-war period, international historiography long neglected the wartime occupation of territories inhabited by large civilian populations. Recently, new research has focused on the … READ MORE
Thematic -
The idea of peace in total war may seem irrelevant, but pacifism, or peace activism, did exist during the First World War. A seemingly robust European peace movement existed before 1914, but it contained internal divisions and mostly collapsed early in … READ MORE
Thematic -
This paper examines major peace initiatives during World War I. It describes efforts by the chief European belligerents to split apart enemy coalitions with separate peace settlements as well attempts by the United States and socialist Russia to spark … READ MORE
Thematic -
The conduct of warfare in 1914-1918 included extensive population resettlement in all theatres of war in Europe, both as a result of pre-emptive decisions by civilians to flee in order to evade the conflict or to avoid the consequences of occupation, and … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article surveys the various movements toward social, national, and political revolution that emerged during and in the wake of World War I. The Russian revolutions of 1917 serve as the first case study, followed by the mutinies in France, and the … READ MORE
Thematic -
Despite what some believe, there is still a lot to say and learn about the First World War, particularly with regard to war aims. A lot of focus is currently placed on the cultural, social and psychological facets of the Great War, much more than on the … READ MORE
Thematic -
It may surprise us to learn that some sectors of the European public were in favour of the war in 1914. The impact of modern weapons was not well understood and many people in the government, military and civilian population imagined that the conflict … READ MORE
Thematic -
This article provides an overview of xenophobia during the First World War - namely, the ways in which the conflict was justified and sustained by the growth of hatred for external enemies, and increasingly perceived internal ones. It discusses the … READ MORE
Thematic
Regional Thematic Articles
-
Between 1914 and 1918, between 150,000 and 200,000 Africans traveled to Europe to labor in support of the war effort. Most came from French colonies, but many also came from British colonies in Africa. They worked in diverse settings and on a variety of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Civilians in the Australian government contended with two types of military power in the Great War: generals of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF), and British army military commanders and the War Office who had operational control of the AIF. In most … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The relationship between civilian and military power in Austria-Hungary during the First World War was determined by a number of factors, including the dual state structure and the controversial nationality question. The joint army leadership tried to … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
From 1916 to 1928, the Republic China was divided among military cliques in the regions of mainland China. Provincial military power holders, by proving the impotence of Beijing, undermined the efforts to centralize power and strengthened the forces of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The responsibilities of politicians and military leaders are defined in times of war. The president commands the armed forces, the government - subject to the representatives of the nation - is in charge of conducting the war and the military operations … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Armed conflicts provide fertile ground for the military’s ambitions to gain authority over civilian institutions and actors, a process that played out in the German Empire between 1914 and 1918. While military authorities and politics were almost on an … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
By the early 20th century the United Kingdom had a well-established tradition of civilian control over the armed forces. This tradition came under strain during the Great War as the line dividing Britain’s military and political … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In Italy, as in the other European states involved in the First World War, the outbreak of hostilities saw extraordinary powers conferred upon the armed forces, so as to free them from the supervision of government and parliament. War legislation … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Like the Sino- and Russo-Japanese Wars, the First World War gave an enormous boost to Japanese military operations and authority. The Imperial Navy deployed for the first time to the South Pacific, the Indian Ocean, and the Mediterranean and the army … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War required the most comprehensive mobilization of men and resources in the history of the empire. It transformed the Ottoman state into a more centralized, authoritarian, and nationalist entity. This article explores the impact of total … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In pre-war South East Europe, both civilian and military powers focused on the creation of independent national states and the reclamation of imperial ''irredenta''. This goal, aggressively pursued, created serious regional tension between imperial and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During World War I, an unprecedented civil-military relationship developed among the U.S. government, its military, and civilian society. America struggled to find fair conscription policies despite class, ethnic, racial, and ideological differences. The … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Portugal went to war in March 1916 with a government and an army that did not sit comfortably with each other. The young republican regime’s relationship with its armed forces was difficult despite its popularity among a small number of officers and a … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the mechanisms, results, and characteristics of the national mobilization in Russia in the conditions of the First World War. Moreover, it considers the forms of cooperation between the government and the public, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When World War I broke out, the military conquest of the countries located between China, Siam and the South China Sea had been over for two decades. Nonetheless, French rule in Indochina was not entirely established and the exploitation of economic … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When the First World War came to Africa, European colonial rule was scarcely established in many parts of the continent. Some twenty years after the initial conquest, large parts of Africa remained beyond colonial control. An uneasy and fragile ceasefire … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In 1914, Allied leaders plunged Africans into a conflict that was not their own. In West Africa, British and French colonial troops quickly occupied Togo, while the conquest of Cameroon proved much more difficult. A relatively short campaign led by white … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Italian colonies, with the partial exception of Libya, played only a secondary role in the Great War. By virtue of not sharing borders with any German colonial territories, Italian overseas possessions were spared the conflict between the European … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The diplomacy of Portugal’s participation in the Great War was largely determined by the desire of elites to improve the international standing of the country, as well as by domestic factors related to the bitter quarrels of the republican … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During World War One, Denmark managed to remain neutral. But, as the country was extremely dependent on economic and political relations with both Germany and Great Britain, the war had great consequences for both foreign and domestic politics. Unlike … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The article focuses on how Norway’s neutrality during the First World War impacted domestic politics. A large majority of the country’s political elite supported neutrality throughout the war. In the early years of the war, the Norwegian economy … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Despite the official neutrality maintained by Spain throughout the First World War, the conflict had a considerable impact on that country’s internal politics. The political stances taken gave rise to a process that divided society into two opposing … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article focuses on how the Swedish neutrality policy during the First World War became a contentious topic''' '''in Swedish domestic politics. The food crisis in 1916–1917, social disquiet in connection with the Finnish Civil War, and the German … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Neutrality is a fundamental problem in modern Swiss history and played a pivotal role in both world wars. During the Second World War the danger came from the outside, while during the First World War Switzerland was also threatened from within. From 1914 … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When the First World War broke out, the Netherlands’ most important political parties put aside their differences to help uphold the country’s neutrality throughout the war. However, the Netherlands could not escape the severe strains the war put on … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The dominions of Australia, Canada, Newfoundland, New Zealand, and South Africa shared an ambiguous constitutional relationship with Britain. The self-governing dominions were free to implement their own policies in matters of defence, but their limited … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Although a military failure, the 1916 rebellion transformed Ireland by destroying the possibility of a political settlement between Irish nationalists and the British state and by popularising a republican movement prepared to use violence to achieve … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Danish government succeeded in maintaining neutrality and thus sparing the country from the most devastating consequences of the war. Denmark spent considerable effort in maintaining good relations with both Germany and Great Britain, its most … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Throughout the Great War, successive Spanish governments tried to advance traditional foreign policy claims – the annexation of Tangier, the return of Gibraltar and the possibility of intervening in Portugal – while at the same time facing the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Until 1917, Swedish neutrality was characterized by a certain “benevolence” towards Germany. Eventually, pressure from food shortages and social unrest, following the government’s reluctance to abide by British blockade regulations, led to the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Kingdom of the Netherlands upheld a foreign policy of strict neutrality during the First World War. That policy revolved around two main precepts: upholding the requirements associated with neutrality in international law (particularly the Hague … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In 1917, with tens of thousands of Canadian soldiers killed and wounded, the end of the war was nowhere in sight. As the supply of volunteers dried up, conscription became the dominant issue in Canada. French Canadians were singled out and accused of not … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Latin America figured prominently in Germany’s global war strategy, though after 1915, intelligence operations primarily focused on disrupting Allied supply lines and agitating for war between the United States and Mexico. Washington’s entry into the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Commonwealth of Australia, a self-governing Dominion of the British Empire, experienced splits during the Great War in the major parties of both the left and right. The Australian Labor Party, in 1914 the most successful social democratic party in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The closing of the parliament in Vienna in spring 1914 led to the consolidation of a wartime regime that was at once autocratic, decentralized, and poorly equipped to handle the demands of competing power centers, both within the government and throughout … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War changed the balance of power in Belgium. From a strongly polarized system dominated by the Catholic Party, the country shifted towards a coalition system, marked by a tradeoff between left and right. That shift was facilitated by the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the shifting nature of Canadian federal politics during the First World War with an emphasis on conscription and the formation of the Union Government. The impact of these issues on national unity is examined, as is the deterioration … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
China’s attempt to participate in the European war was complicated by domestic turbulence. Japan’s bid for supremacy in China compelled President Yuan Shikai to propose the Twenty-one Demands in 1915, and after Yuan’s death, there were two … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Despite its weaknesses, the French parliamentary republic survived the First World War without compromising the constitutional laws that had been in place since 1875. The ''Union sacrée'' was formed on 4 August 1914. While this initially resulted in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
At the beginning of World War I, Germany was a constitutional monarchy in which political parties were limited to the legislative arena. They could control neither the government nor the military. At the end of the war, the political system had been … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Great War marked a period of profound upheaval in British politics. The old controversies of Edwardian politics were replaced by new debates about military strategy, civil-military relations and the capacity of the state to mobilize the nation for … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Political life in the Hungarian part of the Dual Monarchy (particularly the constitutional framework, political traditions and mentality) can only be characterized as very different from that of the Cisleithanian half, with all the consequences upon the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During the period of neutrality, Italian public opinion was divided into two camps: one interventionist, and the other, in the majority, opposed to Italy’s entry into the war. Neutralism brought together the two most important political groupings in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Despite over 7,000 miles of separation from the Western Front, Imperial Japan underwent a political transformation during the First World War almost as dramatic as that in the vanquished capitals of Europe. As was the case with most belligerents, the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Governments, Parliaments and Parties, Labour, Labour Movements and Strikes (Union of South Africa)
By Wessel Pretorius Visser
In South Africa the period between 1914 and 1918 was one of intense political and industrial turmoil. It entailed two violent strikes, eventually suppressed by the South African government, a rebellion against the state by Afrikaner insurgents and the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
New Zealand’s wartime parliament was dominated by a coalition between the two main parties, Reform and Liberal. Labour parliamentarians opposed the coalition and the war was a significant factor in the making of a new Labour … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
After the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) seized power in January 1913, it established a single-party government that dominated parliament from the 1914 elections until the end of the war. The CUP was a party of leaders and factions and not a … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Governments, Parliaments and Parties; Political Movements and Protostate Formation (East Central Europe)
By Klaus Richter and Piotr Szlanta
Political movements in Poland and the Baltics were heavily influenced by the German occupation, the Russian Revolution, and the political agency of their diasporas. While the establishment of an independent Polish State became a war aim of the Entente … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Founded in October 1910, the Portuguese Republic was soon mired in turmoil. The victorious Portuguese Republican Party, in reality a broad ideological coalition united only by the desire to topple the monarchy, soon fragmented acrimoniously, first into a … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
At the beginning of World War I, Russian political parties found themselves in deep crisis. In contrast, the State Duma had become the epicenter of the country’s political life. The “Holy Alliance” established between the authorities and society was … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This essay analyzes domestic politics in the United States during World War I, focusing chiefly on the Wilson administration’s relations with Congress and on electoral politics from 1914 to 1918. Throughout this period, war-related issues became … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article seeks to analyze how the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), the oldest existing humanitarian organization, coped with the outbreak of the First World War and its aftermath. By using innovative methods of work and by deploying an … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Russian Civil War of 1917-20 was closely related to the World War in terms of its cause, conduct, and results. This article discusses the two distinct phases of the Civil War, which were divided by the collapse of the Central Powers. It examines the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the history of the Spanish army during the First World War in the context of the Spanish strategic and security situation. It shows the interrelation between Spanish military weakness and strategic insecurity. Particularly focusing … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Armistice agreement foresaw the occupation of the left bank of the Rhine, the dates of which were set by the Treaty of Versailles. The inter-allied occupation was a long-term endeavour: the French settled in the south and the Belgians in the north of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
While on the Western Front there were only limited territorial movements, the Eastern Front and warfare in southeastern Europe, including parts of Italy, had all the characteristics of mobile warfare. During the course of the war, Austria-Hungary took … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article surveys the occupation of the formerly German-leased territory around the Jiaozhou Bay with Qingdao as its capital city by the Japanese during and after the First World War. It first describes the initial ultimatum of the Japanese to the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the politics of the German (''Generalgouvernement'' Warschau) and Austro-Hungarian (''Militärgeneralgouvernement'' Lublin) occupation of the Kingdom of Poland during World War One. Both occupation governments strove to exploit the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article studies Germany’s experiences of occupation during and immediately after the First World War. The first section examines the French attack on Alsace-Lorraine in August 1914 and the Russian invasions of East Prussia from August 1914 until … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
During and after the First World War, Italy experienced different kinds of occupation. The Italian occupation of the border areas in 1915-1917 was followed by the Austro-German occupation in 1917-1918 after the Caporetto defeat. Then, in 1918-1919, in the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The occupation of the Arab lands of the Ottoman Empire was essentially the by-product of the war, but it had been in the making for a long time. Despite their attempt to appear as liberators rather than occupiers, the British and, later, the French … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Memories of occupation by foreign forces are not usually articulated except when prisoners of war speak of their experiences when debriefed. These are usually shameful episodes in the lives of those who survived. Collaboration with the enemy often … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Occupation played a crucial role in Eastern Europe between 1914 and 1921: the highly mobile front allowed trenches to be shifted over hundreds of miles, resulting in the usurpation of foreign lands. While Russia only managed to occupy Habsburg Galicia and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The occupation of South East Europe 1915-1918 had a complex structure reflecting different and often conflicting territorial claims and goals. In the fall of 1915 Serbia was divided into Austro-Hungarian, Bulgarian and German occupation zones. The … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article examines the German occupation of Belgium and Northern France in 1914–1918. Besides focussing on the occupiers’ motives and logic of action regarding their policy and practices, it gives an idea of the complexity of the occupier/occupied … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
World War One represented a turning point in the relationship between churches and the Portuguese state. Both Catholics and Protestants perceived the conflict as an opportunity to expand their scope of influence in a society then dominated by a sector … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article charts the contours of the Great War as an American religious experience, focusing on the ways in which the study of religion and the Great War in America forces an examination of what is meant by “religion.” American clergy and American … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Great War helped to ease the Church-state tensions that had shaped French politics and society during the preceding generation. However, the very different context of the French colonial empire prevented a similar reconciliation overseas. This article … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Africans across the continent resisted colonial demands and took up arms against European colonizers during World War I. This essay presents three ways of recognizing and analyzing such acts of resistance. First, many Africans refused increased colonial … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Revolutionary movements in India haunted the imagination of post-war British officialdom. They were used in the aftermath of the First World War to justify everything from colonial massacres to the indefinite censorship of the press. But what were these … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article provides an overview of the 1916-1918 Arab Revolt against the Ottoman government during World War I, led by Sharif Husayn bin ‘Ali of Mecca in conjunction with British support. The main aim of the revolt was to establish an independent Arab … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Revolutions and Rebellions: Van Resistance as Rebellion (Ottoman Empire/Middle East)
By Yasar Tolga Cora
Violent clashes took place between the Ottoman troops and the Armenian guerilla bands in the city of Van on the eastern edge of the Ottoman Empire in April-May of 1915. The armed struggle in the city and the subsequent occupation of the region by the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The following pages - focusing on the collapse of the Habsburg Empire and the incidents in Austria in 1918/20 - are subdivided into four different periods and aspects: Firstly, World War One until the increasing protest movements of 1917/18, secondly, … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses the influence the Russian Revolution had on countries in East Central Europe. In the Polish Kingdom and Lithuania there was no direct impact because of the German occupation. The parties which sympathized with the Bolsheviks had no … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article focuses on the upheaval between 1917 and 1923. These years were marked by crumbling empires, national mobilisation, and conflicting ideologies and forms of government. Rather than single out specific revolutionary or counter-revolutionary … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Portugal’s participation in the First World War, never consensual, was marked by a number of violent episodes that first undermined and then overthrew the Sacred Union government. Some of these were rural and urban mutinies occasioned by inflation and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Russian Revolution was one of the most influential events to emerge from the furnace of the First World War. It transformed Russia and its Empire and firmly planted the flag of world revolution at the centre of 20th century world history. … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
''Teşkilat-ı Mahsusa'' (TM), or Special Organization, was a secret paramilitary intelligence organization under the control of the CUP’s inner circle and attached to the Ministry of War. Due to its secrecy, the TM is debated in the scholarship. This … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
From the outbreak of World War I, Woodrow Wilson pursued two goals: a non-punitive peace settlement to end the conflict and a reformation of world politics through an international peace-keeping organization to prevent such wars in the future. Before the … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The First World War led to a renewed imperialist scramble for territory in Africa. Allied victory and African campaigns allowed British, French, Belgian, Portuguese and South African leaders to acquire Germany’s colonies. Their wartime colonial aims … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Although Britain declared war on the Dominions’ behalf, Australia had its own war aims. The most important of these was the survival of the British Empire, which the vast majority of Australians believed was key to the country's cultural identity and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
In July 1914 the Habsburg monarchy went to war with Serbia declaring it sought no territorial gain from the struggle. Soon discussions of possible territorial acquisitions, along with economic and political aims, started among the governing elite and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Belgium’s war aims were a direct consequence of the way in which the country was created. The treaties finalized in 1839 left Belgium with part of Luxembourg and Limburg, and also left the Scheldt access to Antwerp under Dutch control. During World War … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses China’s war aims during the First World War, as well as the intra-Chinese discussion over which side to enter the war on. It surveys the extent of the different aims, most of which were related to regaining control over foreign … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Already in autumn 1914, East Central Europe became a main theatre of operational warfare and an object of strategic planning for the Central Powers, Russia, and later the Entente. After strategic failure in the West, Germany focused on this region as an … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
On 4 August 1914, in his first speech after the declaration of war, Raymond Poincaré, president of the French Republic, did not outline any aims other than the ''Union sacrée'' (sacred union) and the defence of the country’s borders. Once the hopes … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
On 1 August 1914, the government of the German ''Reich'' declared war on Russia. Directly afterwards, an intense debate over its war aims flared up. This article traces the development of the war aims discussion: The nationalist War Aims Movement … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
When Britain entered the First World War its war aims were simple: to restore Belgian sovereignty (as it was obliged to do, by the Treaty of London, 1839), and to maintain the balance of power in Europe by defending France and chastening Germany. … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
At the outbreak of the First World War, Italian diplomacy did not have a clear vision of the goals to be achieved. Therefore, in negotiations with the countries already involved in the conflict, excessive territorial claims were made. The errors of … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article discusses Japan’s war aims during the First World War, as well as the different policy approaches Japanese leaders employed to achieve those aims. It explores Japan’s entrance into the war on the side of its ally Britain, its military … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
The Ottoman Empire fought the First World War for the sake of survival in the short term and independence and security in the long. Its diplomatic, territorial, economic, and domestic war aims were shaped to this end. Its military strategy acknowledged … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Portugal’s wartime governments never formulated a concrete set of war aims. The nature of the country’s intervention did not lend itself to this kind of debate. With a long-defined border with Spain, and more colonial territory than it could … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
Russia reluctantly entered the Great War to preserve its status as a great power. However, once the fighting began, it was the first amongst the Allies to state its territorial desiderata, which were to annex lands along the borders of Germany and … READ MORE
Regional Thematic -
This article offers a survey of the main currents in South East Europe in regard to the war aims of the belligerents from 1914. Some war aims had deep roots in the pre-war years. The author puts emphasis on the emerging Yugoslav state in the Balkans. The … READ MORE
Regional Thematic
Encyclopedic Entries
-
On 25 May 1915, Argentina’s, Brazil’s and Chile’s ministers of foreign affairs signed a treaty to facilitate the peaceful solution of international controversies in Buenos Aires. Mired in diplomatic discussions for more than ten years, this treaty, … READ MORE
Entry -
A minority of the adherents of the Flemish movement were willing to collaborate with the German occupier in the context of ''Flamenpolitik''. This minority labelled themselves “activists”, stressing their dislike of the Belgian patriotic … READ MORE
Entry -
Until his death in 1918, Victor Adler was the most prominent Austrian socialist leader and among the leading personalities of the Second Socialist International. During the war, he aimed to preserve Austrian Social Democracy’s impressive prewar gains … READ MORE
Entry -
Ador was the third president of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and a Swiss minister during WWI. He displayed the charisma, the diplomatic skills and the decisiveness necessary to give the ICRC a crucial role in the protection of … READ MORE
Entry -
Albert I, the third king of the Belgians, played a leading role as supreme commander of the Belgian army during the First World War. For four years he defended the last piece of unoccupied Belgium behind the Yser River, refusing to sacrifice his troops in … READ MORE
Entry -
Albrecht Duke of Württemberg was the commander-in-chief of the German 4th Army from 1914-1917 and the ''"Heeresgruppe Herzog Albrecht"'' ("Army Group Duke Albrecht") from 1917-1918. The 4th Army fought under Duke Albrecht’s … READ MORE
Entry -
Umar al-Da’uq was a merchant and notable of Beirut in the late Ottoman period. He was Mayor of Beirut during WWI and participated in his official and private capacities in the famine relief efforts. He became president of the short-lived Arab government … READ MORE
Entry -
Born Princess of Hesse-Darmstadt, Aleksandra Fedorovna married the future Russian Emperor Nicholas II in 1894 and became empress. She was engaged in charity work and served as a nurse during the First World War. However, she was suspected of treason and … READ MORE
Entry -
Alfonso XIII was a controversial Spanish king during the first decades of the 20th century. During the First World War he established a humanitarian office for prisoners and civilian relief at the Royal Palace in … READ MORE
Entry -
The diffusion of anarchism in Latin America, which began in the 1870s, was boosted by large migration flows. Between 1890 and 1920, anarchism was an essential element in the process of workers’ self-organization. Opposition to the war characterized the … READ MORE
Entry -
A short lived agency, the Arab Bureau (1916-1920), was ostensibly established to co-ordinate British wartime policy in the Near East, track the regional direction of Turco-German activity and disseminate propaganda among Indian Muslims. In fact, its … READ MORE
Entry -
There were a number of Arab intellectuals who actively cooperated with the Entente and Central Powers during the Great War through their actions, writings and speeches. The entry focuses on the actions of Shakib Arslan, Muhammed Kurd Ali and the al-Khatib … READ MORE
Entry -
Armenians contributed greatly to the Allied victories in Europe and Western Asia, both as non-state and state combatants. They scored important victories, but also suffered defeats. The war precipitated an ethnic disaster and the loss of lands, but also … READ MORE
Entry -
With branches in the Ottoman Empire, Russia, and Iran, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (''Hay Heghapokhagan Dashnaktsutiun'') was the leading Armenian political party during the First World War. The party leaders and cadres in the Russian and … READ MORE
Entry -
Shakib Arslan was a prominent Arab politician, polemicist, and man of letters. Arslan, an ardent supporter of the Ottoman Empire, lobbied for the maintenance of the Islamic Caliphate after World War I, becoming an outspoken activist for Panislamism and … READ MORE
Entry -
Asquith was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom at the outbreak of war. He formed a coalition in May 1915 but accusations of ineffectiveness led to his replacement by David Lloyd George in December 1916. He remained out of office and subsequently lost … READ MORE
Entry -
The Republic of Azerbaijan is a majority Turkic and secular Muslim nation in the South Caucasus. This republic was proclaimed on 28 May 1918, during World War I. The Bolshevik invasion on 27 April 1920 ended Azerbaijan’s brief independence. The nation … READ MORE
Entry -
Cemal Azmi was an Ottoman official who served during the Great War as governor (''vali'') of the province (''vilayet'') of Trebizond. Being the mastermind of the Armenian genocide in this province he earned the surname of the butcher of Trebizond. His … READ MORE
Entry -
A lawyer, Progressive, and pacifist, Newton Baker was U.S. Secretary of War during World War I. He oversaw a massive mobilization that relied on a sweeping draft law and cooperation between government officials, business elites, and reformers. Baker’s … READ MORE
Entry -
Arthur James Balfour was a British Conservative politician and statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and was later Foreign Secretary. In the latter post, he issued the Balfour Declaration of 1917 on behalf of the British government, … READ MORE
Entry -
The Balfour Declaration, the document that set the stage for establishing the state of Israel, was the product of months of wordsmithing and political jockeying. The evolution of its final wording sheds light on the goals and agendas of political powers … READ MORE
Entry -
The Imperial and Royal Ministry of the Imperial and Royal House and of Foreign Affairs, informally called “Ballhausplatz” after the Viennese square on which the central office was located, was one of only three joint ministries of Austria-Hungary. … READ MORE
Entry -
Cesare Battisti was the leader of the socialist party of the Italian Tirol (Trentino) and, from 1911, a member of the Austrian parliament. At the outbreak of war he went to Italy to engage in pro-intervention propaganda. In 1915 he joined the Italian … READ MORE
Entry -
The Batum Conference (May 1918) and treaties ended the state of war between the Ottoman Empire and various governments of the South Caucasus. Additional treaties were signed with the North Caucasus. By these treaties, the empire won 20,000 square … READ MORE
Entry -
Max Bauer was a German artillery expert and a key suborndinate in the German Supreme Command. A loyal suporter of Ludendorff, Bauer intrigued against Falkenhayn and consistently pushed for the further militarisation of German everyday life. He played a … READ MORE
Entry -
Otto Bauer was a leading Austro-Marxist and socialist politician who served during the war as an officer in the Austro-Hungarian army. After returning from Russian internment to Vienna in 1917, he joined the Leftist opposition within the Social Democratic … READ MORE
Entry -
Gertrud Bäumer was one of the most well known leaders of the German women’s movement. In 1914, as the president of the Federation of German Women’s Associations (''Bund Deutscher Frauenvereine'', BDF), she co-founded the National Women’s Service … READ MORE
Entry -
Ruijs de Beerenbrouck was a Dutch Prime Minster who successfully dealt with the threat of revolution in November … READ MORE
Entry -
Gertrude Bell’s earlier travels and intellectual interests, alongside her wartime intelligence-gathering activities, prefigured the role she would play in administering the new Iraqi state. In recent years, scholars have drawn more attention to her … READ MORE
Entry -
Edvard Beneš was a Czech politician, diplomat, and close collaborator of Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk. As Secretary General of the Czechoslovak National Council in Paris from 1916 to 1918, he successfully organized Czechoslovak propaganda; helped create the … READ MORE
Entry -
Graf Leopold Berchtold, Habsburg foreign minister from 1912 to 1915, was confronted with military action during and after the Balkan Wars, yet kept peace. Then, the Sarajevo assassinations, blamed on Serbia, convinced him that only war with Serbia would … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, Berlin became an organisational hub for Indian nationalist and revolutionary activities. By September 1914, a group of South Asian emigrants had organized – with permission of and in cooperation with the German Foreign Office … READ MORE
Entry -
Count Bernstorff was German ambassador to the United States from 1908 to 1917. He tried in vain to warn the Reich government against unrestricted submarine warfare which would result in America’s entry into the … READ MORE
Entry -
Hans Hartwig von Beseler was a German general and military engineer who oversaw the conquest of several fortresses early in the war. He was then named commander of German-occupied Poland, a post he held until the end of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Bethmann was a career civil servant who became Imperial Germany’s fifth Reich Chancellor and took Germany into the First World War. Despite heading the imperial German political administration, his power was circumscribed by the role of Kaiser Wilhelm … READ MORE
Entry -
Louise de Bettignies created an intelligence network for the British in occupied France. She was arrested, sentenced to death in March 1916 and deported to the prison of Siegburg. Sick, she died in Cologne in September 1918, and was commemorated … READ MORE
Entry -
Moritz von Bissing was born on 30 January 1844, in Bellmannsdorf, Silesia, then part of the German Empire. He served as governor general of the Prussian Army from December 1914 until his death on 18 April 1917 in Trois Fontaines, a village in … READ MORE
Entry -
This article looks at the Black Hand from its origins to the demise of its leader, Dragutin Dimitrijević "Apis", in the Salonika Trial of 1917, focussing on the role the association played in Serbia’s foreign and domestic affairs before and during the … READ MORE
Entry -
Howard Sweetser Bliss was the President of the Syrian Protestant College (SPC) during the war. His congenial relationship with Jamal Pasha helped to ensure the security of the college and American community throughout the war. At the Paris Peace … READ MORE
Entry -
Jan Bloch was an entrepreneur, social activist and pacifist. At the end of his life, he published a comprehensive work in which he predicted the course and consequences of World War I. He warned of the dangers of a total, destructive war and urged … READ MORE
Entry -
Jan Bloch was an entrepreneur, social activist and pacifist. At the end of his life, he published a comprehensive work in which he predicted the course and consequences of World War I. He warned of the dangers of a total, destructive war and urged … READ MORE
Entry -
Bonar Law was leader of the Conservative Party in Britain during the war. He entered Asquith’s coalition government in May 1915, and in December 1916 played a crucial role in Lloyd George becoming Prime Minister. For the rest of the war, he was a key … READ MORE
Entry -
The borders of the Netherlands were an important site of war experience for the Dutch, as well as a contested site of war interaction for the … READ MORE
Entry -
As a Flemish nationalist, August Borms actively collaborated with the Germans during the First World War. As a result of his ten-year imprisonment and his death sentence he became a true symbol of Flemish … READ MORE
Entry -
After a long parliamentary career, Paolo Boselli became Italy’s 22nd prime minister in June 1916 after the fall of Antonio Salandra’s government. Charged with forming a unity government, his leadership was uninspiring and he was forced to … READ MORE
Entry -
In the narrow sense, the so-called “Bosnian Crisis” (or “Annexation Crisis”) of 1908 and 1909 was a political conflict between Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire caused by the (formal) incorporation of Bosnia and Herzegovina into the territory … READ MORE
Entry -
Venceslau Brás was president of Brazil between 1914 and 1918. On 26 October 1917, he signed the Brazilian declaration of war against … READ MORE
Entry -
Liberal Prime Minister Ionel Brătianu led the charge to transform Romania's foreign policy, after three decades on the same side with the Triple … READ MORE
Entry -
Brazil was the only South American country that participated actively in the First World War. Before the war, the country was economically dependent on European and North American markets and modelled itself on Western culture and science. After the war, … READ MORE
Entry -
At Brest-Litovsk, from 22 December 1917 to 10 February 1918 (Julian calendar: 9 December − 28 January), Soviet representatives and the Central Powers negotiated a separate peace. On 3 March 1918, following the breakdown of the talks and a new German … READ MORE
Entry -
As an imperial diplomat, first Foreign Minister of the Weimar Republic, leader of the German Peace Delegation in Versailles and also first ambassador to the Soviet Union, he acted in decisive positions in pre- and post-war German foreign policy. His … READ MORE
Entry -
Charles de Broqueville, chief of the Belgian government during the First World War, acted as liaison between the king and the Belgian government. He supported the king in his attempts to obtain peace and his efforts to break free from the … READ MORE
Entry -
The Belgian capital was spared the anguish of combat, but the city suffered four long years of occupation. In fact, it became the most important occupied city during the First World War. For the population, these were times of scarcity, repression, and … READ MORE
Entry -
Williams Jennings Bryan was a powerful Democratic politician, from his emergence on the American political scene in the 1890s to his death in 1925. A three-time Democratic nominee for president, Bryan served as secretary of state under President Woodrow … READ MORE
Entry -
During his career as a diplomat and courtier (knighted count in 1899 and prince in 1905), Bernhard von Bülow became Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs (after 1897) and German Chancellor (1900-1909). He hoped to attain a “place at the sun” for his … READ MORE
Entry -
István Burián was a leading Austro-Hungarian career diplomat and politician, rising to become the Monarchy’s longest-serving foreign minister during the First World War. Burián’s wartime policies included trying to pacify neighboring neutrals and … READ MORE
Entry -
Minister plenipotentiary for England in Lisbon, there was consensus about Lancelot Carnegie as a diplomat in Portuguese public opinion. He was recognized as one of the people responsible for the consolidation of the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance. With the … READ MORE
Entry -
For three decades Romania’s foreign policy depended almost entirely upon King Carol I’s will. The secret alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary was his sole political project. His death, which occurred shortly after the outbreak of the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
Following a career as British consul and humanitarian investigator, Roger Casement became involved in the Irish nationalist movement and the Irish Volunteers. On the outbreak of war, he sought help in Germany for Irish independence. On learning of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Mehmed Cavid Bey was born in Thessaloniki to a Sabbatean (''dönme'') family in either 1878 or 1879. After studying in his hometown, he moved to Istanbul and worked in the education ministry. Prior to the 1908 Constitutional Revolution, he was a teacher … READ MORE
Entry -
Cemal Paşa belonged to the top leadership of the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), which ruled the Ottoman Empire during World War I. He served as wartime minister of the navy and autocratic governor general and commander of the Fourth Army in … READ MORE
Entry -
In his youth, the archduke was introduced to the idea of federalism by Archduke Franz Ferdinand. During the first part of World War I, he became a skillful military leader without any political influence. The young emperor’s two main aims, the reform of … READ MORE
Entry -
Virendranath Chattopadhyaya belonged to the transnational networks of Indian political activists who, during the first decades of the 20th century, carried out anti-imperial and anti-colonial propaganda outside India, first in Europe and North … READ MORE
Entry -
Churchill was Navy Minister during the early stages of the war but was widely criticized over his handling of the Dardanelles campaign. He was demoted and soon afterwards resigned from the government in order to serve on the Western Front. He quickly … READ MORE
Entry -
Circassian nationalism refers to national movements among Adyghe people, a North Caucasian ethnic group. The term is also used to include other North Caucasian peoples who share historical commonalities with the Adyghes. By 1914, the overwhelming majority … READ MORE
Entry -
World War I had a profound impact on concepts of citizenship. Not only did hosts of people find themselves under new sovereignty at the end of the war, but many individuals had to contend with the experience of statelessness or redefinition as “enemy … READ MORE
Entry -
Count Heinrich Karl Clam-Martinic was a German-speaking Bohemian high aristocrat and close friend to heir apparent Archduke Franz Ferdinand. Under Emperor and King Charles I, Clam-Martinic was Austrian (Cisleithanian) prime minister from 1916 to 1917 and … READ MORE
Entry -
During the war, Georges Clemenceau fought for a more efficient war effort and for parliamentary control of military affairs and, as a journalist, rejected unlimited censorship. As French premier, he embodied the “integral war” and the struggle for … READ MORE
Entry -
Collaboration is often associated with the military occupations of the Second World War, but there was a precursor to this multi-faceted phenomenon in occupied France and Belgium during the First World War. This article examines the meaning of … READ MORE
Entry -
Michael Collins was a revolutionary leader who rose to become chairman of the Irish provisional government in 1922 and Commander-in-chief of its army in the brief interval that supervened before his death the same year. He sought to use violence in a … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich Naumann’s ''Mitteleuropa'' (1915) was a liberal voice in the largely illiberal German discussion on the future of East Central and South East Europe. His reasoning, based on principles of free trade and voluntary cooperation, did not dominate … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War I, many conscription age-men sought exemptions from combat duty for reasons of conscience. Religious beliefs formed the large majority of objections, but other reasons included humanitarian and political opposition to the war. While most … READ MORE
Entry -
King Constantine I, a brave army officer but rather controversial in his political choices, is mainly known for his strong disagreement with Prime Minister Eleutherios Venizelos over the role of Greece in World War I, which resulted in the painful … READ MORE
Entry -
The Constantinople Agreement, alternatively known as the Straits or Istanbul Agreement, was a secret agreement concluded between Britain, Russia, and France on 18 March 1915. The most important stipulation of the agreement was the Allies’ promise to … READ MORE
Entry -
The Corfu Declaration was a formal agreement between the government-in-exile of the kingdom of Serbia and the Yugoslav Committee (anti-Habsburg South Slav émigrés) that pledged to unify Serbia with Austria-Hungary’s South Slav territories in a … READ MORE
Entry -
P.W.A. Cort van der Linden was the Dutch prime minister from 1913 to 1918. His cabinet managed to preserve Dutch neutrality throughout the … READ MORE
Entry -
Afonso Costa’s name is indelibly attached to Portuguese interventionism. He led the government when Portugal entered the First World War in March 1916; participated in the first Sacred Union cabinet; and led the second, starting in April 1917. He also … READ MORE
Entry -
George Creel is most famous as Chairman of the Committee on Public Information (CPI) in the United States during the First World War. Under his leadership, the CPI pioneered public relations and propaganda techniques that were later used both by … READ MORE
Entry -
Benedetto Croce is an important figure for both Italian intellectual life (through his philosophical and historical writings) and the political history of Italy (through his work as a politician). Croce began his political life in 1910 and was a member of … READ MORE
Entry -
Ottokar Graf Czernin was an Austrian politician and the minister of foreign affairs for Austria-Hungary from 1916 to … READ MORE
Entry -
Josephus Daniels was United States secretary of the Navy from 1913–1921. He democratized, expanded, and modernized the United States Navy, preparing it for service in the First World War. During the war Daniels championed the North Sea mining barrage … READ MORE
Entry -
Ignacy Daszyński was one of the foremost figures on the Polish political scene in the first half of the 20th century. He personified a subset of elites who merged the struggle for social justice with respect for the principles of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Har Dayal was one of the chief architects of a quixotically sketched blueprint to effect a republican-socialist revolution in British India during the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
As a socialist, Eugene Debs unsuccessfully ran for president four times. He served two prison sentences: the first due to his role in the Pullman Strike in 1894, and the second after being indicted under the Espionage Act as result of his criticism of … READ MORE
Entry -
Following the Bolshevik seizure of power in October 1917, Lenin issued his Decree on Peace, calling for a truce and demanding that peace be agreed upon by people’s assemblies to be convened across Europe. There was no popular European uprising, however, … READ MORE
Entry -
The Defence of the Realm Act (DORA) afforded the British government extraordinary emergency powers during the First World War. DORA’s remit was expansive, and grew in severity throughout the war, though public reaction was generally muted. DORA’s … READ MORE
Entry -
A local notable and mayor of Lille during the occupation, Charles Delesalle was forced to work with the Germans but also sought to protect the population as best as possible. In particular, he played an important role in food provision, overseeing … READ MORE
Entry -
De Valera was a prominent figure in the Easter 1916 rebellion against British rule. He subsequently became head of the Irish … READ MORE
Entry -
Roman Stanisław Dmowski was a Polish politician and most importantly the co-founder of National Democracy in Poland before the First World War and during the interwar period. He was also the co-founder of Polish National Committee in 1917 and served as … READ MORE
Entry -
In February 1917 two centres of power emerged to replace the tsarist government: the Provisional Government and the Petrograd Soviet. The Provisional Government had formal authority but the Soviet controlled the actual levers of power, including the … READ MORE
Entry -
W.E.B. Du Bois, sociologist, historian, and socialist, promoted African American advancement and expected the war to improve the position of nonwhite minorities in the United States and globally. He was the editor of the NAACP magazine, which protested … READ MORE
Entry -
The Tsar reluctantly granted an elected legislative assembly, the State Duma, during the 1905 Russian Revolution. The first two Dumas were dissolved amidst bitter conflict and the third did little to resolve Russia’s pressing social and economic issues. … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich Ebert became the most important leader of the SPD during the First World War, alongside Philipp Scheidemann. During the revolution, Ebert rose to the top position within party hierarchy and drew Germany towards parliamentary democracy, first as … READ MORE
Entry -
Queen Elisabeth was the third queen of the Belgians. Her attitude during the First World War propelled her to the mythic rank of "Queen … READ MORE
Entry -
World War I was not simply a conflict among European states but a global war of empires. The fighting took place not only in Europe, but also in Africa, Asia, and across the Middle East, and it involved, as soldiers or laborers, millions of Africans and … READ MORE
Entry -
After leading the coup that brought the Committee of Union and Progress to power, Enver was appointed chief of staff and war minister. Convinced of a German victory, he decided to join World War One. In November 1918, he fled to Germany and then to … READ MORE
Entry -
As a Member of Parliament 1917, Erzberger, the former annexationist, played an important role in drafting the Reichstag’s Peace Resolution and the setting up of the ''Interfraktioneller Ausschuss'' (Interparty Committee). As secretary of state of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Before the war, Ethiopia had many diplomatic connections with European states and found itself in a strong position relative to them, particularly after defeating Italy in 1896. Once war broke out, it positioned itself as neutral. However, it also had an … READ MORE
Entry -
Paul Eyschen, prime minister of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg from 1888 to 1915, insisted on the neutral status of Luxembourg, but practiced a policy of accommodation towards German occupying forces during the war. This policy was disapproved of by the … READ MORE
Entry -
Ludwig Freiherr von Falkenhausen was a German General and military writer who served in different leadership positions during World War One. From 1917 until the end of the war he was governor-general in … READ MORE
Entry -
Faysal ibn Husayn commanded the Northern Army of the Arab Revolt and was raised to the throne of Syria in October 1918. The French invasion drove him from Damascus in April 1921. Made king of Iraq under British tutelage, Faysal guided the country to … READ MORE
Entry -
Tsar Ferdinand I of Bulgaria undoubtedly contributed to the modernization of the country. His name, however, is linked to two national catastrophes: Bulgaria’s participation in the Second Balkan War, and the failure of Bulgarian national ideals during … READ MORE
Entry -
Abel Ferry was a French politician and minister as well as an infantry combatant, who used his first-hand knowledge of the war to try and shape the official war effort. He died as a result of his parliamentary inquiries at the front. His diaries and … READ MORE
Entry -
The German ''Flamenpolitik'' during the First World War aimed to instrumentalise the Flemish movement in order to ensure lasting German control over Belgium. It did not divide the Belgian or even Flemish population as a whole, but managed to split the … READ MORE
Entry -
The First World War engendered a rift within the Flemish movement, with some wishing to pursue the advocacy for Flemish rights and others preferring to await the end of the war to obtain new laws. After the war, the Flemish movement broadened its base and … READ MORE
Entry -
The Fourteen Points were U.S. President Woodrow Wilson’s post World War I blueprint to end territorial disputes in Europe, promote international commerce, and make the world safe for democracy. They were based on the ideas of open trade and collective … READ MORE
Entry -
Under the terms of the 1867 constitution, Francis Joseph retained his prerogatives in foreign policy. His decision to opt for war in 1914 was largely a result of the frustrations of Austria’s policy during the Balkan Wars of 1912-13. Francis Joseph … READ MORE
Entry -
Ludwig Frank was a member of the Reichstag for the Social Democratic Party. When Germany entered the war, he strongly supported voting for war loans and volunteered for war service at the age of forty. He was killed in combat shortly afterwards in … READ MORE
Entry -
This biographical overview of Archduke Franz Ferdinand examines the evolution of his difficult personality through the traumatic experiences of barely surviving tuberculosis and fighting for the right to marry; his political orientation and imperial … READ MORE
Entry -
“Freedom of the seas” was the early 20th century idea that the world’s oceans served as a global commons for carrying cargo and facilitating commerce. As both a communal property and throughway, the seas thus could not be controlled by … READ MORE
Entry -
Juozas Gabrys was one of the major advocates of Lithuanian political aspirations in the international arena from 1911 to 1918. He contributed to the establishment of the Council of Lithuania in 1917. However, by acting mainly abroad, he gradually lost … READ MORE
Entry -
General Joseph-Simon Gallieni was a colonial officer who became the Governor of Paris in 1914 and Minister of War in … READ MORE
Entry -
Arnaldo Garcez was the only official photographer of the Portuguese army on the Western Front, a fact that hints at the importance of his mission. Arriving in France in 1917, he thoroughly reported on a specific sector amidst the British lines, from the … READ MORE
Entry -
Harry Garfield worked in a number of civic positions during his life. When the United States entered World War I, President Woodrow Wilson asked him to oversee the Fuel Administration. As the leader of the Fuel Administration, Garfield successfully … READ MORE
Entry -
Lindley Garrison was a prominent lawyer and politician from New Jersey who rose to the rank of vice chancellor of the state in the early 1910s. Because of his prominence, Woodrow Wilson selected him to be his first secretary of war. However, the two … READ MORE
Entry -
Eric Geddes was the most prominent example of Britain’s deployment of businessmen in government. He was the driving force behind the reorganization of the British Expeditionary Force’s (BEF) logistics on the Western Front and the political head of the … READ MORE
Entry -
After the German Army had occupied wide areas of Belgium, the “Imperial Government General in Belgium” was established on 23 August 1914 with a governor-general at its head. Organized into a military administration (the “Government General”) and a … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1915, Germany set up the “''Generalgouvernement'' Warschau”, or General Governorate Warsaw, as the administrative unit for its occupied territories in Russian Poland. Under the leadership of Governor General Hans von Beseler and Wolfgang von Kries, … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Große Hauptquartier'' (Great Headquarters or GHQ) was the strategic command centre of the German armed forces for the duration of the war. It comprised representatives of all political and military decision-making … READ MORE
Entry -
King George V served as a figurehead for the nations of the British Empire throughout the war. He and his wife, Queen Mary, provided inspiration and support for both the armed forces and the civilian populations through hundreds of official visits and … READ MORE
Entry -
World War One was a catalyst for Georgian independence, which was declared on 26 May 1918. The war demonstrated the significance of Georgian territories as a transit route and source of raw materials for contending empires. During the war, Transcaucasia … READ MORE
Entry -
The German Fatherland Party (1917-1918/1919) aspired to mobilize members of the broader radical right as well as the milieus of the German Conservative Party and the National Liberal Party. It aimed to gather broad support for the annexationist War Aims … READ MORE
Entry -
German-speaking elites in Brazil were traditionally in contact with German colonial actors, and during World War I, many middle-class immigrants sympathized with Germany. This led to a conflict within Brazilian society, where people predominantly sided … READ MORE
Entry -
Germany’s offer of unconditional support to its Austro-Hungarian ally in July 1914 remains one of the most controversial decisions in modern history. Historians have interpreted the blank cheque in several, often contradictory, ways – either as a … READ MORE
Entry -
Although sometimes characterized as a quixotically hatched scheme to overthrow British rule in India, the Ghadar “conspiracy” is best understood as a failed bid to foment a democratic revolution in India in the midst of the First World War. The … READ MORE
Entry -
Giovanni Giolitti favored the increased liberalization of Italy, which encouraged its estrangement from the Triple Alliance. He consistently refused to recognize that Italy’s partners’ aggressive policies could trigger the ''casus foederis'' for war. … READ MORE
Entry -
Colmar von der Goltz was one of pre-war Germany’s most outstanding and controversial military theoreticians. His publications had a considerable impact on military thought and the role of armed forces within society around the world. His ideas were … READ MORE
Entry -
Hermann Göring was a highly decorated and well-known fighter pilot of the First World War and later a high-ranking National Socialist … READ MORE
Entry -
Thomas Watt Gregory served as Attorney General of the United States during World War I. He played a key role in developing the Espionage and Sedition Acts to suppress dissent during World War I and enforcing Selective Service draft laws. He served as an … READ MORE
Entry -
Grey was the longest-serving British foreign secretary of the 20th century. His time in office is controversial for his role in the outbreak of the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
Grigorovich was Navy Minister between 1911 and 1917. He sought cooperation with parliament and secured funds to rebuild fleets ravaged by war with Japan. His support for mobilisation in 1914 helped push Russia into a conflict for which the navy was … READ MORE
Entry -
Robert Grimm was the most powerful socialist politician in Switzerland throughout the first half of the 20th century. As the organiser of the Zimmerwald and Kiental Conferences, he was one of the prominent figures of the international socialist … READ MORE
Entry -
As head of the Railway Section at the General Staff, Groener was responsible for the timely transport of troops to the front in August 1914. He was sacked from the Supreme Army Command (''Oberste Heeresleitung'', OHL) in August 1917 and deployed to the … READ MORE
Entry -
General Vassillii Iosifovich Gurko was a Russian military commander during the First World War. Between November 1916 and February 1917 he was the chief of staff in the General Headquarters of the Russian … READ MORE
Entry -
Hugo Haase was a prominent social democrat in the ''Kaiserreich'', who opposed German war aims and formed the Independent Social Democratic Party (USPD) of Germany in 1917. He co-chaired the Council of People’s Representatives (''Rat der … READ MORE
Entry -
İsmail Hakkı was an experienced civil servant. He collected and published detailed statistics on the population, economic activities, education, natural resources and means of transportation in his provinces, and attempted relief efforts to alleviate … READ MORE
Entry -
Liberal Secretary of State for War 1905-1912. Haldane’s reforms of the British Regular Army and its auxiliaries were instrumental in ensuring that Britain could dispatch an expeditionary force to assist the Belgians and French in August … READ MORE
Entry -
Maurice Hankey was responsible for adapting the British government’s administrative machinery to the needs of modern war. He became an influential behind-the-scenes adviser to British prime ministers during the … READ MORE
Entry -
Georg von Hertling was the chancellor of Germany from 1 November 1917 to 3 October … READ MORE
Entry -
Gustave Hervé’s dates of birth and death (1871-1944) correspond broadly to those of the Third Republic (1870-1940). His path is strongly linked to it and his ideas partly reflect its contradictions. Fervently anti-militarist and anti-patriotic before … READ MORE
Entry -
Paul von Hindenburg shot to fame after the Battle of Tannenberg in August 1914. He was Germany’s national hero of wartime, soon eclipsing the Kaiser. Appointed to the Supreme Command in 1916, he increasingly took on a political role. His myth survived … READ MORE
Entry -
After the First World War, Hitler created a mythical account of his war years for political gain. This account was a far cry from the realities of his war experience on the Western … READ MORE
Entry -
The Great War had a decisive influence on Hồ Chí Minh. In France, his acquaintance with the history of the 1789 French Revolution drove him to socialism, then to the 1917 Russian Revolution in its Leninist guise, which led him to … READ MORE
Entry -
After working first as a lawyer and legal scholar, Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. accepted positions on the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts and the United States Supreme Court. As a Supreme Court justice Holmes wrote opinions that shaped the debate on … READ MORE
Entry -
Herbert Hoover obtained political prominence during World War I through his roles as chairman of the Committee for the Relief of Belgium (CRB) and the U.S. Food Administration. Following the war, Hoover served as head of the American Relief Association … READ MORE
Entry -
Horthy was a naval officer of Austria-Hungary. During the First World War he was first in command of a cruiser and then chief commander of the navy. After the war he took part in the counter-revolution in Hungary against the Bolshevik regime; following … READ MORE
Entry -
Edward House was an advisor to President Woodrow Wilson. He aided Wilson in diplomatic matters and in crafting the Fourteen Points that became the framework for the League of … READ MORE
Entry -
Elias Hoyek was Patriarch of Antioch for the Maronites. He is considered to be one of the fathers of Lebanonism, a symbol of resistance against Ottoman hegemony, and the founder of Lebanese … READ MORE
Entry -
Husayn ibn Ali launched the Arab Revolt in alliance with Great Britain. His relations with his European allies remained uneasy and deteriorated further when a unified Arab state under his rule failed to materialize after the war. Ibn Sa‘ud’s conquest … READ MORE
Entry -
Husayn Kamil was the first sultan of Egypt after the declaration of the British protectorate, from 1914-1917. After ascending to the throne on 18 December 1914, he survived two assassination attempts and collaborated with British military … READ MORE
Entry -
The Husayn-McMahon Correspondence mapped out with studied ambiguity the terms of the wartime alliance between Great Britain and Hashemites that underpinned the Great Arab Revolt (July 1916-October 1918) against Ottoman … READ MORE
Entry -
Italy entered the First World War in May 1915, roughly ten months after it began. During those ten months, the battle of opinions for and against intervention raged on. Public meetings, demonstrations, and street clashes that occasionally left partisans … READ MORE
Entry -
A Romanian politician, Dumitru Ionescu, commonly known as Take Ionescu, was considered by his contemporaries to be one of the most erudite statesmen in Eastern Europe. He was one of the main politicians who manoeuvred Romania’s entrance into the First … READ MORE
Entry -
The campaign for Irish Home Rule lasted from 1870 until 1914. When Home Rule became a realistic possibility in 1912, a period of political turmoil ensued. Parliamentary solutions to the impasse were overtaken by the emergence of rival armed paramilitary … READ MORE
Entry -
This article examines the history of Italian irredentism before 1915; and its place its role in Italy’s entry into the war in May 1915 and in Austro-Hungary’s military governance of the Italian-speaking Habsburg territories until 1918. It also … READ MORE
Entry -
Russian-Jewish author, playwright, journalist, orator, and political activist; co-founder of the Zion Mule Corps (1915-16) and the Jewish Legion (1917-21, the unofficial name of the 38th Battalion of the Royal Fusiliers), composed of Jewish volunteers who … READ MORE
Entry -
Gottlieb von Jagow was a German diplomat. He served as the German Foreign Secretary from January 1913 to November … READ MORE
Entry -
A philosopher, historian, and journalist (creator of'' L’Humanité''), Jean Jaurès defended the socialist program for workers and small farmers in the Chamber of Deputies and throughout France. Within the Second International, an organisation of … READ MORE
Entry -
Bishop Jeglič was one of the most prominent Slovenian Church figures in the era leading up to the outbreak of the First World War. His political actions during the war decisively shaped the people’s perspective on the Habsburg Monarchy and had an … READ MORE
Entry -
In October 1916, the Prussian War Ministry conducted the ''Judenzählung'', also referred to as the “Jew Count” or “''Judenstatistik'',” a census of Jewish soldiers serving in the German army. The ''Judenzählung'' operated on unfounded … READ MORE
Entry -
In July 1917, economic chaos and unpopular preparations for military action provoked armed demonstrations by workers and troops demanding the Petrograd Soviet take power from Russia’s Provisional Government. The uprising failed and reprisals were … READ MORE
Entry -
Peter I Karadjordjević was King of Serbia from 1903 to 1918, and King of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes from 1918 to 1921. He also translated the essay “On Liberty” by John Stuart Mill (1806–1873) into … READ MORE
Entry -
Mustafa Kemal Pasha gained fame during World War I both as a successful commander on three Ottoman fronts and as a fierce critic of the Young Turk government and its German allies. After the war, his reputation enabled him to position himself as the … READ MORE
Entry -
Aleksandr Kerenskii was Minister of War in Russia’s Provisional Government from April to October 1917 and Prime Minister from July to October. He embodied the hopes of the February Revolution of 1917, the doomed military offensive of June 1917, and the … READ MORE
Entry -
The "khaki" general election of 1918 was held in Great Britain almost immediately after the Armistice. It was the first held under what was almost universal adult suffrage. The result was a crushing victory for a coalition comprised of Liberals supporting … READ MORE
Entry -
The King’s African Rifles (KAR) were the British colonial military within East Africa before and during the First World War. While initially rarely involved in the British operations in East Africa, the continued resistance of the German … READ MORE
Entry -
Aleksandr Vasil'evich Kolchak was a Russian admiral and political figure. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War, the First World War, and the Russian Civil War. He was one of the leaders of the White movement in eastern Russia and was proclaimed … READ MORE
Entry -
Prince Fumimaro Konoe was a pivotal figure in Japanese history during the first half of the 20th century. He is primarily recognized for his tenure as prime minister and his significant involvement in formulating the concept that became known … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War I, V. K. Wellington Koo worked in the Chinese foreign ministry before becoming Chinese minister to the United States and a member of the Chinese delegation at the Paris Peace Conference. In these capacities, Koo utilized international law … READ MORE
Entry -
Béla Kun was a Hungarian communist politician. He began his career as a social democrat. During the First World War he was captured by the Russians and later became a Bolshevik in Russia. From 1918 onward, he filled significant positions in the … READ MORE
Entry -
La Dame Blanche was an intelligence network created in Belgium in 1916. It was essentially devoted to the observation of railways. At the end of the war, it was comprised of over 1,000 agents and covered a large part of the occupied … READ MORE
Entry -
Although he was a Nobel Prize winner, the name of Henri La Fontaine has somewhat fallen into obscurity. At the time of his Nobel Peace Prize award in 1913, however, he was a fundamental figure in the pacifist movement. The prize was a reward for his … READ MORE
Entry -
Johan Laidoner, Estonian general and statesman, started his career in the Russian army during World War I. He was crucial in establishing an Estonian army, which he commanded in the War of Independence (1918-20). In 1934 he participated in a coup … READ MORE
Entry -
Robert Lansing served as U.S. Secretary of State from June 1915 until February 1920. A career lawyer, Lansing was a leading proponent of “benevolent neutrality” in the years before the United States entered the war. He also served as a member of the … READ MORE
Entry -
T.E. Lawrence’s exploits during the Arab Revolt have acquired mythical status, making it difficult to distinguish between what he actually achieved and what was the product of his overactive imagination. Less contested is his role in brokering the … READ MORE
Entry -
In 1921 and 1922 the highest German court, the ''Reichsgericht'' in Leipzig, under pressure from the Allied powers, put seventeen Germans on trial for suspected war crimes in twelve trials. The trials and their results were criticized in both Germany and … READ MORE
Entry -
Vladimir Il’ich Lenin was the founder and leader of the Bolshevik Party and of the Soviet state up until his death. Theoretically and practically he combined the strategy of a socialist revolution with imperialism and war. After thus successfully … READ MORE
Entry -
Karl Liebknecht was the leading German socialist opponent of the First World War. He was the first member of parliament to vote against the financing of the war. On 1 May 1916 he was arrested and imprisoned for giving an anti-war speech in central Berlin. … READ MORE
Entry -
Lloyd George was a leading Liberal politician before World War I, who went on to play a central role in the United Kingdom’s war effort as Chancellor of the Exchequer (1908-1915), Minister of Munitions (1915-1916), Secretary of State for War (1916) and … READ MORE
Entry -
Henry Cabot Lodge was a Republican senator from Massachusetts. Close friend to Theodore Roosevelt, Lodge supported imperialist endeavors and favored military preparedness following the outbreak of World War I. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of London was a secret agreement signed by Italy, Great Britain, France, and Russia on 26 April 1915, bringing Italy into the First World War on the Entente side. It therefore had a crucial impact on the conflict. Its content, however, included … READ MORE
Entry -
Louis Loucheur was a French industrialist and politician. From December 1916 until the end of the war, he served as undersecretary of state for artillery and munitions and later as armaments minister. After the war, he continued a brilliant political … READ MORE
Entry -
Erich Ludendorff was the effective commander of the German armed forces during the war. He also became a quasi-dictatorial figure, the ruthless symbol of the army’s political power. After the war he became the new republican government’s most bitter … READ MORE
Entry -
Named after the German ''chargé d’affaires'' in Buenos Aires, Count Karl von Luxburg, the Luxburg Affair was the diplomatic issue that brought Germany and Argentina to the brink of war in … READ MORE
Entry -
A Socialist and a vocal critic of the German Social Democratic Party’s (SPD) war policies, co-founder of the anti-war Spartacus League in 1916 and the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) in 1918, Rosa Luxemburg supported the German Revolution of 1918. In … READ MORE
Entry -
Ramsay MacDonald opposed British entry into the European conflict in 1914. Although often represented as anti-war, he subsequently supported the Allied cause. He criticised balance of power diplomacy in the hands of a cloistered elite. Despite tensions, … READ MORE
Entry -
Macedonia was one of the main battlefields on the Balkan Front during World War I. The article describes the pre-war activities of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO), its role in the Bulgarian occupation regime, and the fall of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Bernardino Machado was the prime minister of Portugal during the July Crisis of 1914. As president of the Portuguese Republic (1915-1917) he promoted the formation of a Sacred Union Cabinet that dispatched expeditionary forces to Flanders and to … READ MORE
Entry -
Nestor Makhno was a commander of peasant insurgents who fought the Bolsheviks, Whites and Ukrainian nationalists in the South East of present-day Ukraine. His espousal of anarchism has won him supporters among many Western anarchists, but some historians … READ MORE
Entry -
French Interior Minister when the war was declared, Louis Malvy embodied the Union sacrée and the quest for social peace. In 1917, he was accused of treason and involved in a political scandal that led to the fall of the … READ MORE
Entry -
A Finnish aristocrat, Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim served as cavalry commander in the Imperial Russian army during the First World War. After the Russian Revolution, he commanded Finnish White forces in the Finnish Civil War of 1918. He served as the Head … READ MORE
Entry -
Marie Adelheid reigned from 1912 to 1919 as the Grand-Duchess of Luxembourg. Because of her friendly attitude towards the German occupying forces during World War I, the Luxembourgers and Allies accused her of sympathizing with the Germans. Failing to … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Marinegebiet'' on the Belgian coast was the Imperial German Navy’s base for attritional warfare against Entente shipping in the North Sea. The resulting occupation regime was particularly harsh on civilians; their plight was compounded by British … READ MORE
Entry -
Martial law refers to the exercise of governmental power over the civilian population by military authorities. The use of martial law varied among belligerent countries, and its geographical scope and material extent changed over the course of the war. … READ MORE
Entry -
The notion of “martial races” was formally developed and codified in the wake of the Indian Uprising of 1857 and became an important basis for the recruitment policy of the Indian Army. Constantly manipulated and adapted to changing political and … READ MORE
Entry -
The terms "martyrs" and "separatists" refer to the decentralist Arabists of Syria who were executed by Cemal Pasha during World War I as a result of their alleged plot to separate the Syrian land from the Ottoman … READ MORE
Entry -
Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk was a Czech politician who started the Czechoslovak independence movement abroad. As head of the Czechoslovak National Council from 1916 to 1918, he provided an ideological basis for Czechoslovak propaganda, helped create the … READ MORE
Entry -
Mata Hari was a famous Dutch female dancer, who spied in France for the German intelligence during the war. Arrested by the French, she was condemned to death and executed in October … READ MORE
Entry -
Mata Hari was a famous Dutch female dancer, who spied in France for the German intelligence during the war. Arrested by the French, she was condemned to death and executed in October … READ MORE
Entry -
Norton de Matos was minister of war during the first two years of Portuguese participation in the conflict (1916-1917). He was the main organizer of the Expeditionary Corps that fought on the Western Front. In December 1917, he was deposed by a military … READ MORE
Entry -
Adolphe Max, the mayor of Brussels, was known for his peaceful resistance against the Germans and his resulting jail-time. He was considered by the Belgian public as a hero of the Great … READ MORE
Entry -
For many years Prince Maximilian of Baden was portrayed as a positive figure in German history - the liberal Chancellor who in 1918 helped to turn Germany into a republic. This view has been considerably altered by recent scholarship, including letters … READ MORE
Entry -
William G. McAdoo was an American politician and businessman. During World War I, he served as Secretary of the Treasury and director of the US Railroad Administration. In these positions he was the architect of the USA's wartime financial planning and … READ MORE
Entry -
Ioannis Metaxas was a conservative army officer and politician, who influenced decision-making in Greece during World War I by collaborating with King Constantine I. In 1936 he became head of an oppressive dictatorial regime and in 1940 he was responsible … READ MORE
Entry -
It was the complex and far-reaching transformation of the Mexican Revolution rather than the First World War that left its mark on Mexican history in the second decade of the 20th century. Nevertheless, although the country maintained its … READ MORE
Entry -
Georg Michaelis is usually portrayed as the politically failed chancellor of 1917. His resignation after fourteen weeks in office was the first overthrow of a Reich chancellor initiated by Reichstag political parties. Before he was appointed chancellor, … READ MORE
Entry -
Micronesia
By Niko Tillmann and Yuko Maezawa
Japanese interest in expansion into the South Pacific began in the 1870s. World War I provided a long sought after chance for the Japanese Imperial Navy to enhance its standing and gain a strategically important base. Japanese claims to the South Sea … READ MORE
Entry -
One of the founders and leaders of the Constitutional Democratic Party, Pavel Nikolaevich Miliukov took an active part in the organisation of the Progressive Bloc. He made a famous speech in the Duma on 1 November 1916 (“Stupidity or Treason?”) … READ MORE
Entry -
Between 1890 and 1925, Alexandre Millerand was one of France’s leading politicians. From August 1914 to September 1915, he served as war minister in the first ''Union sacrée'' government. In 1920, he was elected president of the republic, but he had to … READ MORE
Entry -
E. D. Morel was one of the earliest critics of the secret diplomacy and alliance system that led to the start of the Great War. Imprisoned during the war by the British government for his writings, he later became a foreign policy leader in the Labour … READ MORE
Entry -
Naturalized American lawyer, real estate investor, and Jewish activist, Henry Morgenthau Senior served as United States Ambassador to the Ottoman Empire from 1913-1916. During 1915-1916 Morgenthau reported extensively on the wholesale ethnic cleansing and … READ MORE
Entry -
The two Moroccan crises represent the product of “rapacious joint imperialism.” Morocco could not escape the ambitions of its immediate neighbours, Spain and France, who secretly plotted to divide the country between them in 1904. The Reich provoked … READ MORE
Entry -
The Movement of National Defence was an organisation of Venizelist army officers and politicians who rose up against the royalist government in Athens in August 1916. They established a separate Provisional Government of National Defence in Thessaloniki … READ MORE
Entry -
Lauro Müller was the Brazilian minister of foreign affairs between 1912 and 1917. A pro-German politician and intellectual, he was heavily criticised during World War I by the Brazilian press and pro-United States intellectuals. Brazil maintained … READ MORE
Entry -
Italian Socialist Benito Mussolini envisioned war as the prerequisite for revolution. He helped push Italy into World War I. After combat service and medical discharge in 1917, he demanded war until victory. In 1919, he founded the Fascist movement. Using … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich Naumann was a key figure in German liberalism in the late Kaiserreich, where he tried to reunite Left and National Liberals. In 1915, he published a widely read book on “''Mitteleuropa''” (Central Europe) which sought to give a liberal … READ MORE
Entry -
The Anglo-German naval race was the most spectacular strand of the general maritime arms build-up before World War I. Often, albeit misleadingly, described as both the first and the prototypical arms race among modern industrial nations, this arms race … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Neuilly was signed on 27 November 1919 between Bulgaria and the Allied and Associated Powers in Neuilly-sur-Seine, France. Its territorial clauses were considered by Bulgarian society to be a national catastrophe and the definitive failure … READ MORE
Entry -
During the 19th century, neutrality evolved into a set of legal and political tools designed to limit the impact of wars on the international system. This form of neutrality did not survive the first “total war”; remaining neutral was still … READ MORE
Entry -
Nicaragua’s experience during the First World War was influenced by the geopolitics of the Central American isthmus. The American occupation of Nicaragua between 1912 and 1925 impacted both Nicaraguan neutrality, which ended once the United States … READ MORE
Entry -
Nicholas II ruled Russia from 1894 and was commander of the army from September 1915 until his abdication in March 1917 amidst popular demonstrations against bread shortages, the war and autocracy. Historians dispute the relative importance of … READ MORE
Entry -
Nikolai Nikolaevich, a senior Russian officer and close relative of Tsar Nicholas II, was involved in attempts to reform the Russian army from 1905. He was named Commander-in-Chief at the onset of war in 1914 but was removed a year later following … READ MORE
Entry -
Francesco Nitti was minister of the Treasury in the Orlando Cabinet after the defeat of Caporetto in 1917 and prime minister of Italy in 1919. During his mandate he signed the treaty of Saint-Germain, started the economic reconversion of the country and … READ MORE
Entry -
Gustav Noske was a social democratic politician and the first politician to be awarded with military responsibilities. His role as first ''Reichswehrminister'' (Reich minister of defense) during the revolution was controversial and ambivalent. He was … READ MORE
Entry -
Over the entire course of German occupation in Eastern Europe during the First World War, the Ober Ost administration wavered between domination by military leaders – and their efforts to create a settlement colony – and continued attempts by … READ MORE
Entry -
The so-called “''Oberstenaffäre''” (colonel’s affair) was a political scandal in Switzerland which erupted after details of a close cooperation between Swiss, German, and Austro-Hungarian military intelligence agencies emerged during World War I. … READ MORE
Entry -
The violation of Luxembourg’s neutrality started with the invasion on 1 August 1914, with the real occupation beginning on 2 August and lasting until 21 November 1918 when the first Allied troops arrived in … READ MORE
Entry -
A renowned jurist with lasting influence, Vittorio Emanuele Orlando served as justice and interior minister between 1916 and 1917, implementing liberal policies despite strong opposition. As prime minister after the Caporetto crisis he rallied Italy, … READ MORE
Entry -
Ignacy Jan Paderewski was a virtuoso pianist. He made use of his popularity in the United States and western Europe to propagate the idea of Polish independence and state sovereignty. In 20th century Poland, he became a symbol of patriotism and … READ MORE
Entry -
Paul Painlevé was a prominent French political leader from 1914-1917. He was the head of the Inventions Committee in charge of defining modern warfare. In 1917, at the turning point of the war, he was the minister of war and president of the Council. His … READ MORE
Entry -
The army major and university teacher Sidónio Pais served as the Portuguese minister (ambassador) in Berlin between August 1912 and March 1916. In December 1917, after a military coup, Pais became president of the Republic. He was murdered in December … READ MORE
Entry -
The First World War elicited various responses from the Wilson administration based on Pan Americanism, a conception of regional integration under U.S. leadership that calls for more political cooperation and greater trade and investment. The first goal … READ MORE
Entry -
The Pan-German League (''Alldeutscher Verband'') mobilized members of the ''Bildungsbürgertum'' and the broader middle classes in the service of a class-based vision of ''Volksgemeinschaft'', territorial expansion, and cultural homogeneity in Germany. … READ MORE
Entry -
Pan-Islamism was one of the major geopolitical and civilizational concepts of the First World War. The German-Ottoman alliance campaigned for Muslim solidarity against European colonialism both by anti-imperial and imperial means. Pan-Islamism altered the … READ MORE
Entry -
Pan-Turkism is the nationalist ideology that emphasizes the common ethnic, cultural, and linguistic roots of Turkic peoples living across Eurasia. Developed as a social and political movement among the Turkic-Muslim peoples of the Russian Empire, the … READ MORE
Entry -
A talented administrator but a mediocre general, Cavit Pasha served in various parts of the empire, including commander of Iraq during the first year of the … READ MORE
Entry -
A first father of modern Turkey before Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, and the driving force of the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) during the war, Talat organized the removal of Armenian and other Christian citizens to secure exclusive Turkish power in … READ MORE
Entry -
Nikola Pašić was a Serbian/Yugoslav politician and statesman. He served twenty-two terms as prime minister and fourteen terms as foreign minister, some only a few months … READ MORE
Entry -
Konstantin Päts, a leading Estonian politician, was a key figure in the establishment of Estonian independence during and after World War I. In 1934, he and Johan Laidoner organized a putsch and Päts became an authoritarian … READ MORE
Entry -
Alice Paul was an American suffragist and political rights activist. Jailed repeatedly for her activities running up to and during World War I, her work in the United States led to the passing of the 19th Amendment and the introduction of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Friedrich von Payer was vice-chancellor of the German Empire from November 1917 to November 1918. In November 1918, he was offered the position of Reich chancellor, which he declined. After the First World War, Payer became a founding member of the German … READ MORE
Entry -
Patrick Pearse was one of the leaders of the 1916 Easter Rising in which the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB), an extremely nationalist organization, attempted to establish an independent Ireland by force. His execution was an important catalyst for the … READ MORE
Entry -
During the Russian Civil War, peasant uprisings swept the former Russian Empire. In 1918 and 1919, these uprisings were mainly local responses to requisitioning and conscription. In 1920 and 1921, the uprisings became larger in scale, above all in Tambov. … READ MORE
Entry -
Epitácio Pessoa served as the president of Brazil between 1919 and 1922. He led the Brazilian delegation to the Paris Peace Conference. He was also a member of the Permanent Court of International Justice in The … READ MORE
Entry -
Gabrielle Petit was a secret intelligence agent working for the British General Headquarters (GHQ) in occupied Belgium. She collected information on the German Sixth Army in the Tournai-Lille area. She was condemned to death and executed in the spring of … READ MORE
Entry -
Józef Klemens Piłsudski was a Polish statesman, socialist politician, freedom fighter, and soldier. He commanded the Polish Legions during the First World War, and served as the first chief of state (1918–1922), marshal (from 1920 onward), prime … READ MORE
Entry -
Raymond Poincaré, the president of the French Republic, asserted his authority as early as 1914, in a manner contrary to institutional practices that had prevailed since 1877. After his August 1914 call for a political truce or “''union sacrée''”, … READ MORE
Entry -
Polish paramilitary organizations were active in Galicia from 1910 to 1914 with the permission of the Austro-Hungarian army’s intelligence service. Their ostensible aim was to militarily train young people and improve their shooting skills. The actual … READ MORE
Entry -
Although not directly involved in military operations, Portuguese India was linked to World War I through the capture of German and Austrian ships and the imprisonment of their crewmen. This period was also one of internal political turmoil and there was … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War One, Macau's main problem was its relationship with China. This stemmed from the consequences of its internal tensions and the lack of recognition of the Portuguese borders. However, its defence was weak, mainly based on local … READ MORE
Entry -
The Portuguese territory of Timor was affected by the war mainly because of its proximity to the Dutch colony, the Dutch East Indies. Furthermore, without lines of transportation and communication, Timor became more isolated and imports and exports … READ MORE
Entry -
The Prochaska Affair was a diplomatic dispute between Austria-Hungary and Serbia, ostensibly concerning the fate of the Austro-Hungarian consul in Prizren. However, it carried deeper implications for the Austro-Hungarian efforts to prevent the Serbians … READ MORE
Entry -
When the tsarist government collapsed in February 1917, liberal politicians from the State Duma (parliament), later joined by moderate socialists, formed a Provisional Government. Unable to satisfy popular expectations for peace, or to enact social and … READ MORE
Entry -
This entry revisits the political upheavals that swept across several towns and cities of Punjab in April 1919, in protest against the passage of the Rowlatt Act in the Imperial Legislative Council. It argues that the moment marks a fundamental break in … READ MORE
Entry -
Dr. Vasil Radoslavov was a Bulgarian politician and Prime Minister from 1913 to 1918. As Prime Minister he played a decisive role in Bulgaria’s decision to enter the First World War on the side of the Central … READ MORE
Entry -
Rasputin was a peasant turned pilgrim who became a close associate of the Russian royal family. Accounts of his wartime influence on government may be exaggerated but public perceptions of his power and rumours of his debauchery undermined the authority … READ MORE
Entry -
Walther Rathenau was one of the most influential entrepreneurs before the First World War. In 1914/1915 he became one of the main organizers of Germany’s war economy. After World War I he supported the “policy of fulfilment”. As German Minister of … READ MORE
Entry -
On 25 May 1913 Colonel Alfred Redl, the former head of Austria-Hungary’s military espionage, committed suicide in Vienna. As it turned out, Redl had betrayed Austria-Hungary’s spy-network in Russia and had sold sensitive information on war … READ MORE
Entry -
The Red Scare was a period of heightened fear of radicalism in the United States after World War I. Labor unrest, the growth of bolshevism internationally, and a series of bombings triggered a number of government raids on suspected radicals, often in … READ MORE
Entry -
The ''Renascença Portuguesa'' (1912-1932) was an important cultural movement during the republican regime (1910-1926) in Portugal. This intellectual group was founded in Porto, in the northern part of Portugal. It supported the participation of Portugal … READ MORE
Entry -
Karl Renner quickly became one of the main theoreticians of a policy of support for the war effort. He saw World War I as a chance for social democratic advance, with state intervention laying the groundwork for socialism. He made the case for the … READ MORE
Entry -
In occupied Belgium and France, citizens opposed the German army with organized but non-violent resistance. They created networks dedicated to military intelligence gathering, escape lines, clandestine postal networks and underground newspapers. Many of … READ MORE
Entry -
Social and political unrest swept the Russian Empire in 1905, forcing the autocratic tsarist regime to grant the creation of a popularly-elected legislative body; the State Duma. However, the army remained largely loyal to the Tsar, unlike in the wartime … READ MORE
Entry -
Alexandre Ribot belonged to the French political elite for more than forty years. During the war, he was finance minister from 1914 to 1917 and prime minister (''Président du Conseil'') from March to September … READ MORE
Entry -
Riezler was a German politician, diplomat, journalist and philosopher, as well as a trusted assistant of the chancellor. Although some of his surviving diary entries dated from July and August 1914 as representative of the German Foreign Office’s Press … READ MORE
Entry -
The Russian occupation of the eastern Ottoman Empire entailed the wartime administration of captured territory comprising approximately 95,000 square kilometers. A military governorate-general was established in 1916; this was replaced by a … READ MORE
Entry -
Said Nursi was a prominent Kurdish intellectual. He fervently supported constitutionalism and sought to improve the Kurds’ condition during the late Ottoman Empire. After World War I and the consequent fall of the Ottoman Empire, Nursi founded the … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Saint-Germain was signed by Austria and twenty-seven Allied and associated countries in the ''Château Neuf'' in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, southwest of Paris, on 10 September 1919. It officially ended World War I for the successor states of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Antonio Salandra was an important Italian politician in the early 20th century. When the Great War broke out, he was prime minister of Italy and had a decisive yet controversial role in the Italian … READ MORE
Entry -
The Sarajevo incident refers to the events surrounding the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife Archduchess Sophie during a state visit to Sarajevo on 28 June 1914. It is traditionally regarded as … READ MORE
Entry -
Sergei Sazonov became Russian Foreign Minister in autumn 1910. In July 1914 he argued for a firm stance against Austrian aggression and general mobilisation of the army, but historians dispute his responsibility for the outbreak of war. His wartime … READ MORE
Entry -
Philipp Scheidemann was a key figure in the German Social Democratic Party (SPD) during the First World War. On 9 November 1918, Scheidemann proclaimed the republic in Germany and became the first head of government in the Weimar … READ MORE
Entry -
Heinrich Schnee was the governor of German East Africa between 1912 and 1919. During the war, he remained with the German colonial troops under the command of Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck until their surrender in November 1918. In the interwar years, Schnee … READ MORE
Entry -
The Scutari Crisis illustrates questions surrounding the creation of the new Albanian state at the beginning of the 20th century. It also shows the transformation of the aims of the First Balkan War, which was seen as a liberating war against … READ MORE
Entry -
Much attention has been accorded to the massive scale of military operations in the European theatre. However, sea power, which determined the control of global communications and was the key to exploiting global resources of manpower, food, industrial … READ MORE
Entry -
The Selective Service Act of 1917 was the official name of the military draft signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson following the United States’ entry into World War I. It authorized the federal government to expand the American armed services … READ MORE
Entry -
Marcel Sembat was one of the leading French socialists of the pre-war years. As minister of public works, he represented the socialist party in the ''union sacrée'' government formed at the end of August … READ MORE
Entry -
Bahaeddin Şakir was the reorganizer of the Committee of Union and Progress, a political party that became the government of the Ottoman Empire during the war. As a major functionary of the Special Organization, a paramilitary network which took orders … READ MORE
Entry -
An Irish-born writer and critic, best known as a playwright, George Bernard Shaw was an ardent opponent to World War I. Already in his fifties at the start of the war, Shaw was outspoken in his antiwar speeches and also published a pamphlet entitled … READ MORE
Entry -
Boris Shtiurmer was Prime Minister from January to November 1916, also serving as Interior Minister between March and July 1916 and Minister of Foreign Affairs from July to November. Denunciations of Shtiurmer in Russia’s parliament, or Duma, for … READ MORE
Entry -
The Sixtus Affair was the failed attempt by Emperor Charles I. of Austria and his bother-in-law Prince Sixtus of Bourbon-Parma to conclude a compromise peace with the members of the Entente-Powers between January and May … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, political writer and editor of Lithuanian magazines, Antanas Smetona in 1917 became chairman of the Council of Lithuania, which declared Lithuania as an independent state in 1918. He was twice President of Lithuania, 1919-1920 … READ MORE
Entry -
Jan Smuts was a South African lawyer and statesman who ultimately became deputy prime minister of the Union of South Africa. During the war, Smuts was Minister of Defence, Finance and Mines. He served for a time in German South West Africa before … READ MORE
Entry -
At the outbreak of the First World War, the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) voted, as the largest party in the German Empire, for the granting of war loans. However, the thus-introduced "truce" policy was rejected by more and more members of … READ MORE
Entry -
The privately organized SSS existed from October 1915 to July 1919 to prevent Swiss companies from forwarding goods and raw materials produced by the Entente to the Central Powers. The SSS grew from an international agreement between the governments of … READ MORE
Entry -
Wilhelm Solf, long-term governor of German Samoa, served as Colonial Secretary between 1911 and 1918 and as the last imperial Foreign Secretary in winter 1918. During the war Solf supported expansionist war aims in Africa and a policy of restraint in … READ MORE
Entry -
Sidney Sonnino was the Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs during World War I. He negotiated the Treaty of London, defining the terms with which Italy would enter into the war alongside the Triple Entente. His actions during the Paris Peace Conference … READ MORE
Entry -
The painter Adriano de Sousa Lopes was the only official Portuguese war artist in the Great War, stationed on the Western Front. Like most of his international colleagues, he produced remarkable field drawings and etchings. This article explores his … READ MORE
Entry -
Spain became a centre of international espionage in 1914. Its strategic location in terms of the Anglo-French trade soon attracted German attention. The Germans waged an economic and propaganda war against the Allies from Spain, while the British took … READ MORE
Entry -
The Spanish government maintained a benevolent neutrality policy towards the Entente Powers during the First World War. Liberal and Conservative cabinets decided it was the only position consistent with their country's traditionally friendly relations … READ MORE
Entry -
Milan Rastislav Štefánik was a Slovak astronomer, diplomat, politician, general, one of the organizers of the Czechoslovak legions and one of the founding fathers of Czechoslovakia. In today’s Slovakia he is seen as a national … READ MORE
Entry -
This article summarises the main wartime stereotypes that defined war propaganda in Germany, France, Great Britain, the USA and Russia. It focuses less on particular details of each national enemy image and more on the basic make-up of wartime stereotypes … READ MORE
Entry -
Hugo Stinnes was a highly successful and politically influential heavy industrialist. During the First World War, he adopted a German nationalist position and advocated the colonisation of Belgium and parts of France. After the defeat, Stinnes negotiated … READ MORE
Entry -
The Stockholm Conference, or Third Zimmerwald Conference, was held from 5 to 12 September 1917. The subject of the discussions was the way in which a certain part of the socialist movement conceived peace and its approach to fighting war. The genesis of … READ MORE
Entry -
Stresemann was a leading wartime annexationist and proponent of moderate domestic reforms. Committed to restoring national strength after defeat and revolution, he became one of the Weimar Republic’s foremost statesmen. He served as chancellor during … READ MORE
Entry -
Karl Graf von Stürgkh was an Austrian member of the Imperial Council, Minister for Education, and Minister President of Cisleithania from 3 November 1911 until his assassination on 21 October 1916 by the Social Democrat Friedrich Adler. Stürgkh was one … READ MORE
Entry -
In May 1916, the German government issued a pledge to the United States that the Imperial navy would not attack passenger ships and would further allow the crew of merchant ships which carried war material to exit their vessels before they would be … READ MORE
Entry -
Ivan Šušteršič was a leading figure in the Slovenian and Habsburg political milieu prior to and during World War One. A prominent member of the Catholic People’s Party, he was at the forefront of the pro-Habsburg political currents in Carniola, … READ MORE
Entry -
Bertha von Suttner (1843-1914) was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1905. She wrote an internationally acclaimed antiwar novel ''Die Waffen nieder!'' (''Lay Down Your Arms!'') and co-founded the Austrian Peace Society (1891) and the journal, ''Die Waffen … READ MORE
Entry -
In dividing the Fertile Crescent into British and French spheres, the wartime Sykes-Picot Agreement laid the foundation of the colonial division of the region ratified at the St. Remo (1920) and Lausanne (1923) conferences, when Palestine … READ MORE
Entry -
Albert Thomas was a French socialist who served as minister of armaments in the French government during the war. In the postwar period, he became the first director of the International Labour … READ MORE
Entry -
Federico Tinoco Granados was the Costa Rican president from 1917-1919 who declared war on Germany in April 1917. With his support for the United States during the last two years of the war, he tried to gain President Woodrow Wilson’s acceptance. The … READ MORE
Entry -
István Tisza was a Hungarian politician and minister. He served as Prime Minister from 1903 to 1905 and from 1913 to 1917. Austria-Hungary entered the First World War during Tisza's second period as prime … READ MORE
Entry -
During World War I, Arnold J. Toynbee, as a member of the Political Intelligence Department, was charged with preparing analyses on the Middle East for the Paris Peace Conference. The global war was pivotal for the elaboration of his philosophy of … READ MORE
Entry -
Trentino
By Nicola Fontana and Mirko Saltori
Trentino is an Italian-speaking region which was the southernmost part of the Tyrol. With Italy’s entry into the war, it found itself in the front area. After the war it was annexed to the Kingdom of … READ MORE
Entry -
As prefect of the ''département ''of the Nord at the outbreak of war, Félix Trépont encouraged the defence of Lille during the invasion, eventually oversaw the evacuation of men and material, and resisted collaboration with the Germans during the … READ MORE
Entry -
Before and at the beginning of World War I, various proposals concerning the creation of a third part of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy were brought up for discussion. Each of the aspiring groups (Czech, South Slavic and Polish) assumed that becoming a new … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Trianon is one of the Paris peace treaties that ended the First World War. It was concluded between Hungary and the Allied and Associated Powers on 4 June 1920 in the Grand Trianon Palace situated in the Versailles Palace park. It sanctioned … READ MORE
Entry -
Troelstra was a charismatic socialist leader who overestimated his influence and called for a socialist revolution in November 1918. His call was ignored and after suffering a nervous breakdown, he re-entered … READ MORE
Entry -
Leon Trotsky's communist leadership was partially responsible for bringing about the October Revolution of 1917, after which Russia exited the First World War. Starting as an activist, he became People’s Commissar for Foreign Affairs and People’s … READ MORE
Entry -
Ante Trumbić was a Croat politician who played an instrumental role in the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslavia) in December 1918. Between 1905 and 1934, he served in a range of influential posts including as mayor of Split; … READ MORE
Entry -
The province of Turkestan - modern-day Central Asia -, a Russian military colony since 1865-1875, truly entered WWI in 1916, when Tsar Nicholas II and his military staff decided, on 7 July (Gregorian calendar), to conscript a new labour force from the … READ MORE
Entry -
At the beginning of the 20th century Ukrainian lands were part of the Austro-Hungarian (Galicia, Transcarpathia, Bukovina) and Russian (the nine right-bank and left-bank provinces) Empires. Therefore, with the beginning of the First World War … READ MORE
Entry -
Kārlis Ulmanis was the first prime minister of the Republic of Latvia. His four terms of office saw the successful conclusion of the Latvian War of … READ MORE
Entry -
The Union of Democratic Control was a prominent opposition group in Britain that particularly criticised the operation of British foreign policy and the role of "secret diplomacy". It advocated public oversight of diplomacy and was an early advocate of … READ MORE
Entry -
Since the beginning of the 20th century, political conflicts determined relations between the German Empire and the USA. The Caribbean became one of the scenes of these conflicts during and following World War I. General reasons were the … READ MORE
Entry -
One of the most prominent and important statesmen in modern Greek history, Eleutherios Venizelos full-heartedly favored Greek participation in World War I on the side of the Entente. This caused tension with King Constantine I, who favored neutrality. … READ MORE
Entry -
The Treaty of Versailles was the first peace treaty that the victorious powers signed with a former adversary. The treaty with Germany was the most important treaty for the Allied and Associated Powers, and served as a blueprint for subsequent agreements … READ MORE
Entry -
Victor Emmanuel III played an important, if often overlooked part in Italy’s decision to intervene in World War I on the side of the Entente. During the war, he managed to solve two political crises and to defend Italy’s position within the Entente … READ MORE
Entry -
Rodrigo de Saavedra y Vinent, Marqués de Villalobar was the diplomatic representative of Spain to Belgium from 1913 to 1926. During the war, his humanitarian activities in occupied Belgium alleviated the suffering of the … READ MORE
Entry -
René Viviani was a leading French politician in the early 20th century. When the war broke out, he was prime minister (''Président du Conseil'') and contributed to the formation of the ''Union … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, as professor at the University of Perm (Russia), Augustinas Voldemaras actively participated in the activities of Lithuanian exiles in Russia. In 1917 he argued for Lithuanian independence. On 11 November, 1918 he headed the … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, the Swiss federal government imposed a state of emergency, which was established to ensure the maintenance of Swiss neutrality, supply and integrity. As the war progressed, legal measures under this regime became more frequent … READ MORE
Entry -
The latter Austrian ''Land'' Vorarlberg saw the rise of a grass root movement for a political union with Switzerland between autumn 1918 and spring 1919. These ideas never materialized, however, as the Paris Peace Treaties vetoed their … READ MORE
Entry -
Baron Hans von Wangenheim was the German ambassador to the Ottoman capital between 1912 and … READ MORE
Entry -
The War Requirements Acts were passed in Austria-Hungary in 1912. They placed military requisitions under parliamentary control and helped the army to obtain the most needed products and services during wartime in a more organized … READ MORE
Entry -
During the First World War, Austria-Hungary implemented a state of emergency with several emergency laws overseen by the ''kaiserlich und königlich ''(''k.u.k.'') ''Kriegsüberwachungsamt'' (war surveillance office, abbreviated KÜA). Although it … READ MORE
Entry -
The Washington Conference was held from November 1921 to February 1922 with the aim of creating a new order in the Asia-Pacific. The main agenda were naval disarmament and an improvement of China’s status, and the conference negotiated the Five-Power … READ MORE
Entry -
As an adviser in the imperial office of the treasury (1916-1918), the Heidelberg economist Alfred Weber helped establish Poland and Lithuania as satellite states under the hegemony of the German Reich (''Mitteleuropa''). During the Weimar Republic, he … READ MORE
Entry -
Brand Whitlock served as the U.S. minister and ambassador to Belgium from 1914–1921. During the war, Whitlock facilitated the humanitarian activities of the Commission for Relief in Belgium, which imported food for more than 9 million civilians in … READ MORE
Entry -
Wilhelm Friedrich Heinrich Prince of Wied, born to a German Protestant noble family, reigned briefly as Prince of Albania from 7 March 1914 until 3 September 1914. In addition to domestic issues and his lack of political experience, the outbreak of the … READ MORE
Entry -
Kaiser Wilhelm II’s ambitious policies played a major part in bringing about the First World War, yet with the onset of hostilities he was sidelined by his generals. In certain key areas, however, notably in appointments to top positions and in the … READ MORE
Entry -
Queen Wilhelmina was by nature a forceful leader. The First World War showed that she lacked the meekness and patience that the head of a small neutral state … READ MORE
Entry -
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the twenty-eighth president of the United States (1913-1921). Wilson unsuccessfully attempted to bring the belligerents to the negotiating table, but in 1917 reluctantly concluded that the U.S. should join the war as an … READ MORE
Entry -
At the end of the First World War, Workers’ and Soldiers’ Councils spread throughout Germany, culminating in a mutiny among sailors at the end of October in Kiel that inaugurated the revolution of November 1918. Their leaders wanted to erect a … READ MORE
Entry -
Hipólito Yrigoyen was president of Argentina during a critical moment of the First World War. He maintained neutrality despite internal and external pressures, and promoted Pan-Hispanism to counteract United States … READ MORE
Entry -
Referred to as the “grandmother of German communism” at the time of her death in 1933 by the ''Manchester Guardian'', Clara Zetkin was a prominent feminist leader within the German social democratic movement and the Socialist International in the … READ MORE
Entry -
Nikola Zhekov was a Bulgarian infantry general, the Bulgarian minister of war from August through October 1915, and commander-in-chief of the Bulgarian army during the First World War, from 1915 to … READ MORE
Entry -
Named for its author, the German minister of foreign affairs Arthur Zimmermann, the so-called Zimmermann Telegram threw a disturbing light on German wartime diplomacy in Mexico and it catalyzed the United States' entry into the First World … READ MORE
Entry -
Anti-war socialists from ten countries met in Zimmerwald in September 1915. They adopted a manifesto and founded the International Socialist Commission (ISC), with its headquarters in Bern. A subsequent conference in Kiental in April 1916 criticised … READ MORE
Entry -
Zionism is a movement that aspired to the creation of a sovereign Jewish state. Having emerged at the end of the 19th century, the Zionist ambition was achieved in 1948 with the founding of the state of … READ MORE
Entry